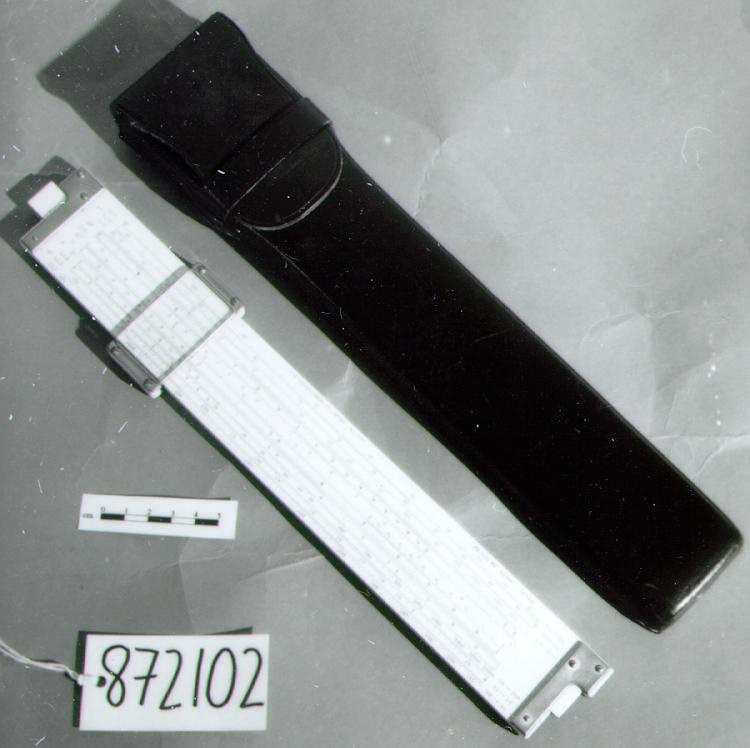
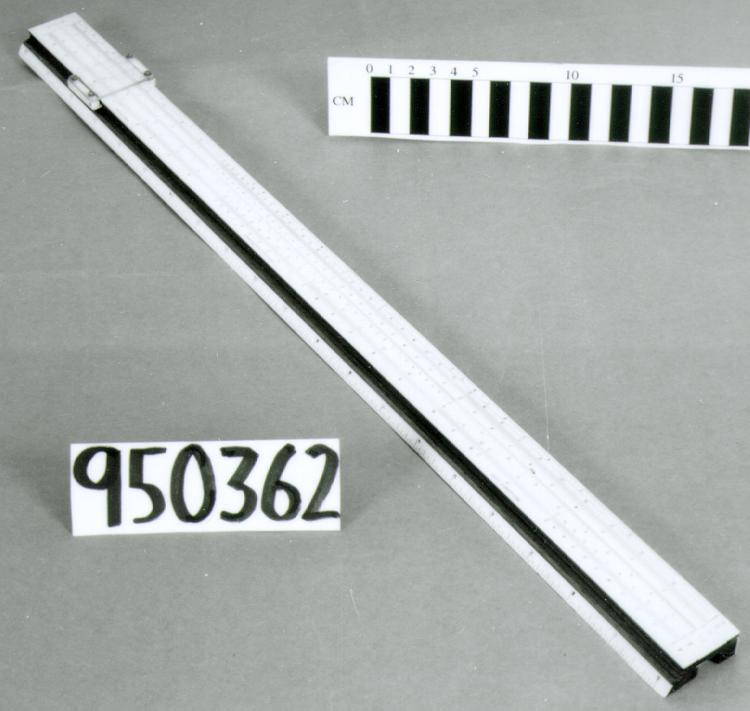
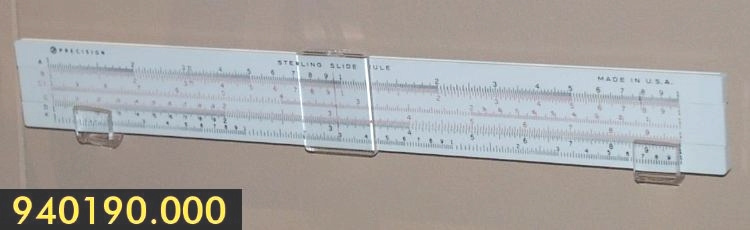
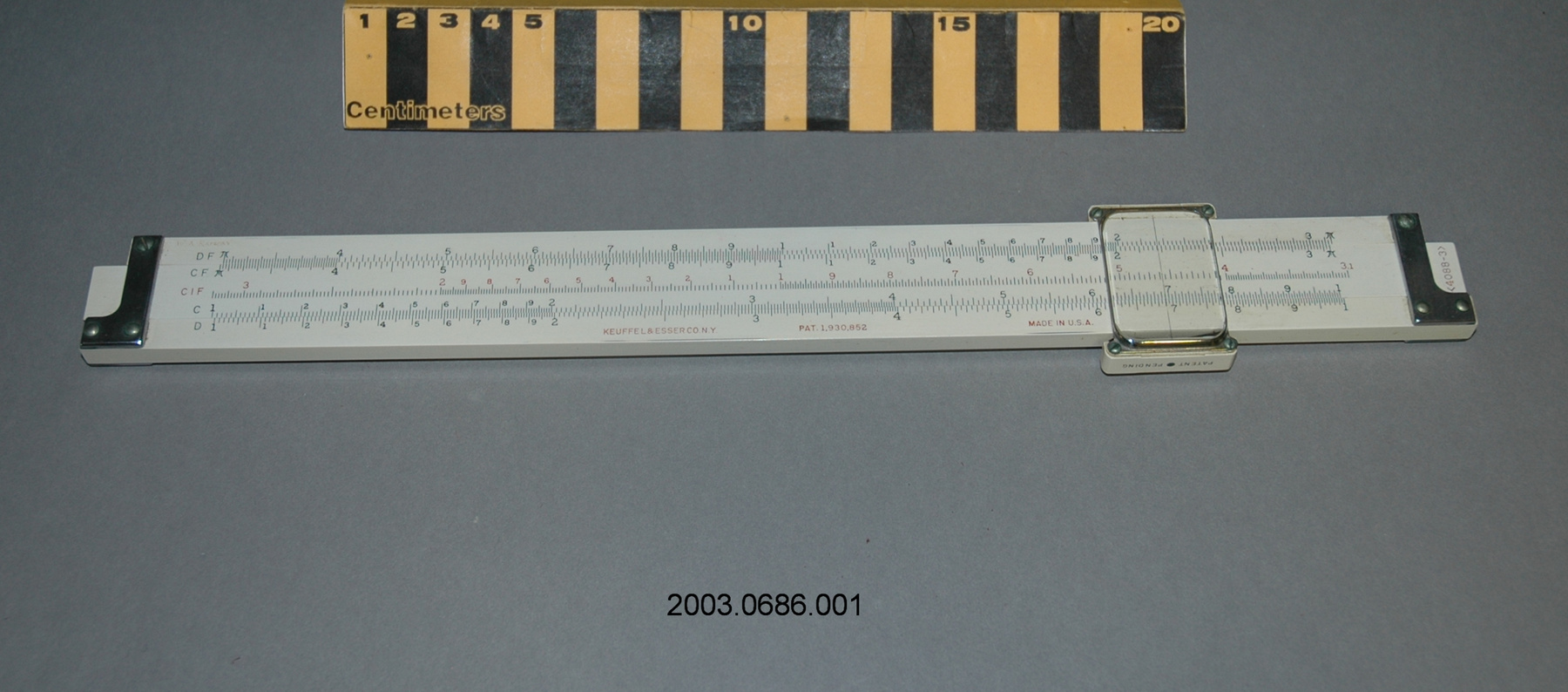
Slide rule
Use this image
Can I reuse this image without permission? Yes
Object images on the Ingenium Collection’s portal have the following Creative Commons license:
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUTE THIS IMAGE
Ingenium,
2006.0043.001
Permalink:
Ingenium is releasing this image under the Creative Commons licensing framework, and encourages downloading and reuse for non-commercial purposes. Please acknowledge Ingenium and cite the artifact number.
DOWNLOAD IMAGEPURCHASE THIS IMAGE
This image is free for non-commercial use.
For commercial use, please consult our Reproduction Fees and contact us to purchase the image.
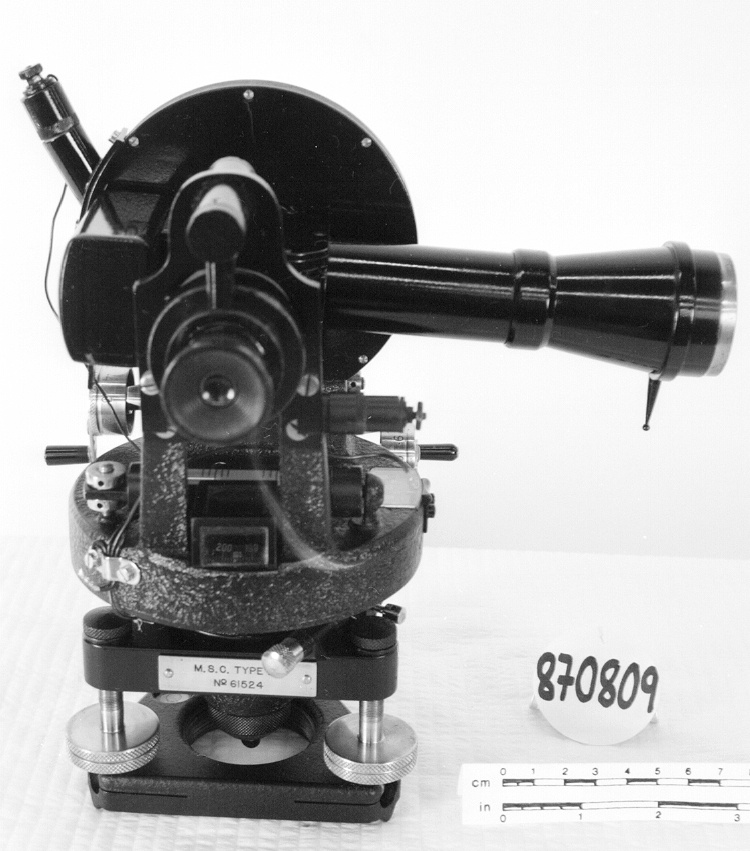
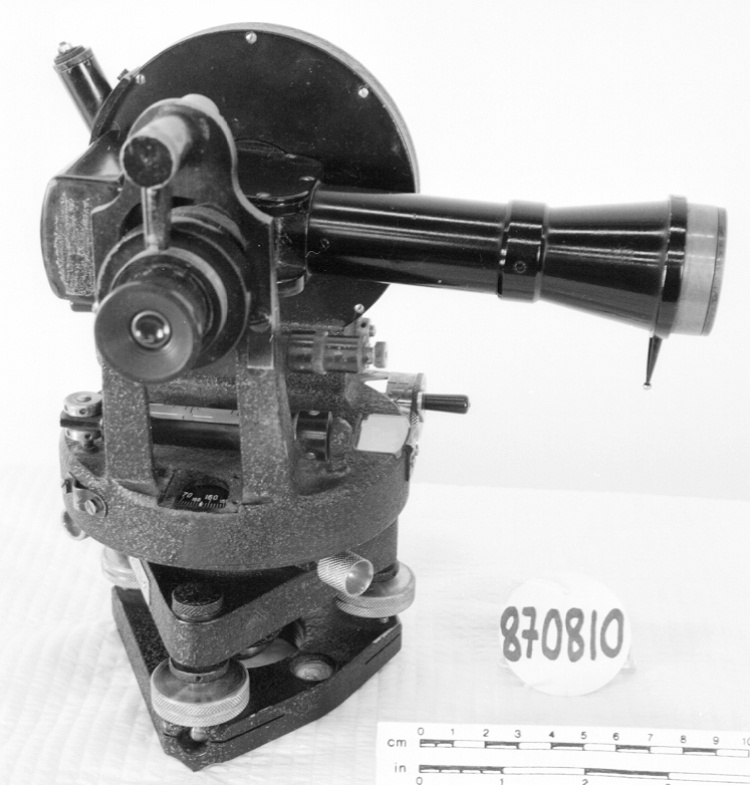
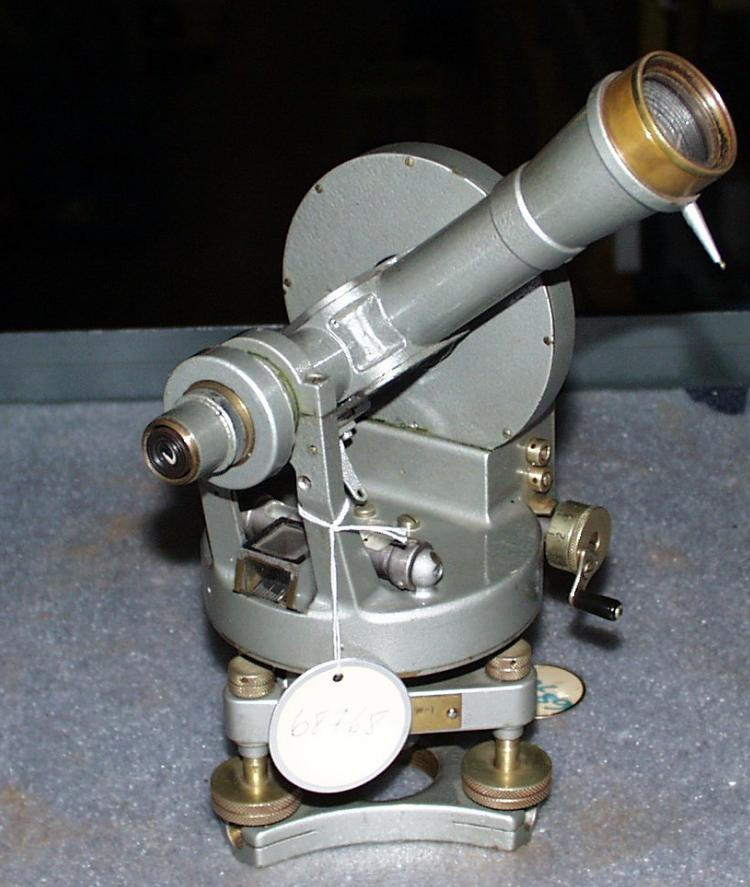
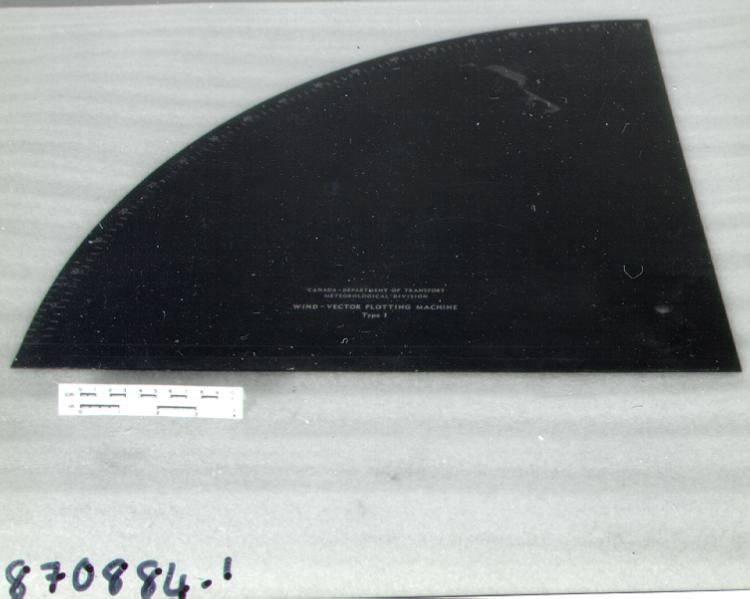
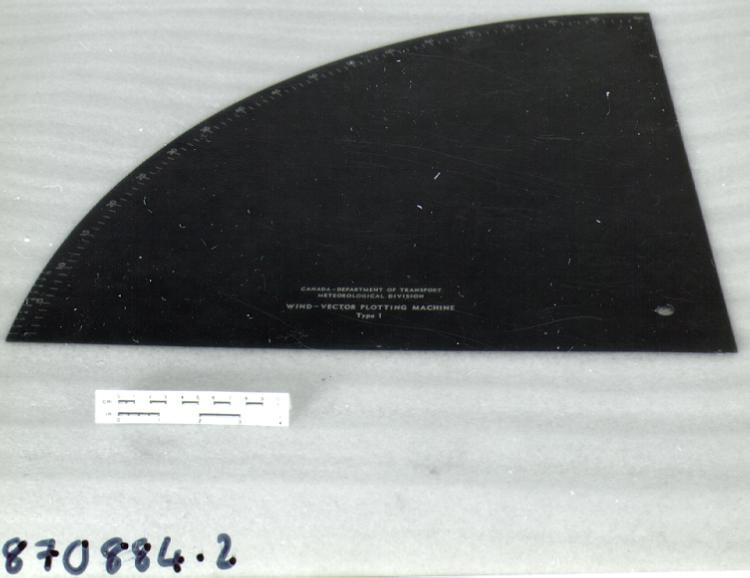
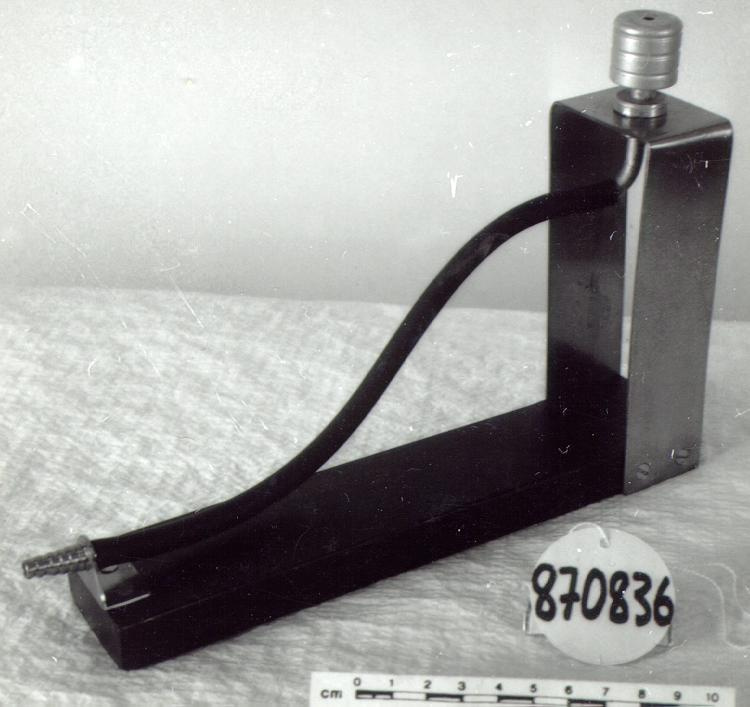
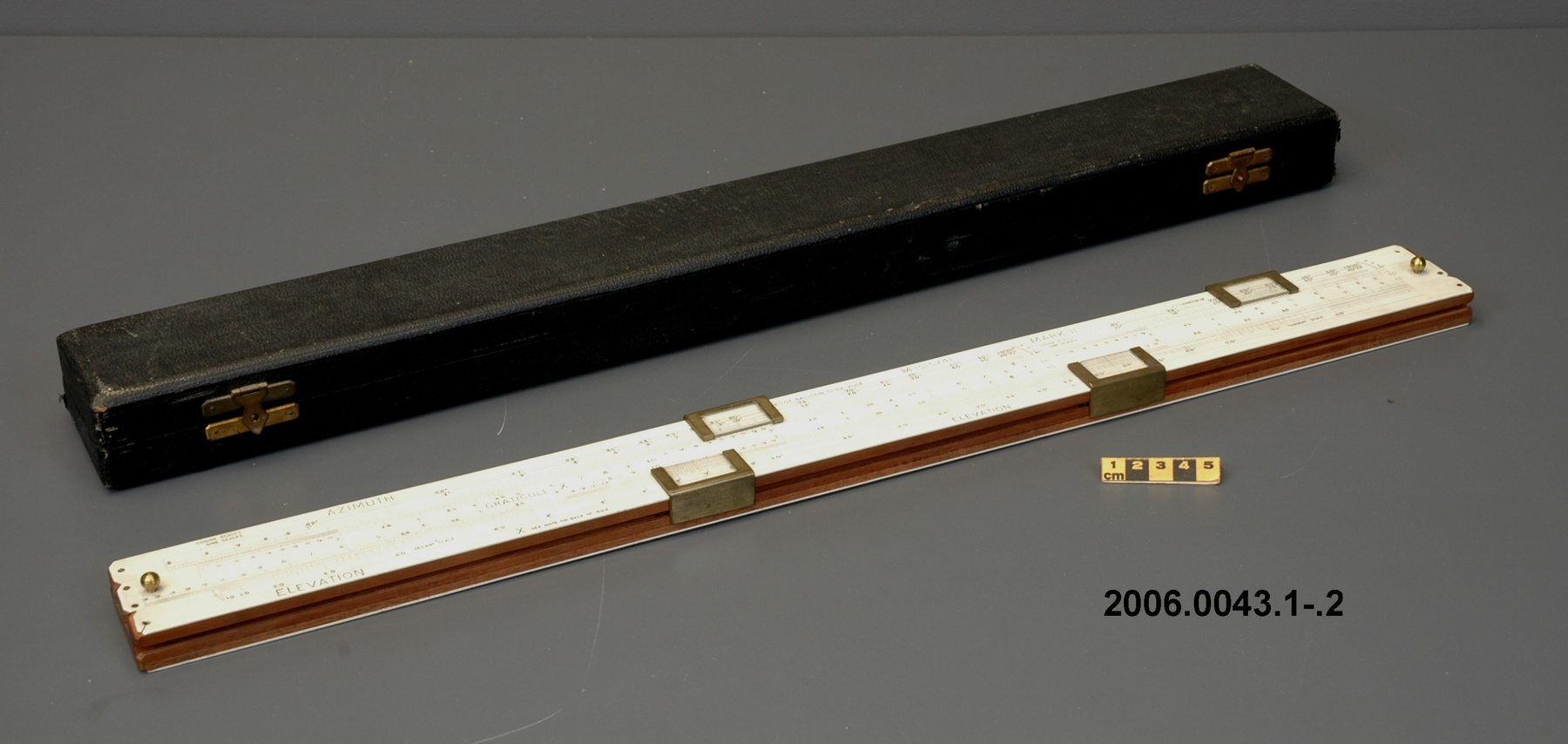
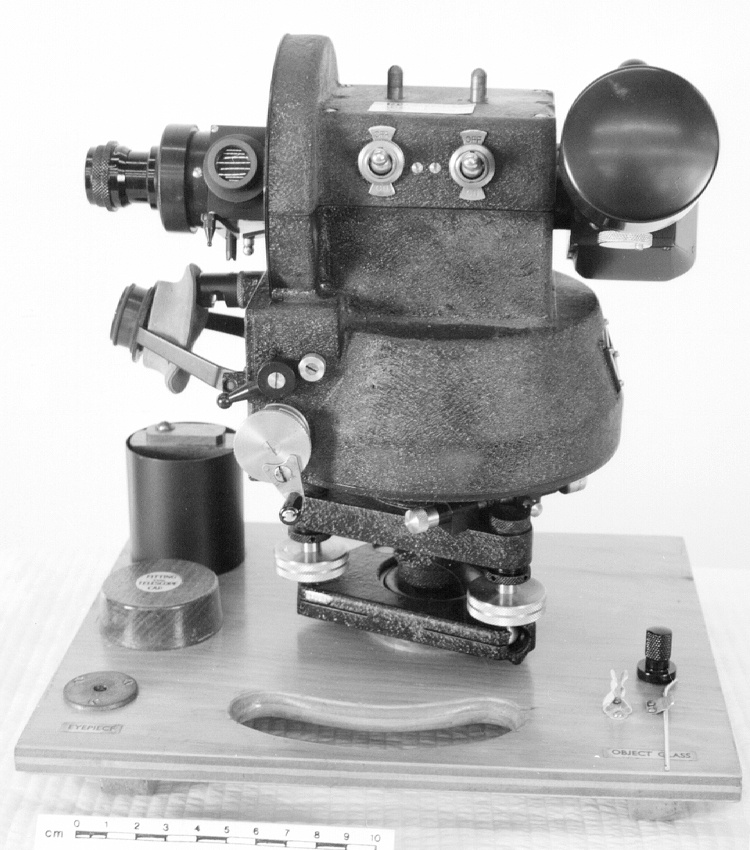
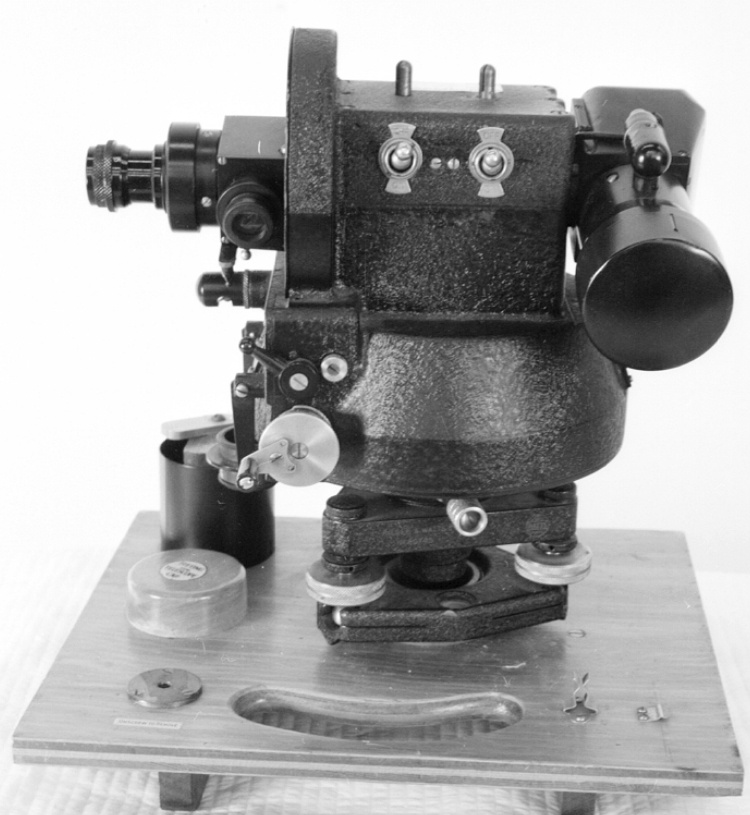
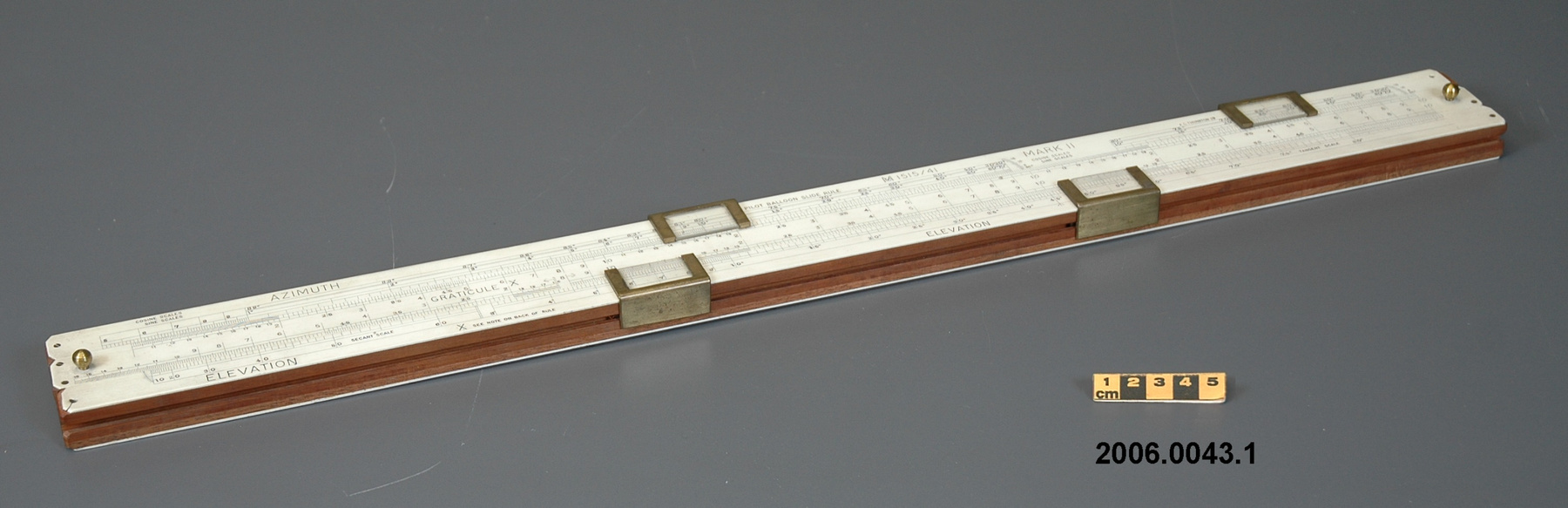
- OBJECT TYPE
- wind/pilot balloon/theodolite
- DATE
- 1941
- ARTIFACT NUMBER
- 2006.0043.001
- MANUFACTURER
- THORNTON, A.G. LTD.
- MODEL
- Mk.II
- LOCATION
- Manchester, England
More Information
General Information
- Serial #
- M1515/41
- Part Number
- 1
- Total Parts
- 2
- AKA
- N/A
- Patents
- N/A
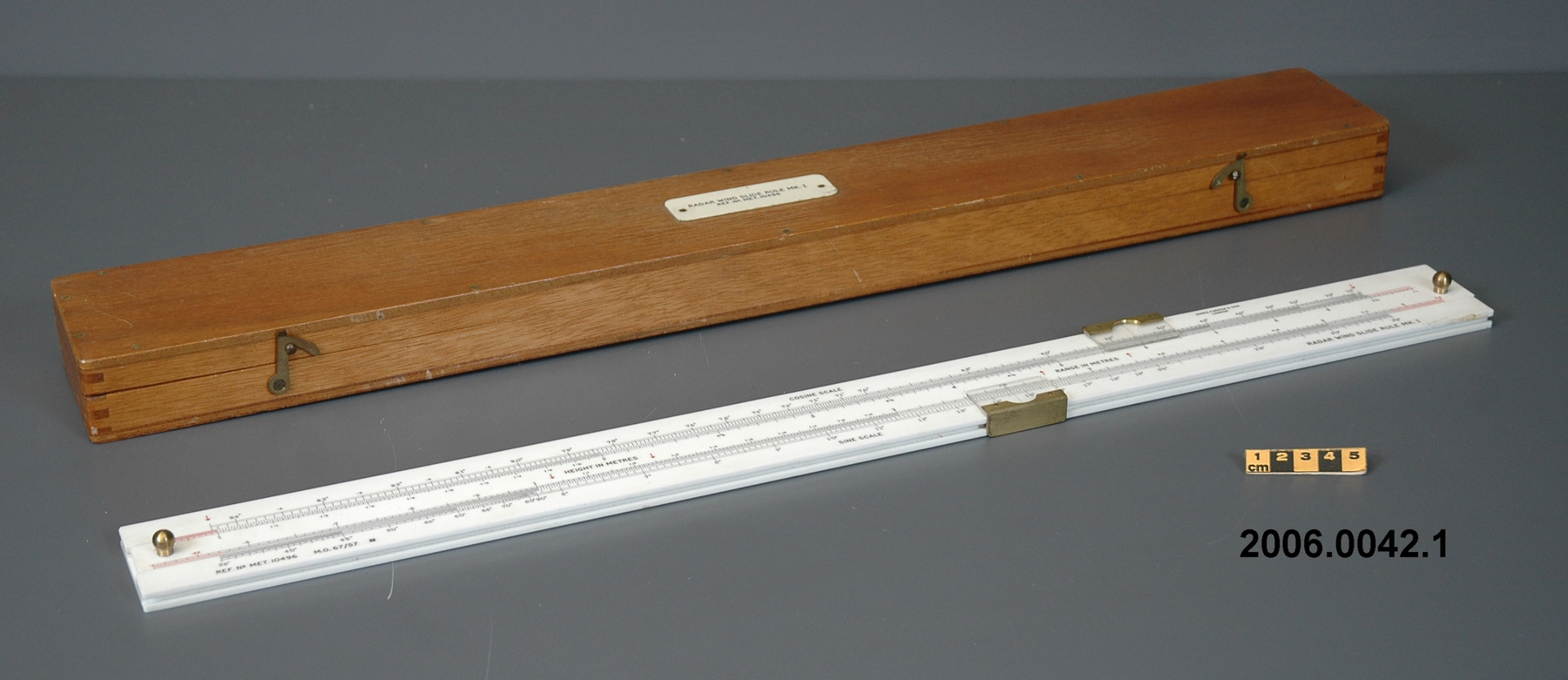
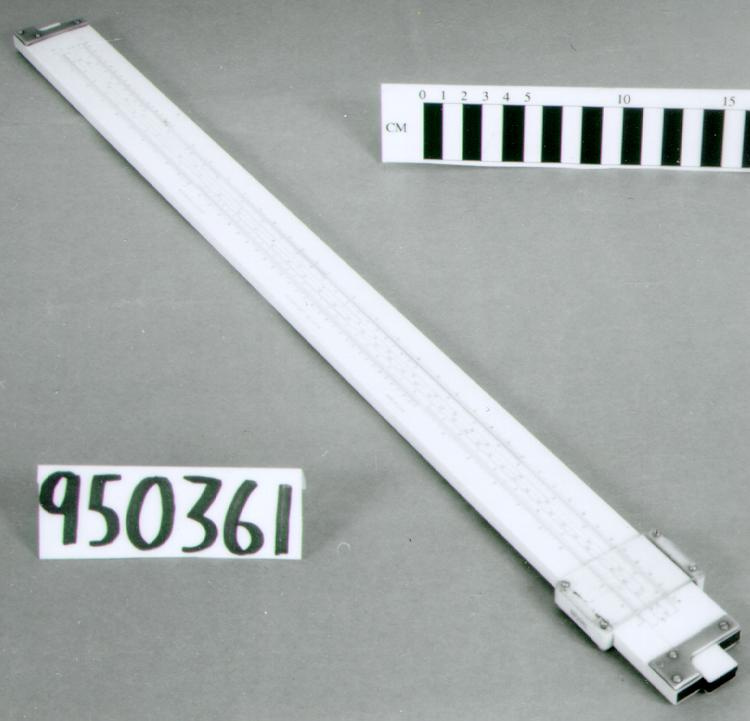
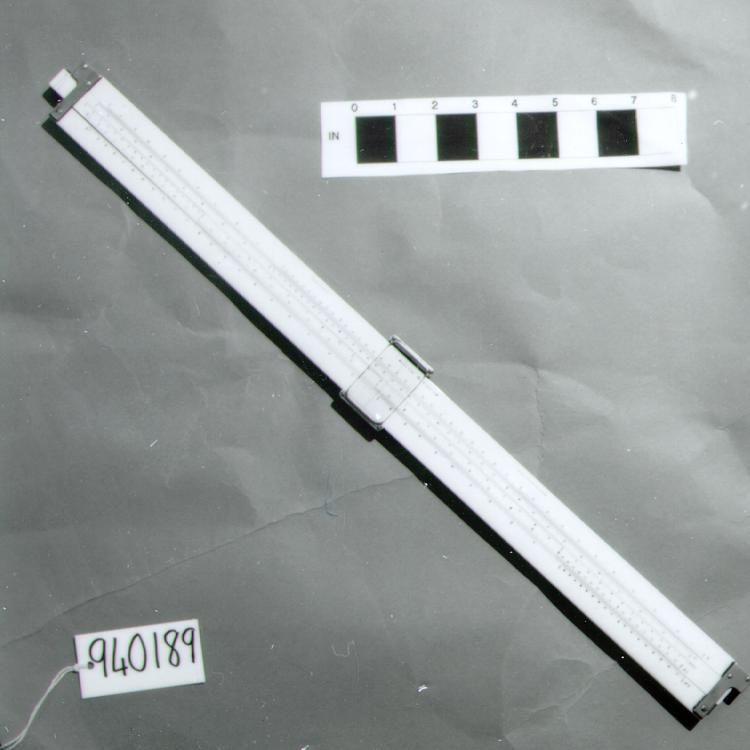
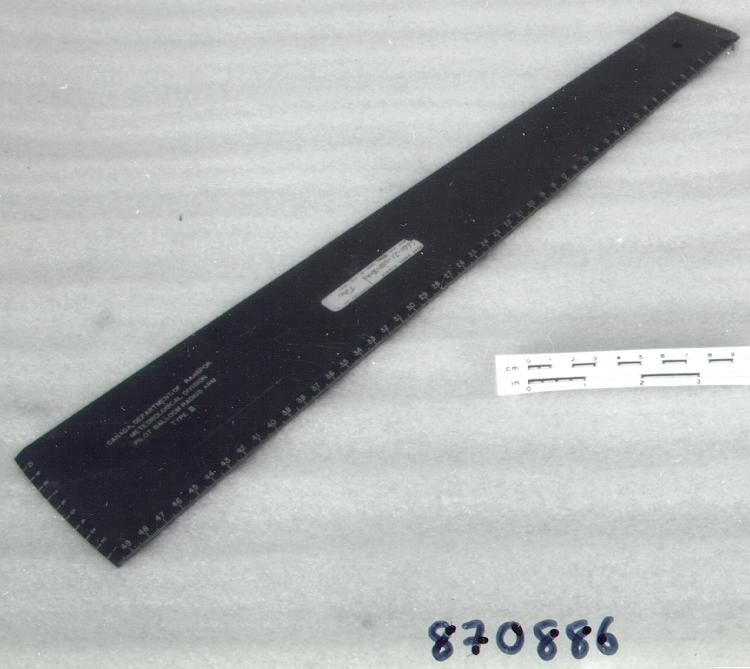
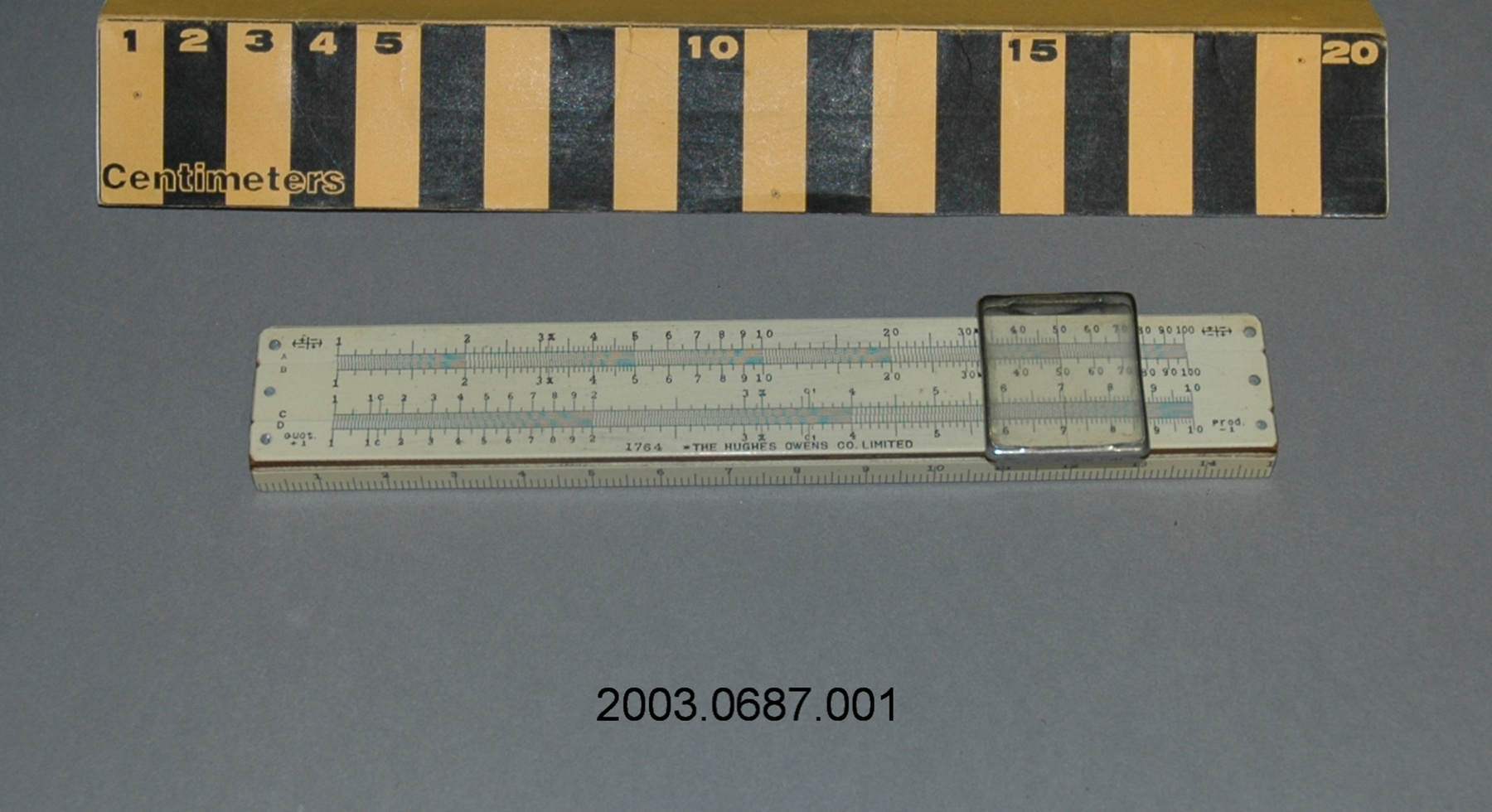
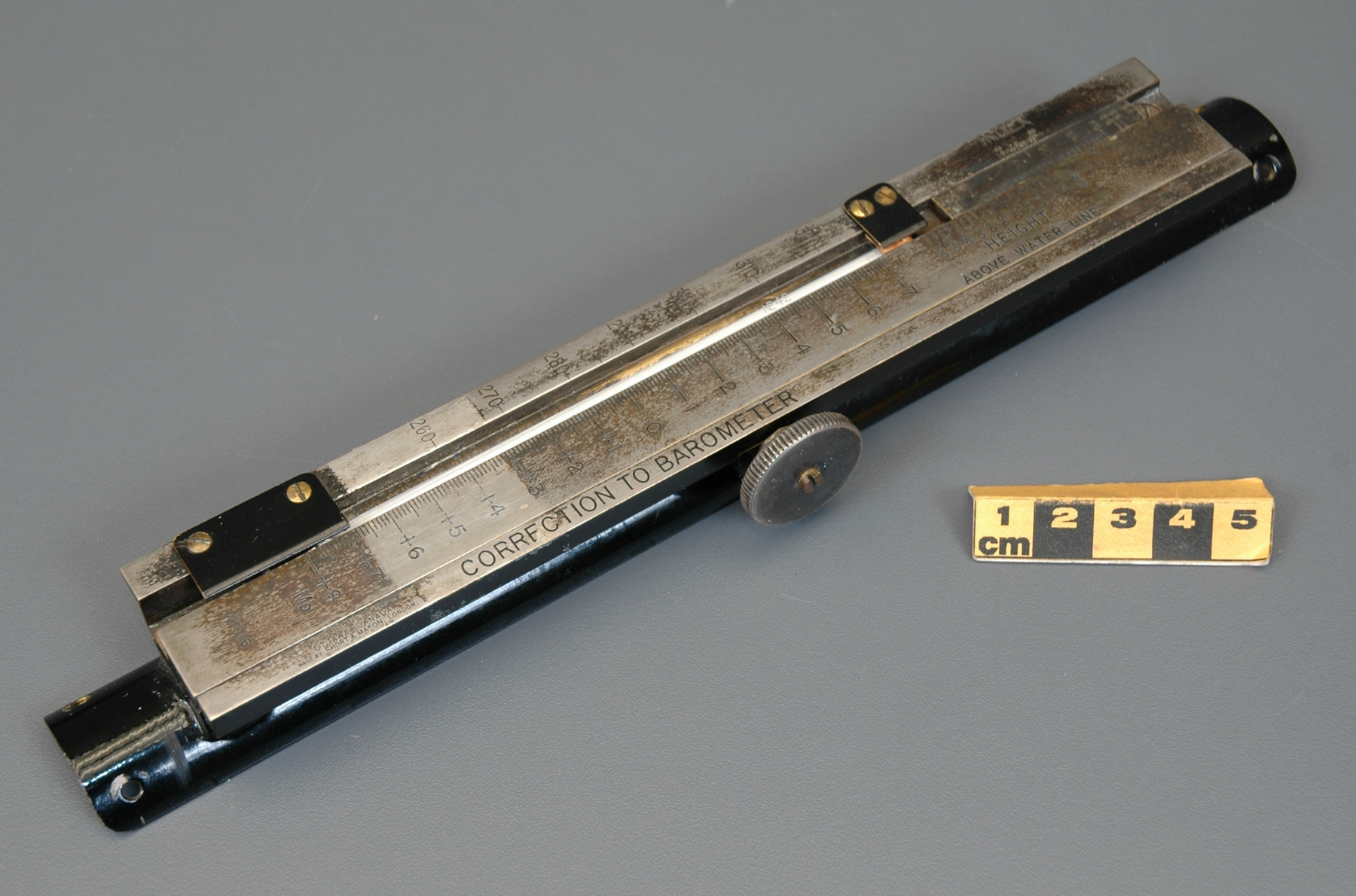
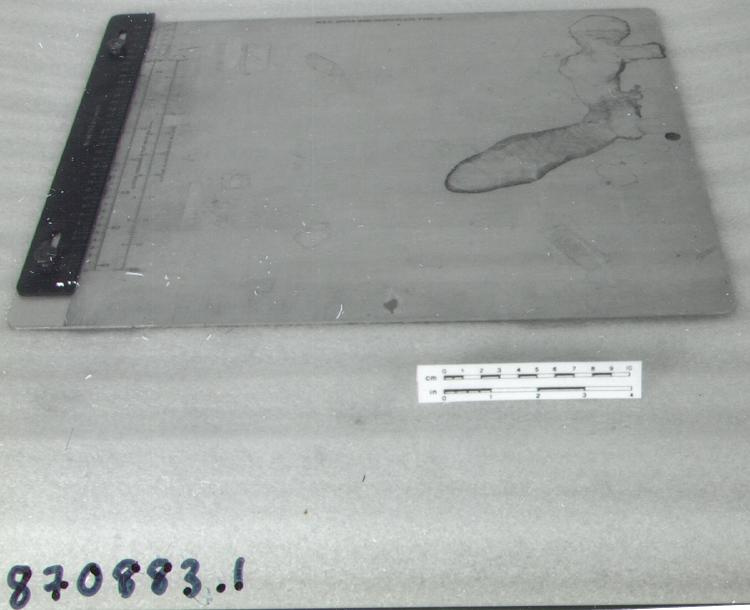
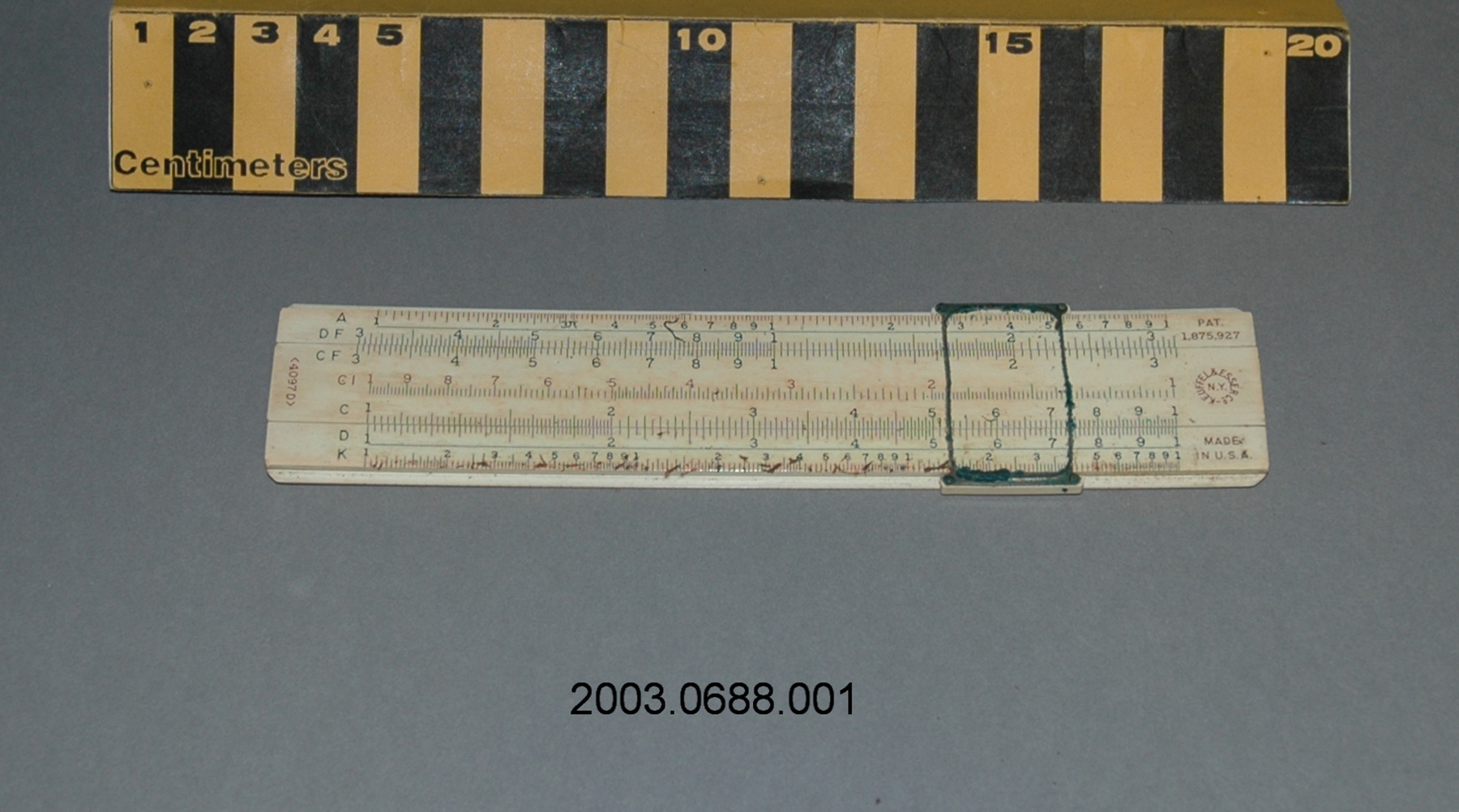
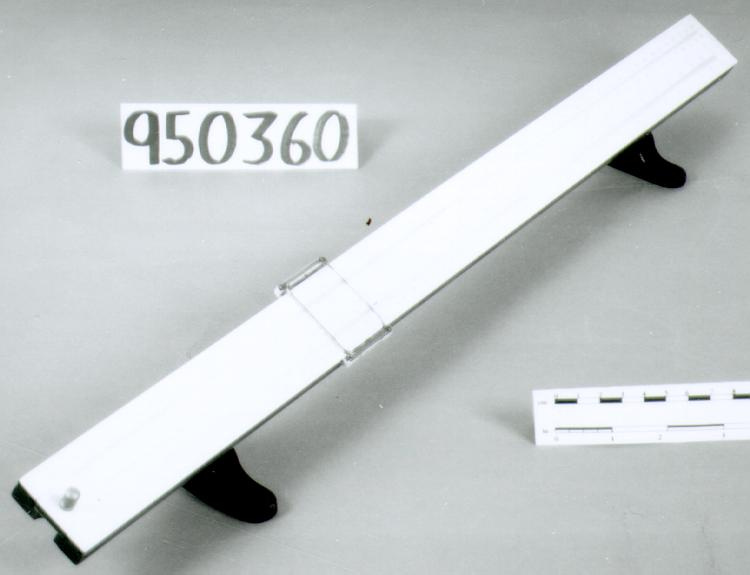
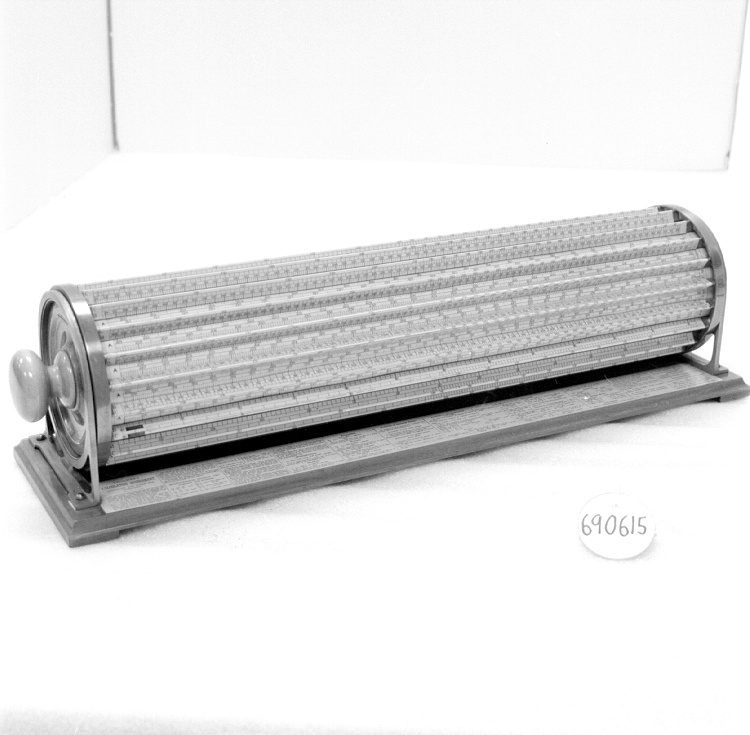
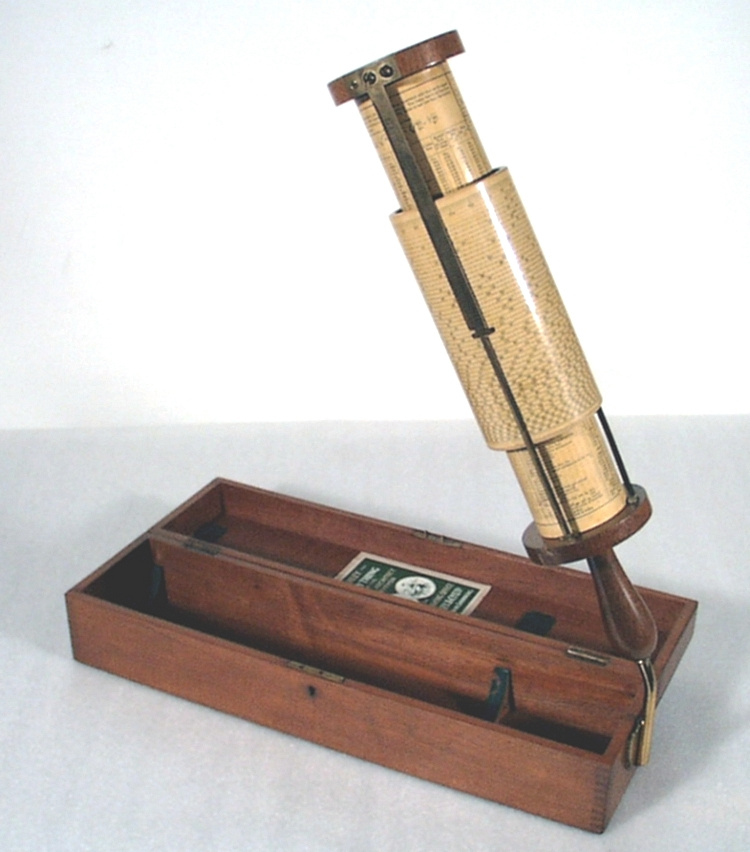
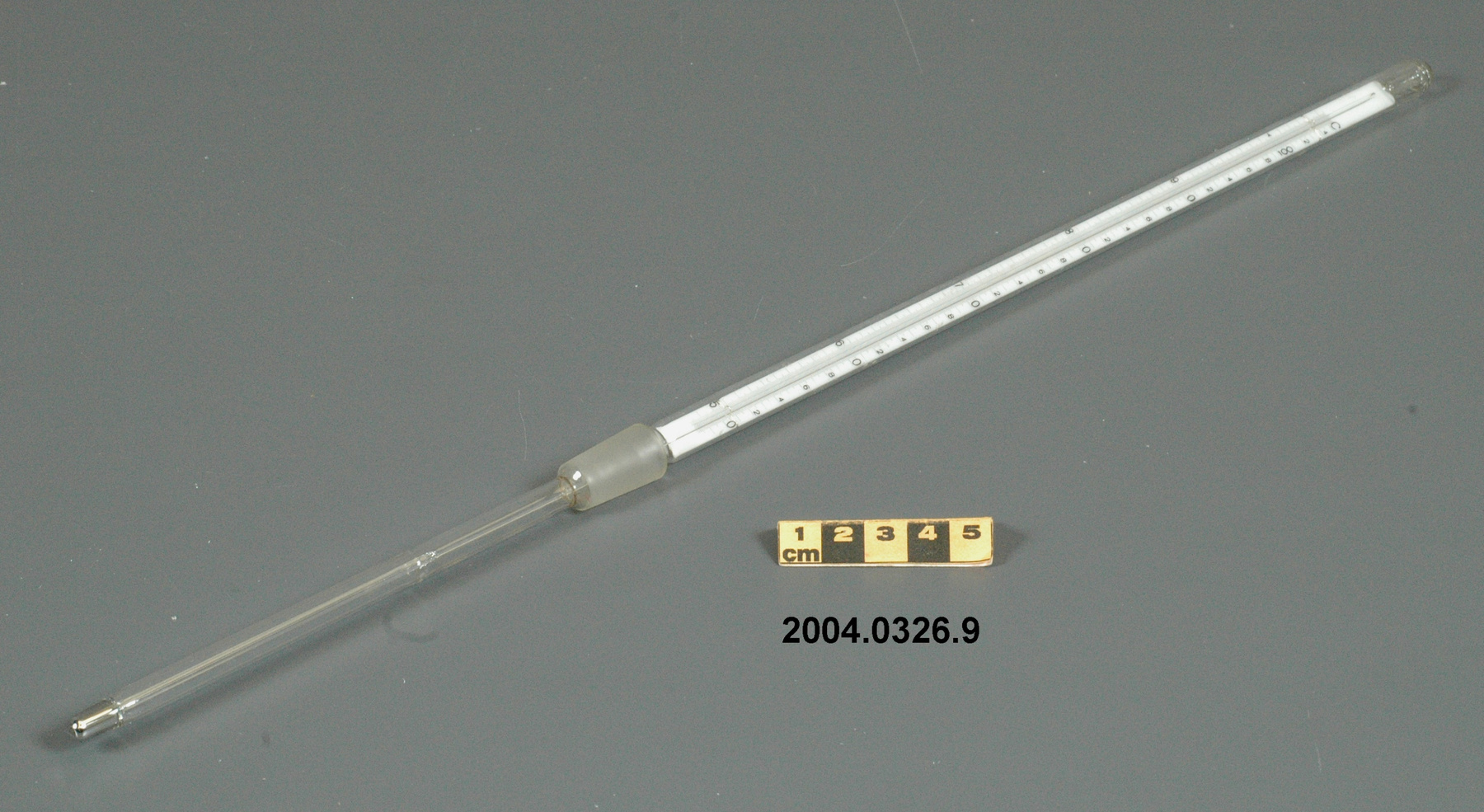
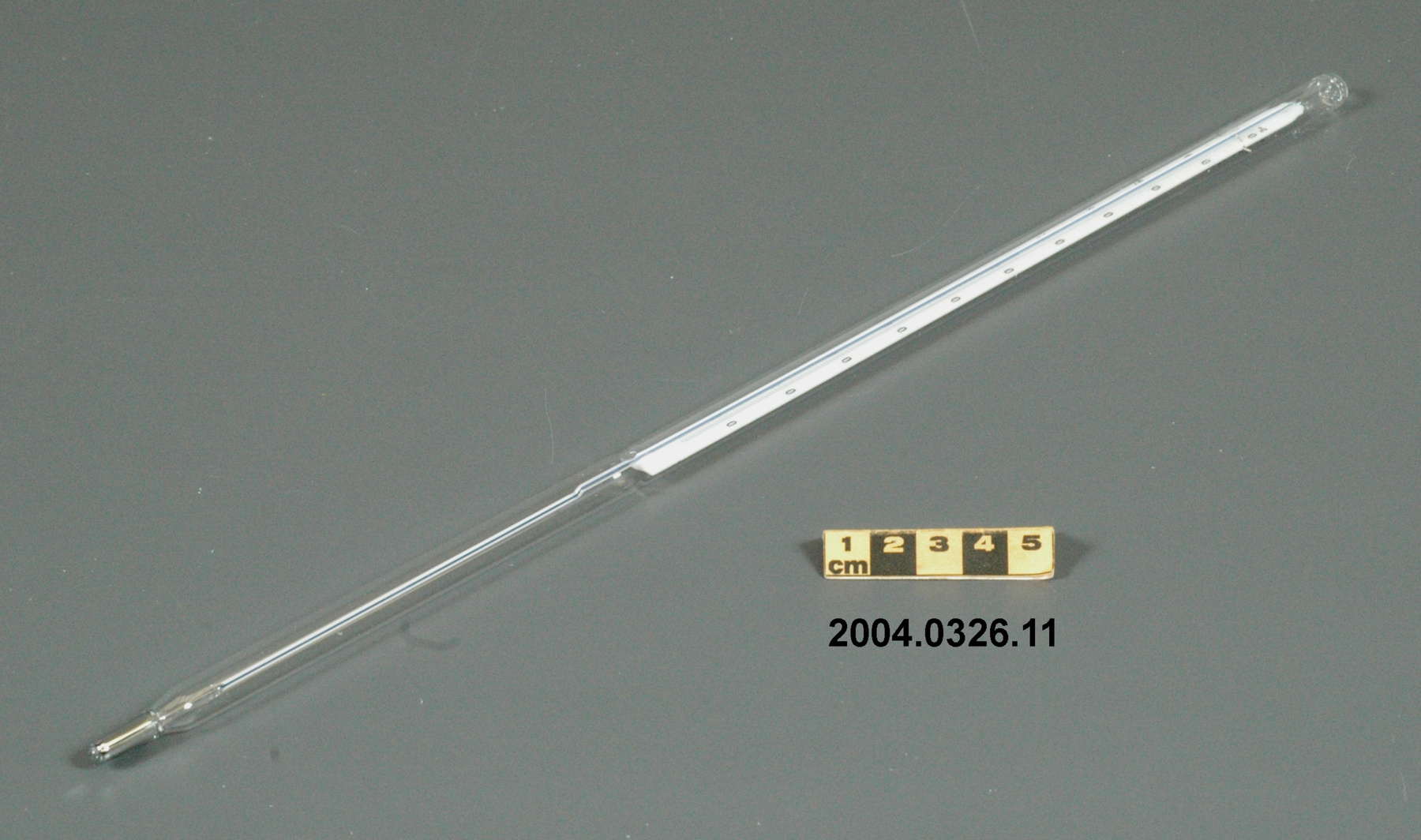
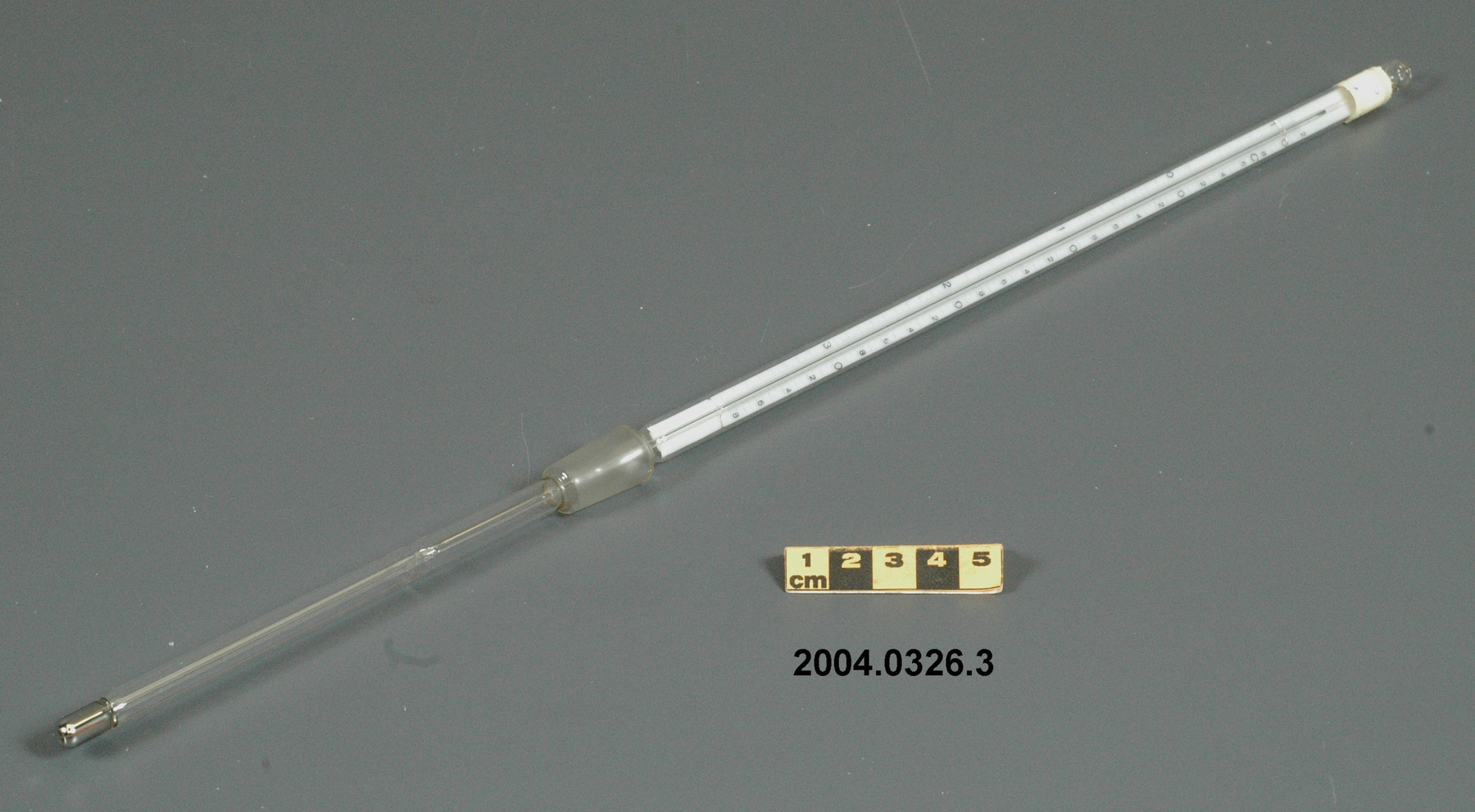
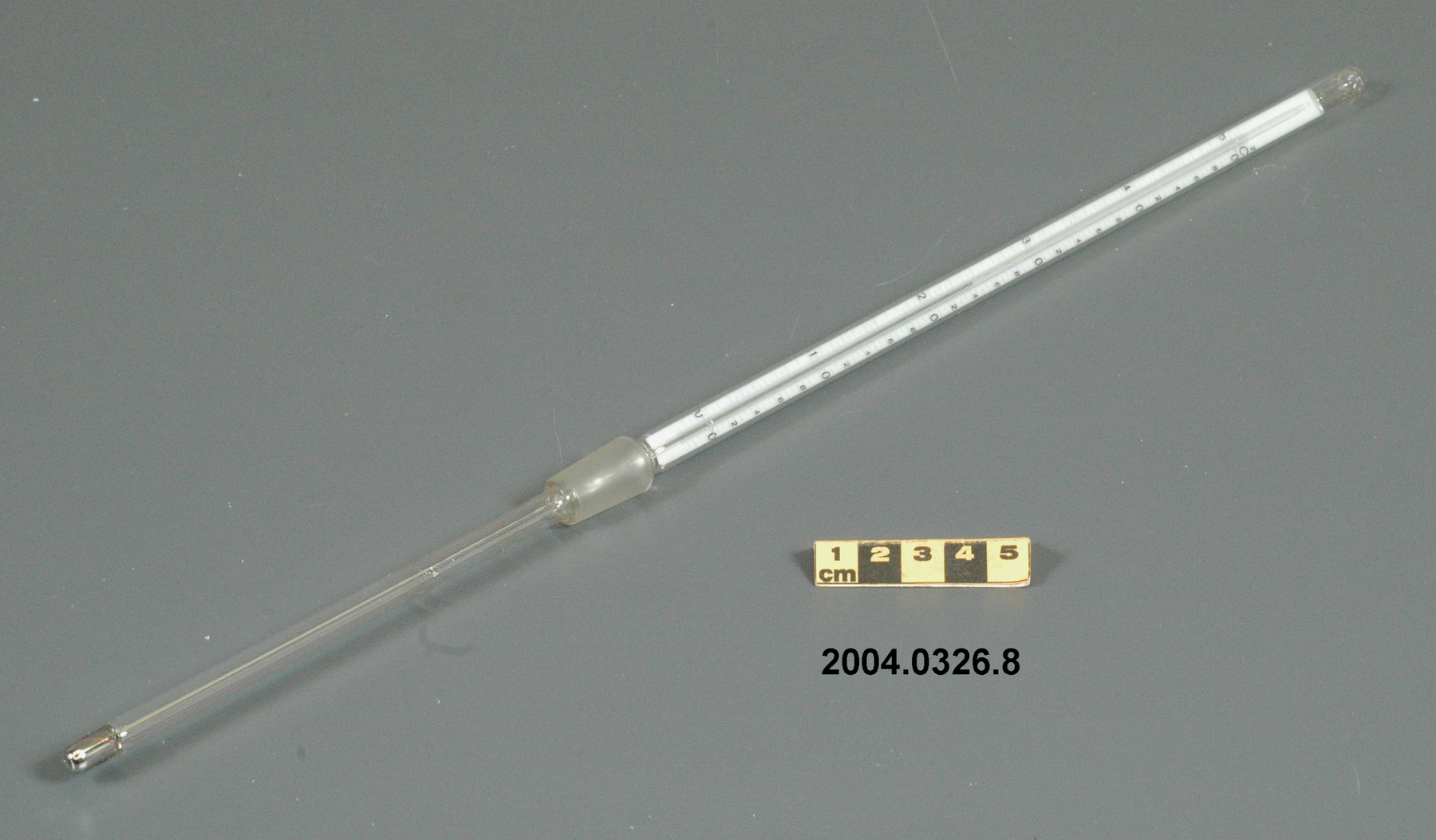
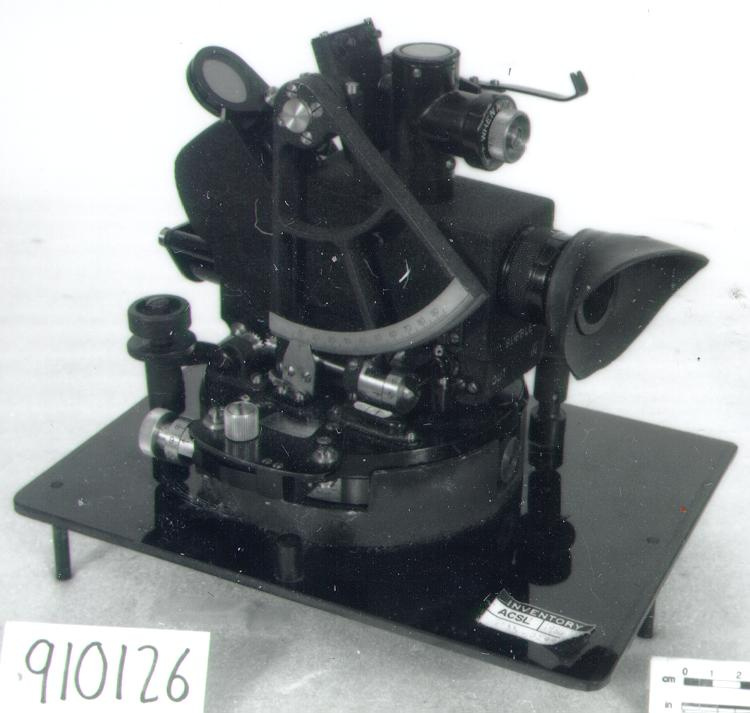
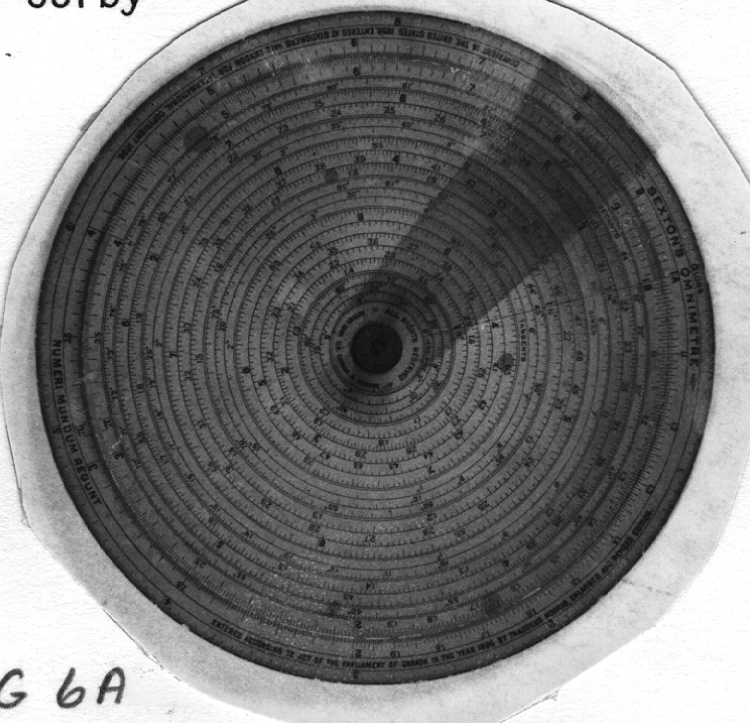
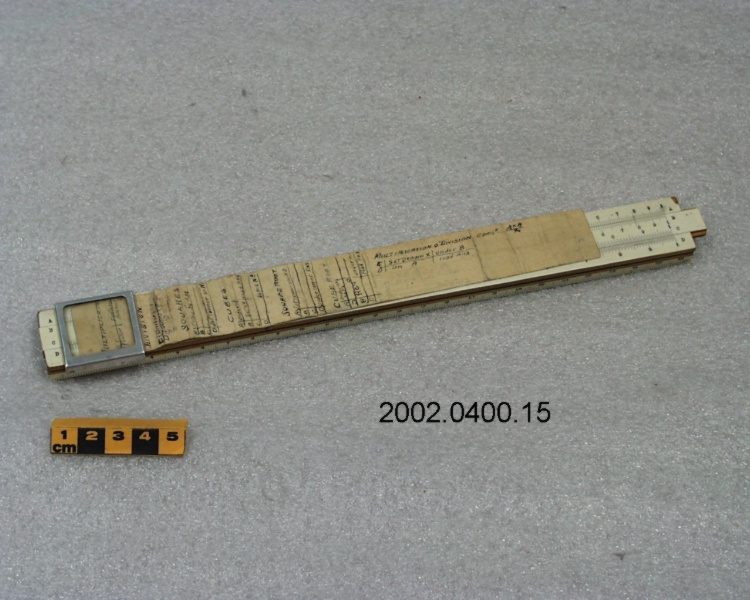
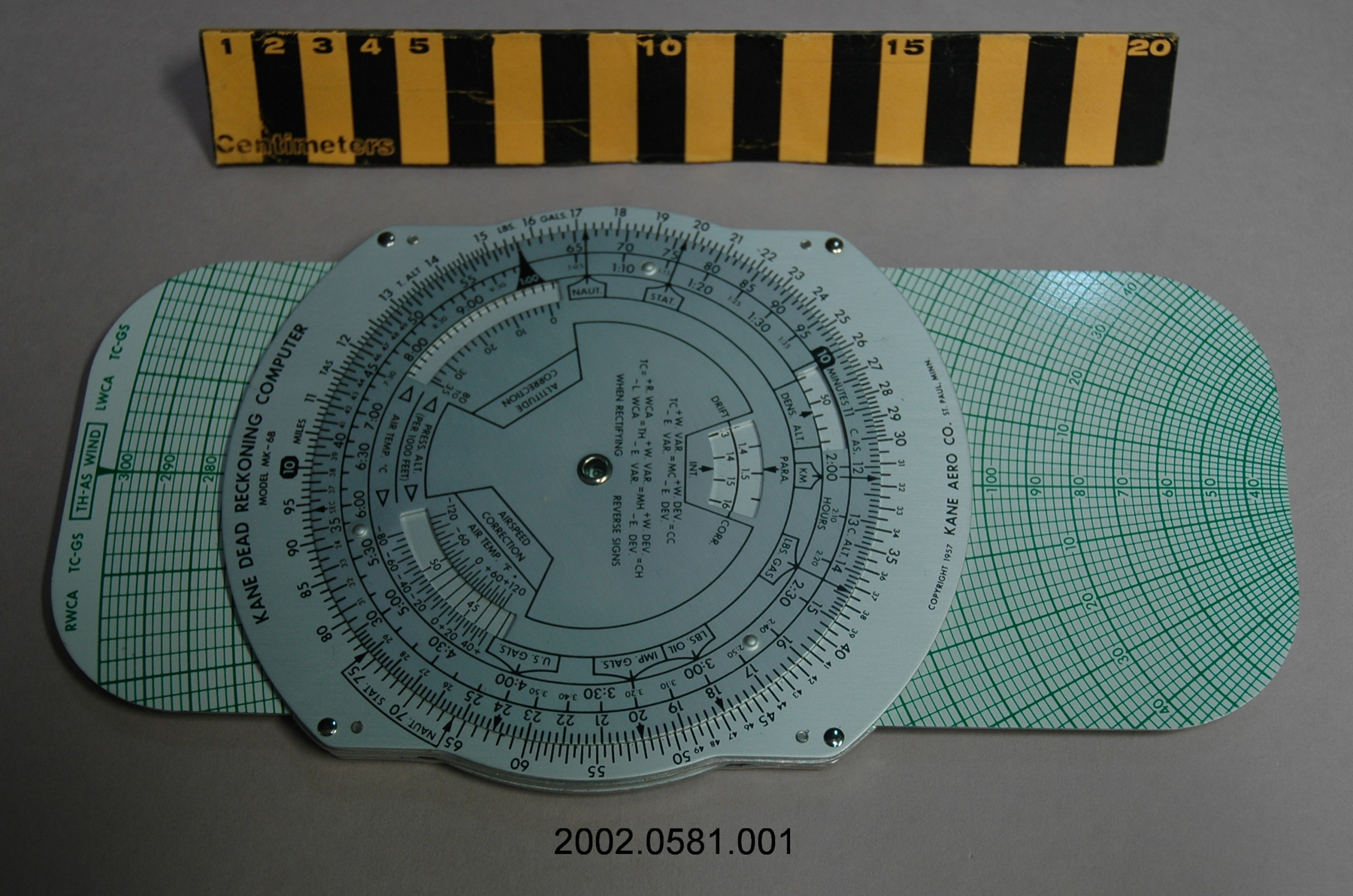
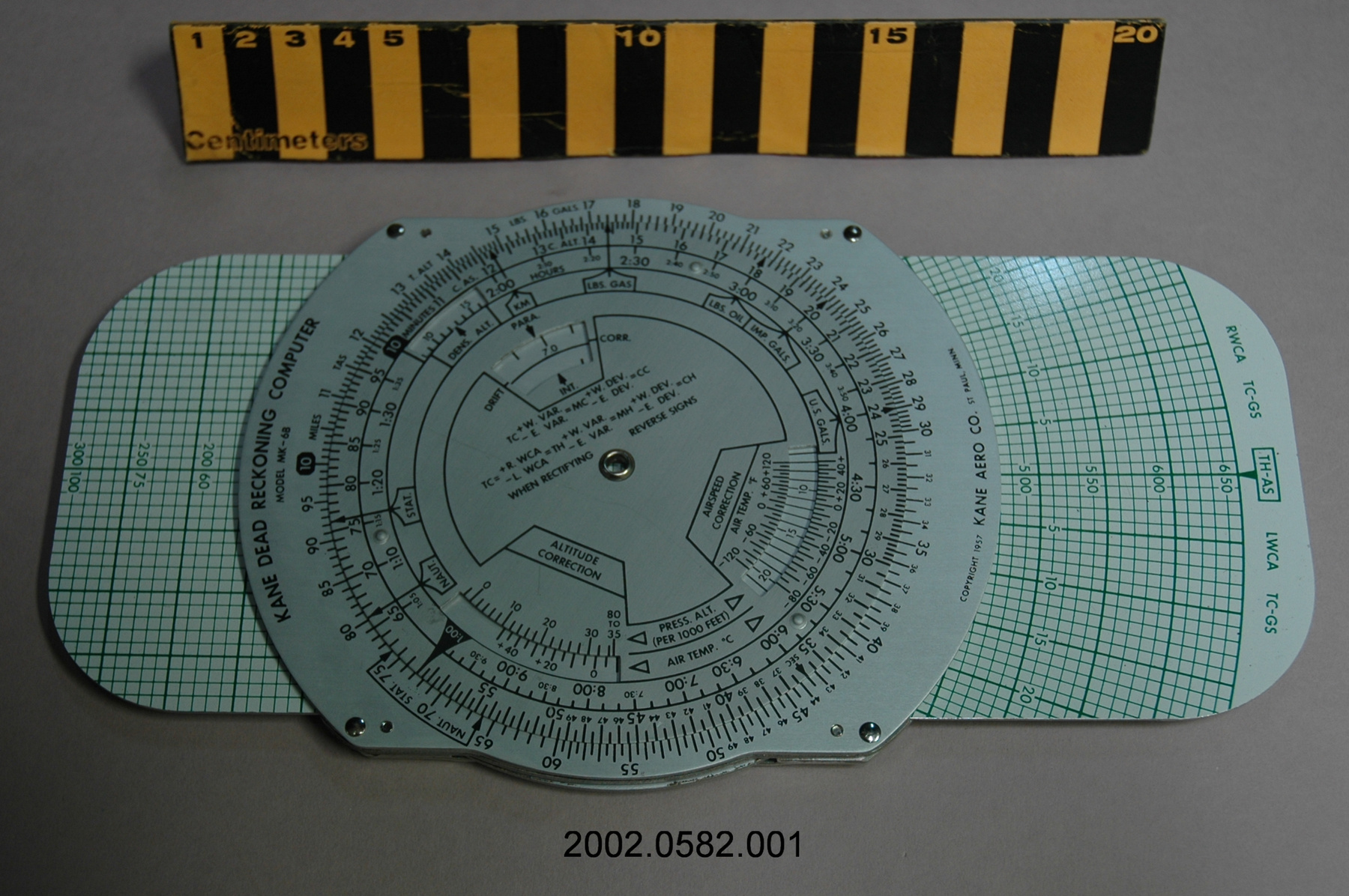
- General Description
- wood core with celluloid vernier/ brass framed cursors with glass substrate for the graticules/ brass knobs
Dimensions
Note: These reflect the general size for storage and are not necessarily representative of the object's true dimensions.
- Length
- 62.8 cm
- Width
- 5.8 cm
- Height
- N/A
- Thickness
- 2.5 cm
- Weight
- N/A
- Diameter
- N/A
- Volume
- N/A
Lexicon
- Group
- Mathematics
- Category
- Calculating devices
- Sub-Category
- N/A
Manufacturer
- AKA
- THORNTON
- Country
- England
- State/Province
- Unknown
- City
- Manchester
Context
- Country
- United Kingdom
- State/Province
- Unknown
- Period
- early 1940's +
- Canada
-
A British made instrument possibly used by the Meteorological Service of Canada, though the specific use there is not known. With the 1941 date, it was likely used at an airport in support of military operations or for related research. Part of a large collection of meteorological instruments acquired from the MSC (previously Atmospheric Environment Service) by the CSTM since 1967. MSC is the government agency responsible for collecting and disseminating meteorological data and forecasts in Canada. It was founded in 1871 in Toronto where it is still headquartered. The MSC was originally on the University of Toronto downtown campus but moved to Downsview in 1971 on land owned by UofT. The headquarters houses laboratories, research facilities and calibration and instrument maintenance facilities. - Function
-
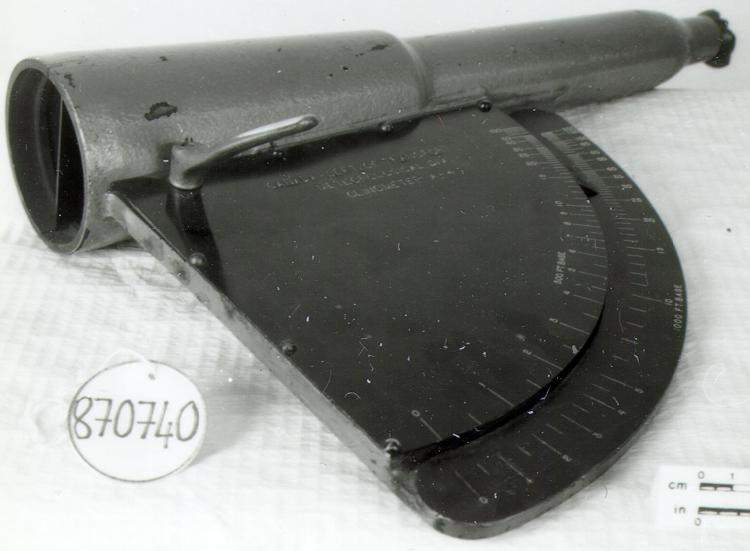
An instrument used to carry out the computations based on observations (altitude, azimuth and distance) of pilot balloons with theodolites in order to measure the speed and direction of wind in the upper atmosphere. - Technical
-
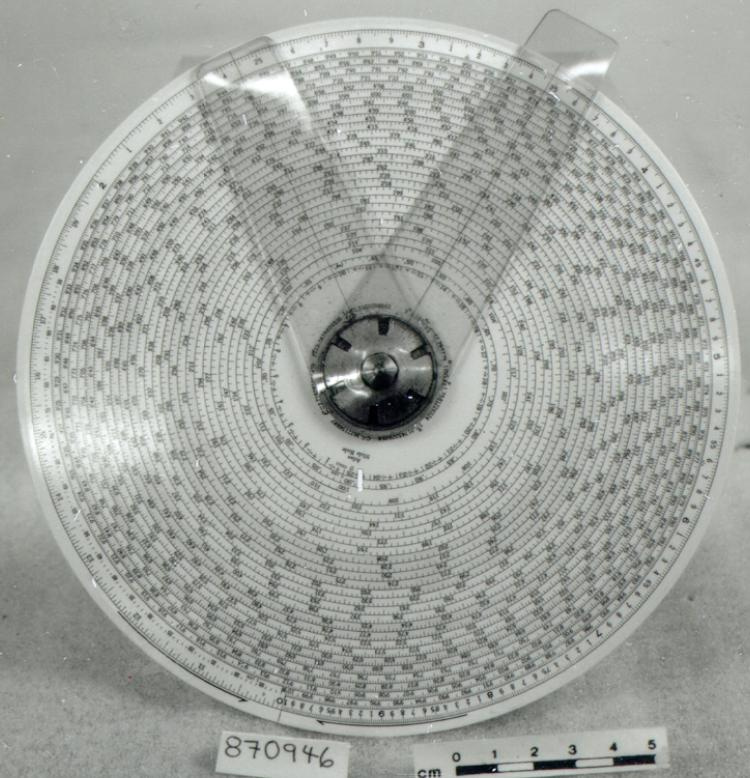
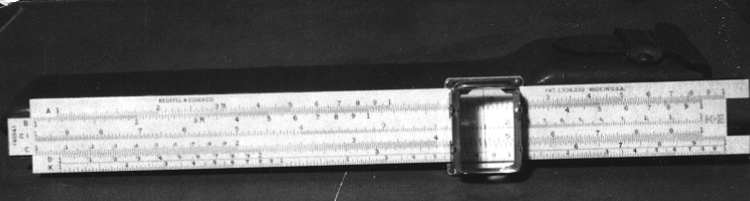
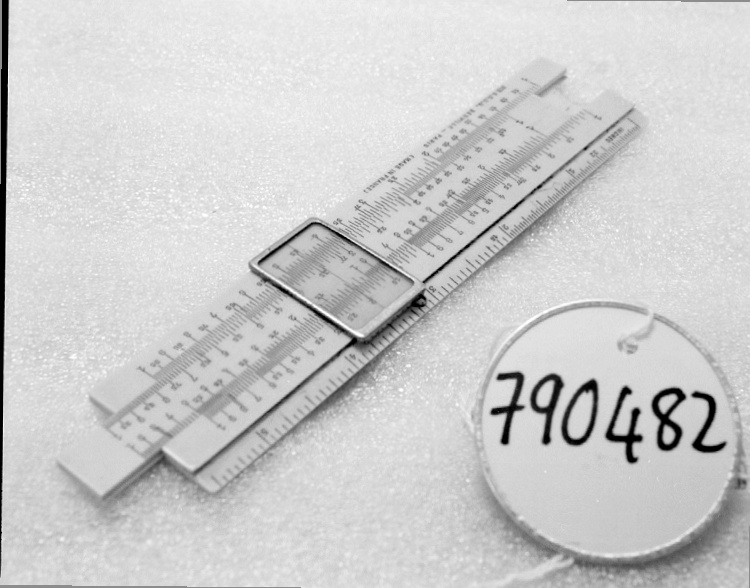
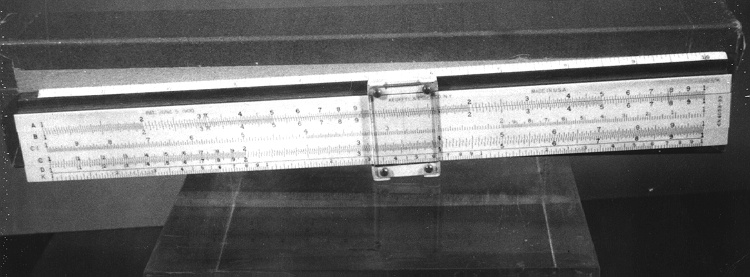
An example of a specialized function slide rule used to make meteorological calculations. It is a typical looking slide rule but with scales only on one side and with scales suited to determining the height of a pilot balloon for meteorological measurements - specifically wind speed and direction. Scales include since, cosine, secant and tangent. 3 scales have unusual small curved scales -- 2 marked 90, 5, 10 and 15 but reading to approx.. 20. The third is not marked. The slider is marked "Graticule X" and there are 4 cursors with graticules. It has a Meteorological Office mark (O stamped over M). The serial number 1515/41 is consistent with UK's Air Ministry codes used on air sextants made during WW II. This particular slide rule was designed by the Meteorological Office of the Air Ministry (UK) in 1926/27. The SML caption states: Pilot balloons were used as tracers for wind in the upper air, and to carry lightweight meteorological instruments. They would be monitored by meteorologists on the ground, either visually using adapted theodolites, or by radar. The slide rule was specially devised to help with the subsequent calculations from the actual readings and many forms were developed. This is the United Kingdom Meteorological Office pattern, Mark Two. It was devised by F J W Whipple, then superintendent of the Kew Observatory, and made by Hicks. Slide rules have been used in various from since the early 17th c soon after John Napier invented logarithmetic tables. Wherever calculations were required that involved logs or trigonometric functions, slide rules provided an efficient way to do the computations. Mechanical and electromechanical calculators supplemented slide rules beginning in the 18th c but their expense limited the impact. More models, particularly de Thomas' Arithometer and Curta calculators (ca. 1948) further impacted the scientific use of slide rules but they were not made obsolete until the HP-35 electronic calculator appeared in 1972. - Area Notes
-
Unknown
Details
- Markings
- Black lettering on rule reads 'PILOT BALLOON SLIDE RULE MO [logo] 1515/41' MARK II A.G. THORNTON LTD.'/ black scale markings and lettering reading 'COSINE SCALES/ SINE SCALES', 'ELEVATION', 'SECANT SCALE', 'TANGENT SCALE' and 'GRATICULE X'
- Missing
- appears complete
- Finish
- brown stained rule/ white scales/ gold coloured brass/ colourless transparent parts
- Decoration
- N/A
CITE THIS OBJECT
If you choose to share our information about this collection object, please cite:
THORNTON, A.G. LTD., Slide rule, 1941, Artifact no. 2006.0043, Ingenium – Canada’s Museums of Science and Innovation, http://collection.ingeniumcanada.org/en/id/2006.0043.001/
FEEDBACK
Submit a question or comment about this artifact.
More Like This