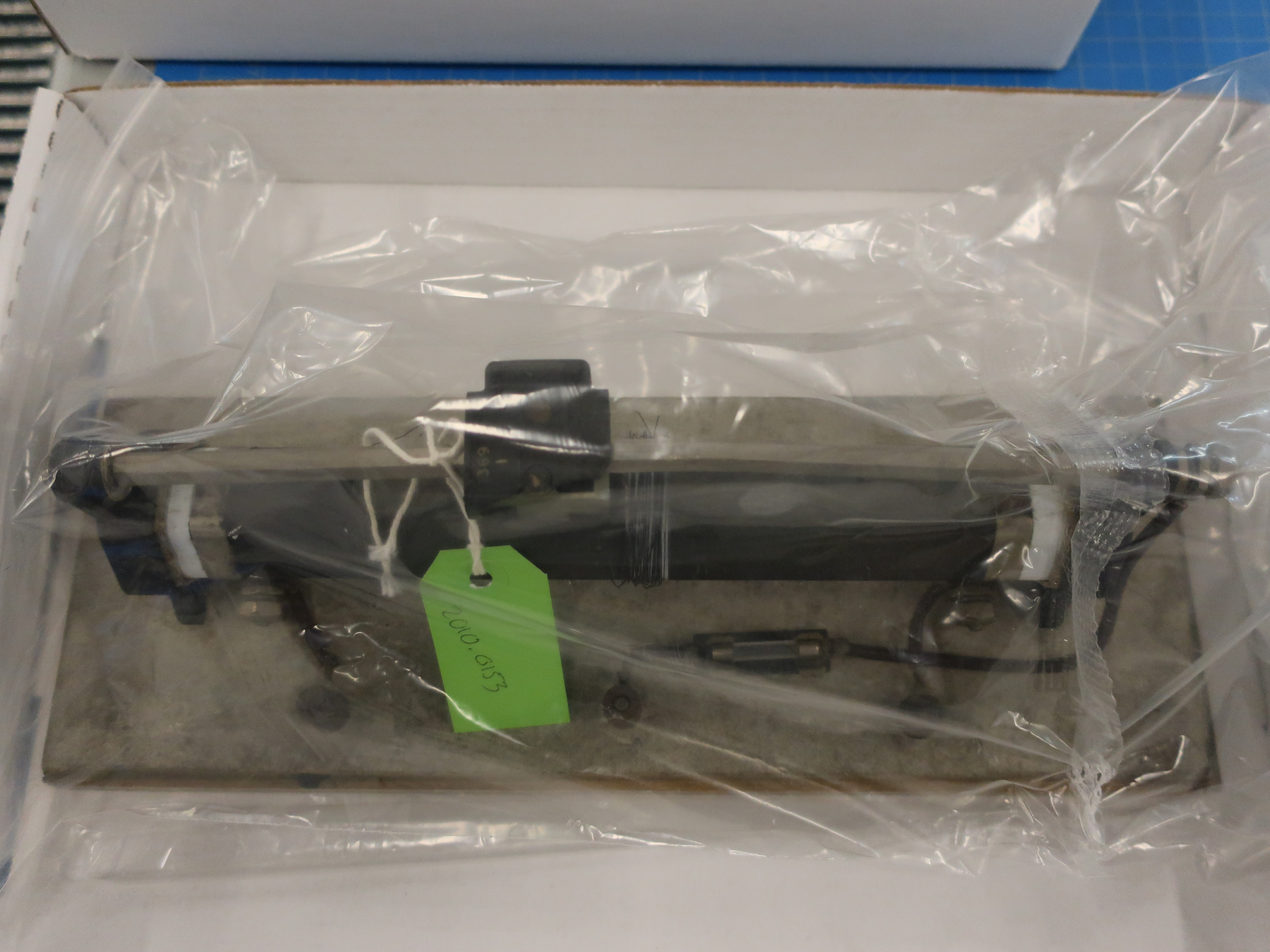
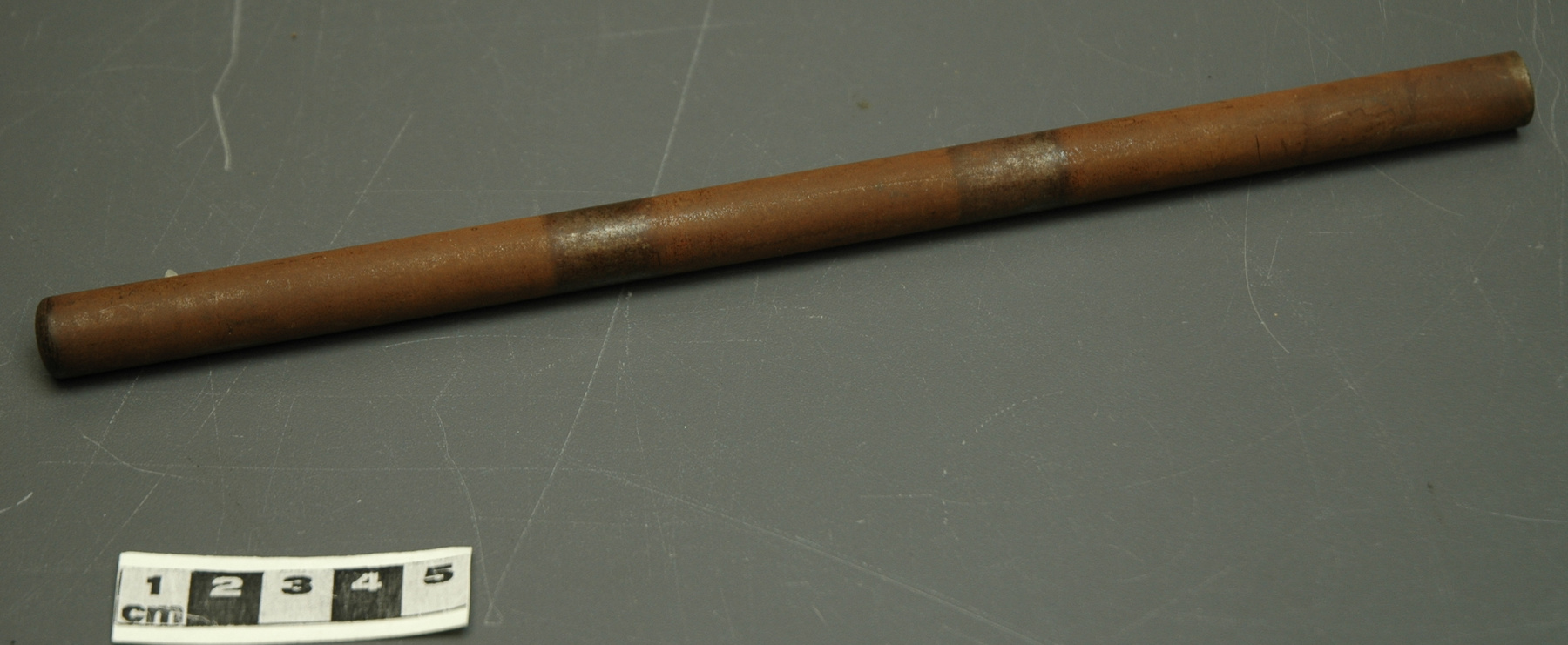
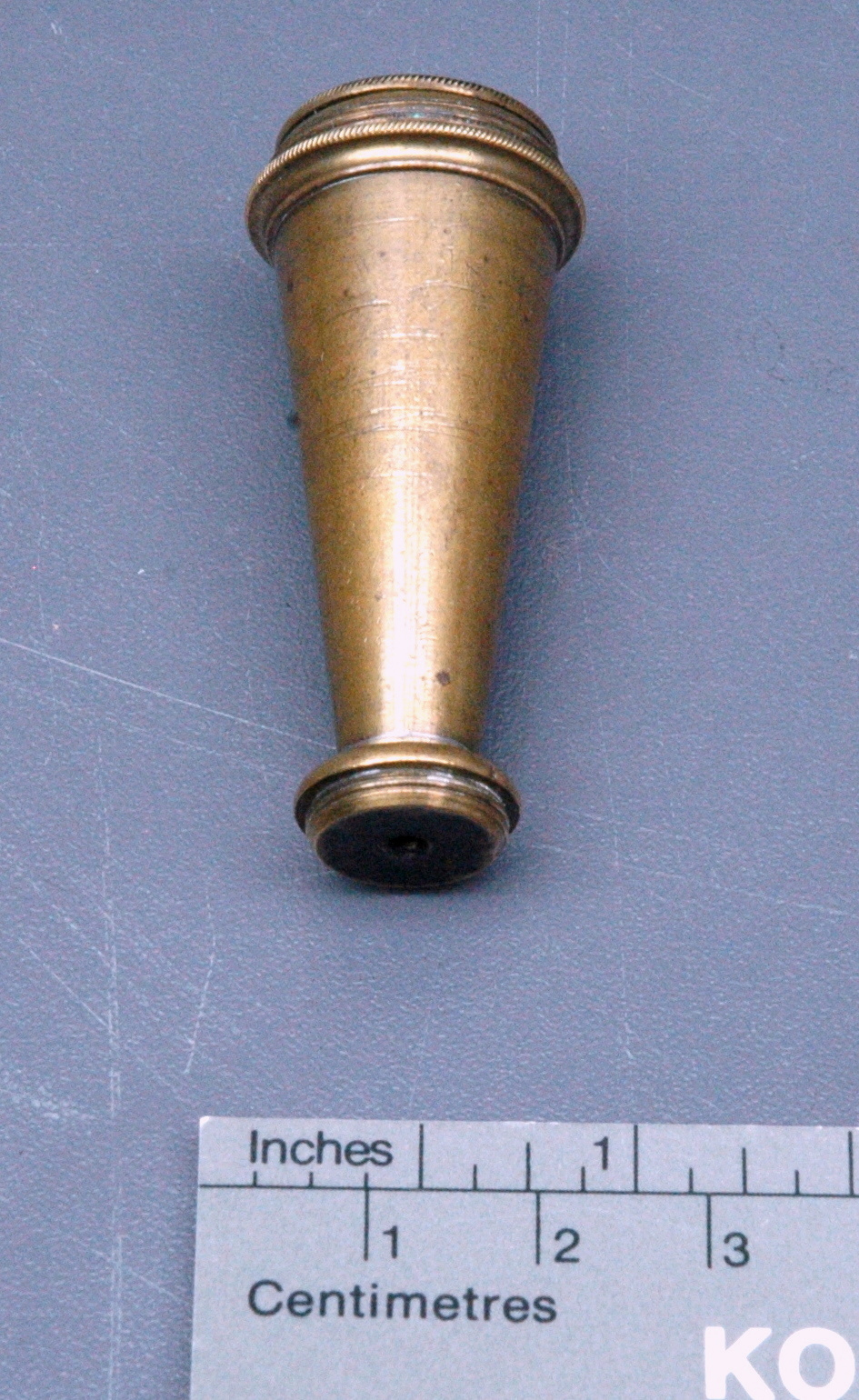
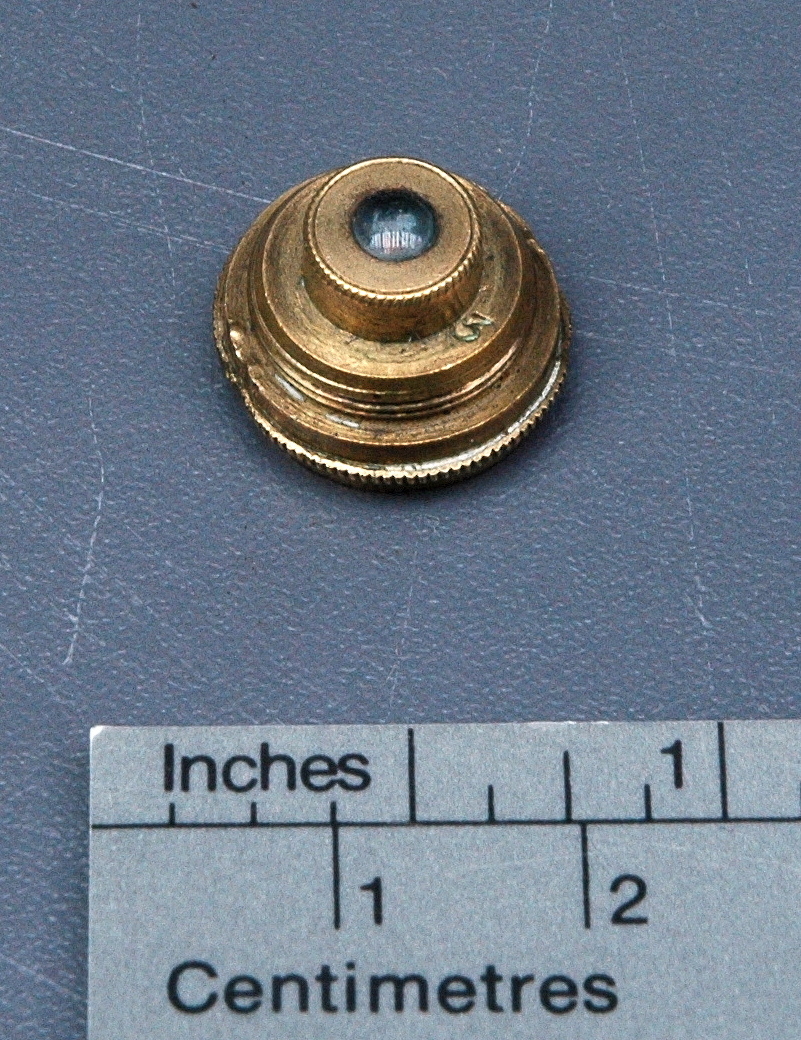
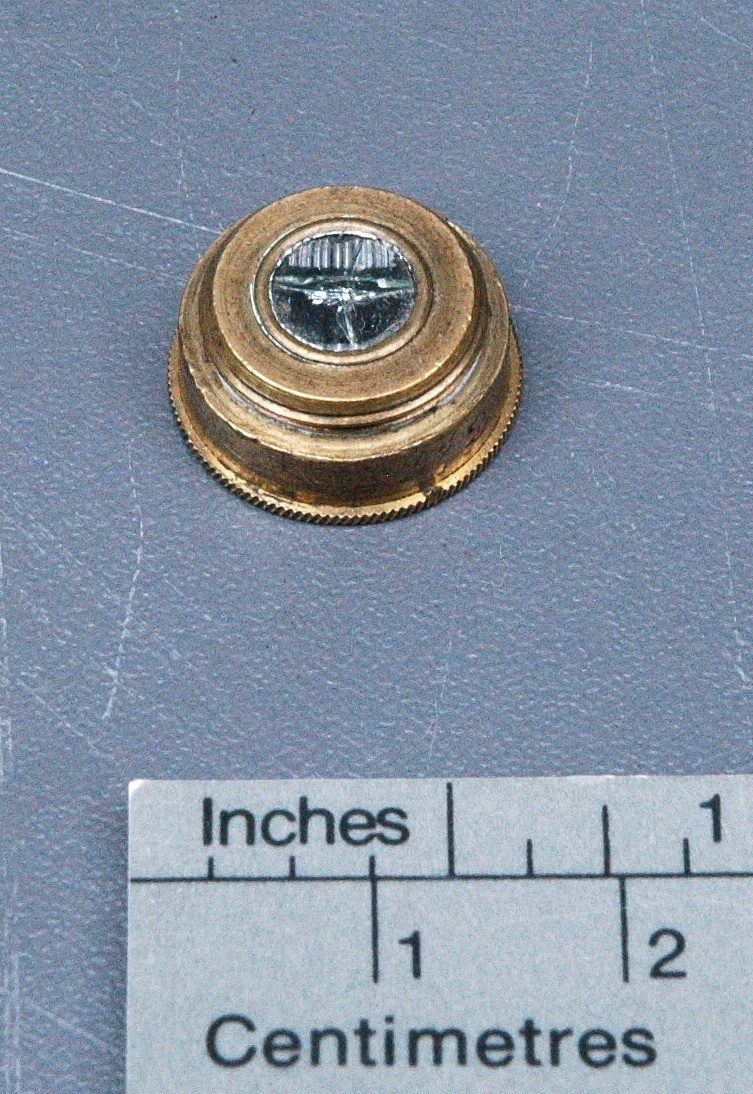
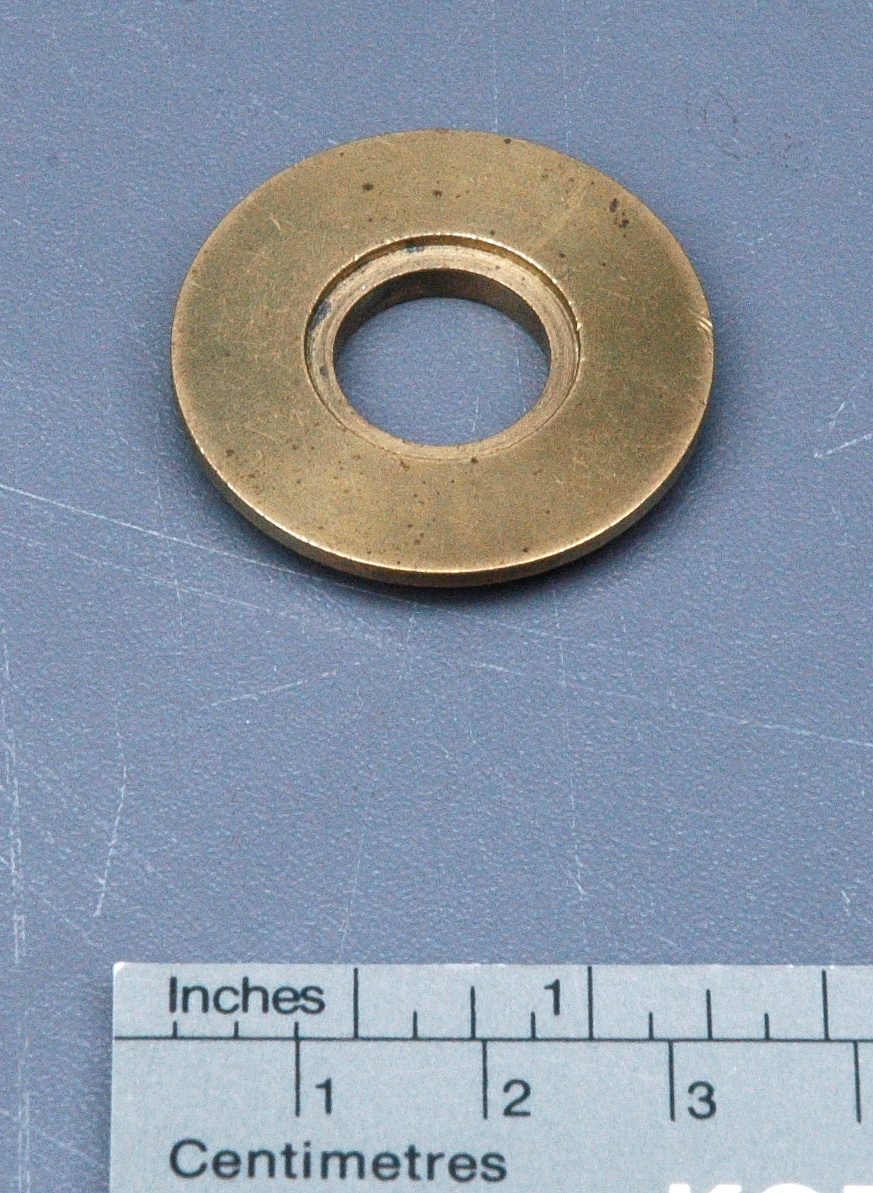
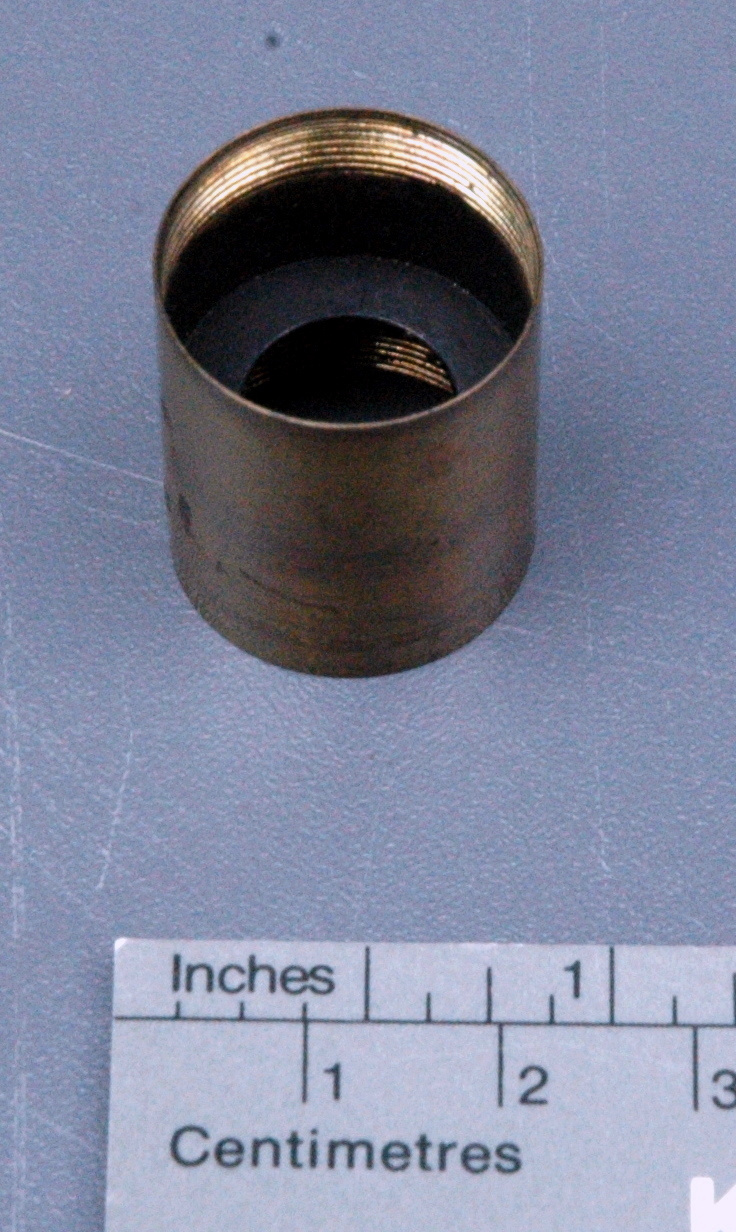
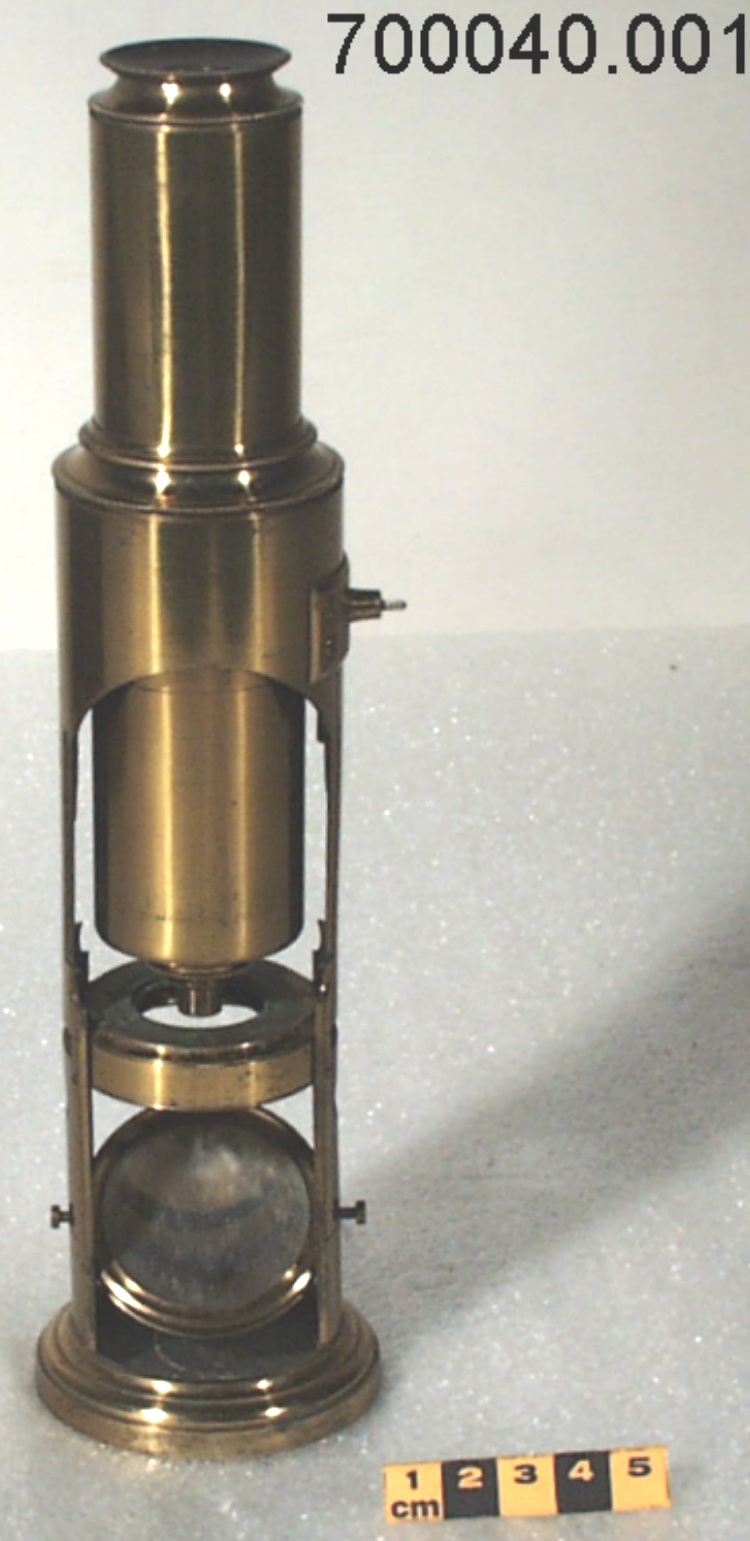
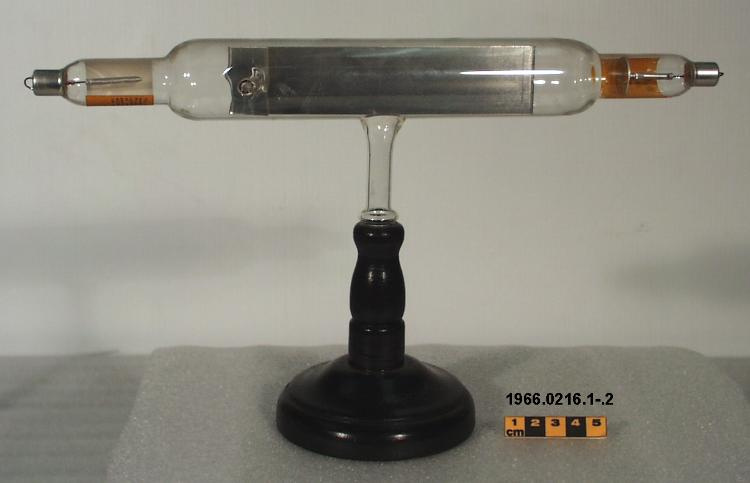
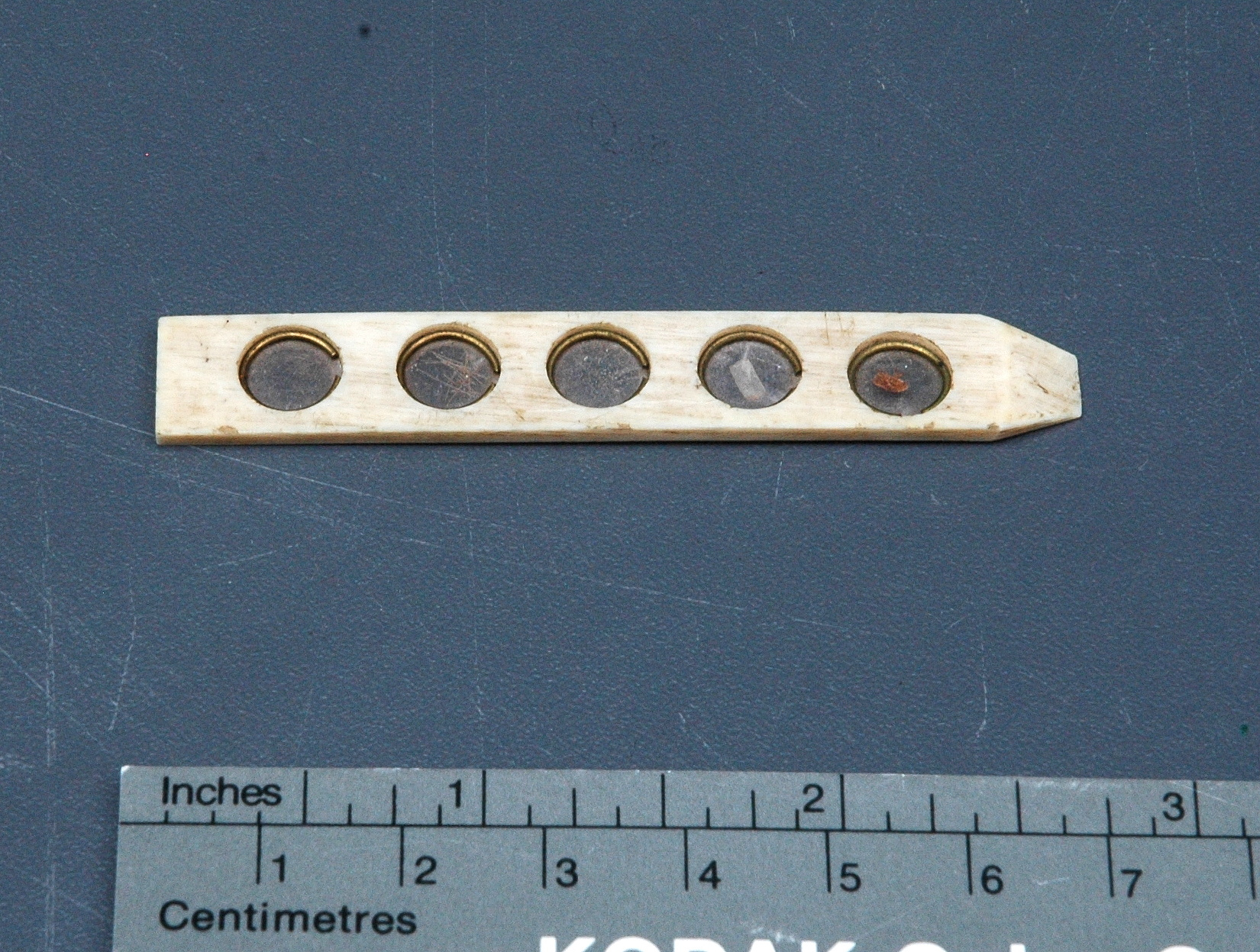
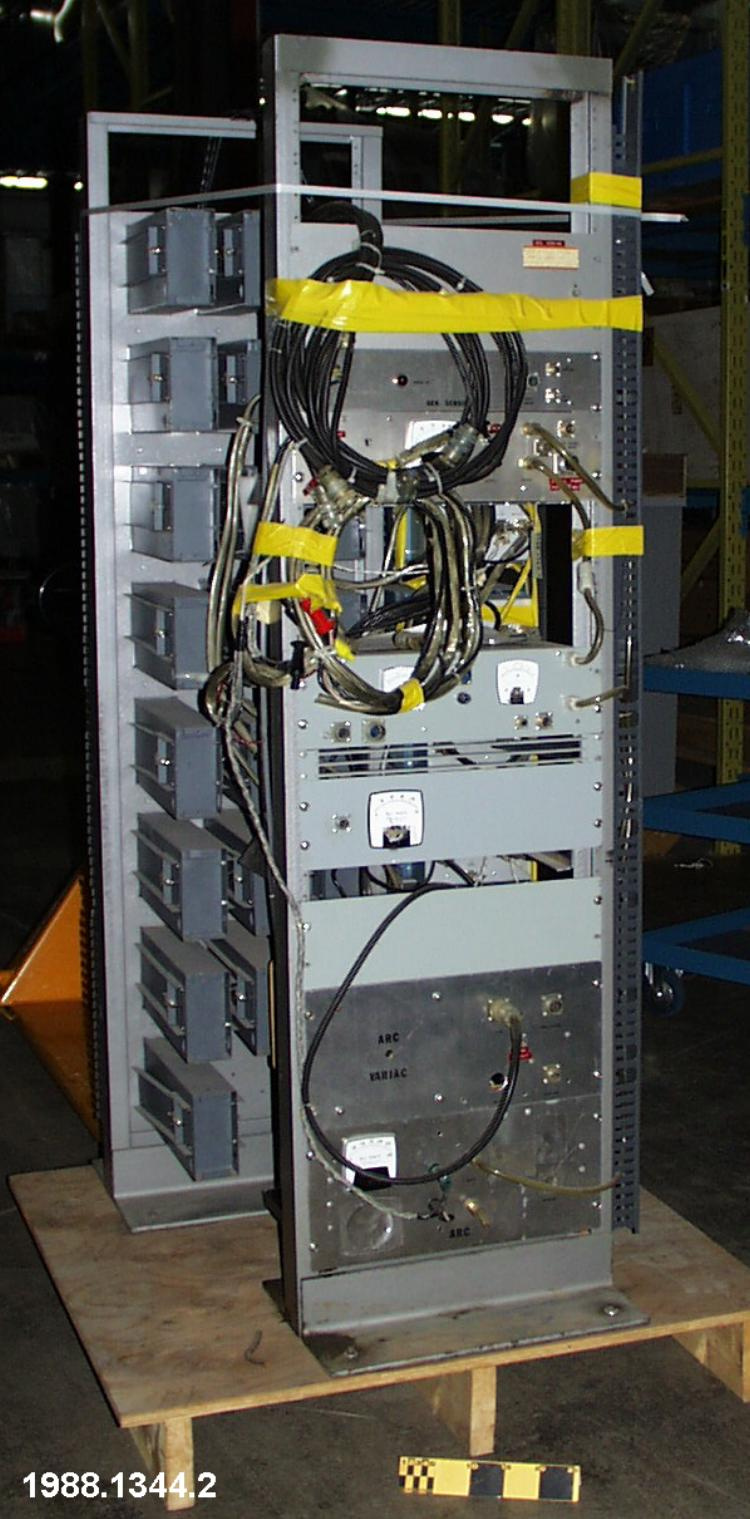
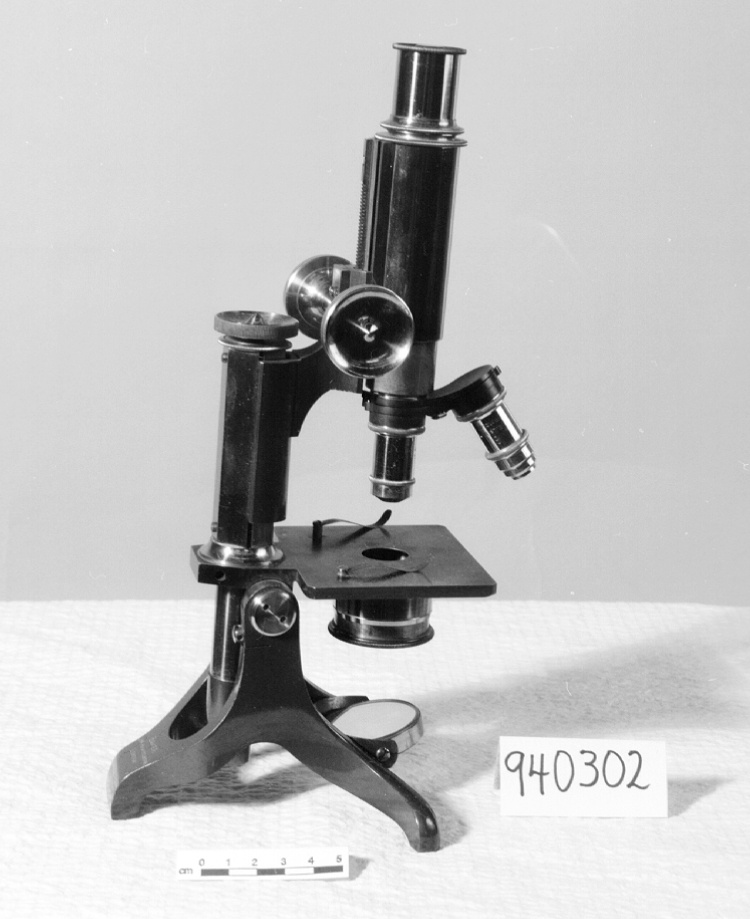
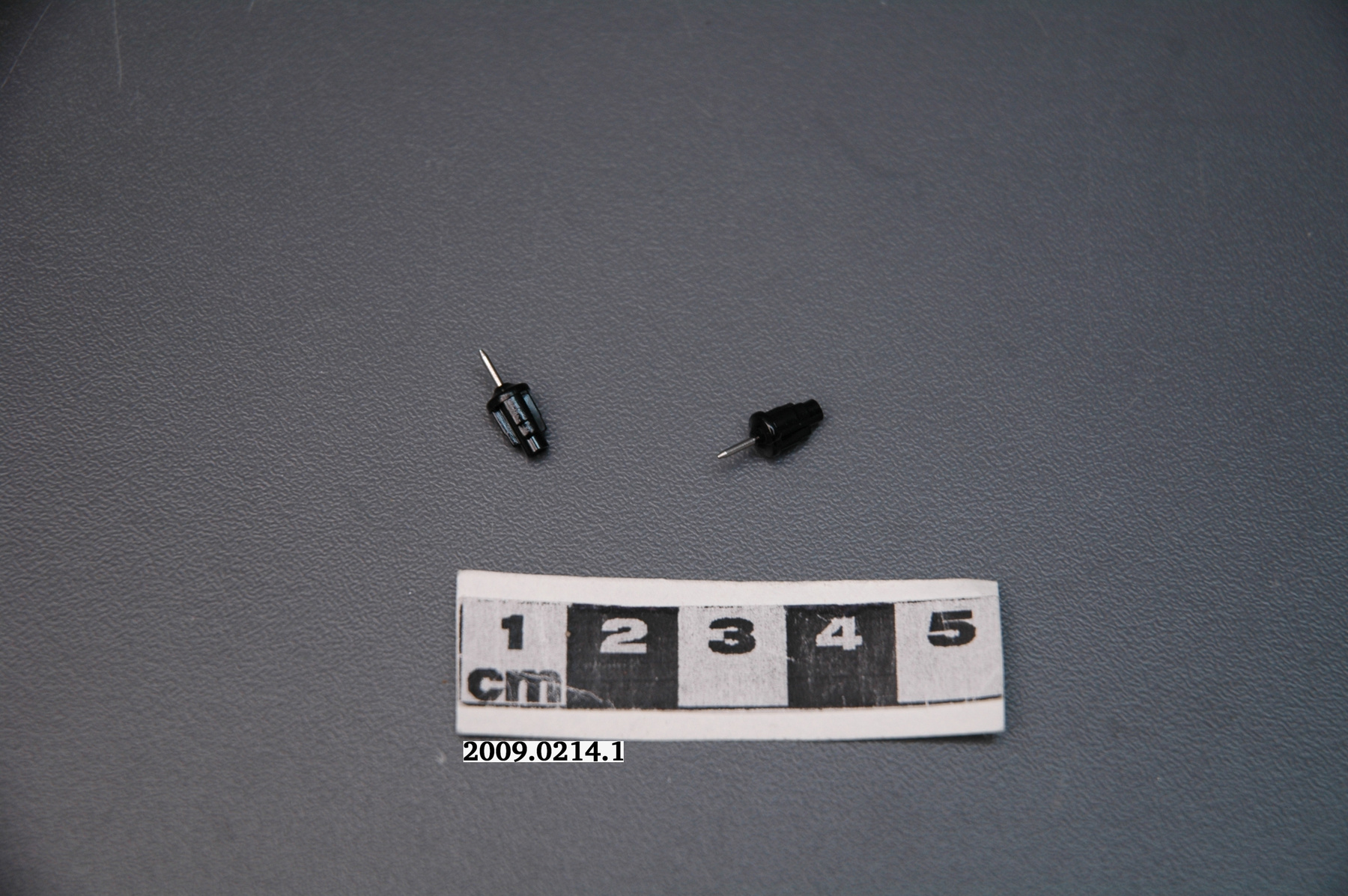
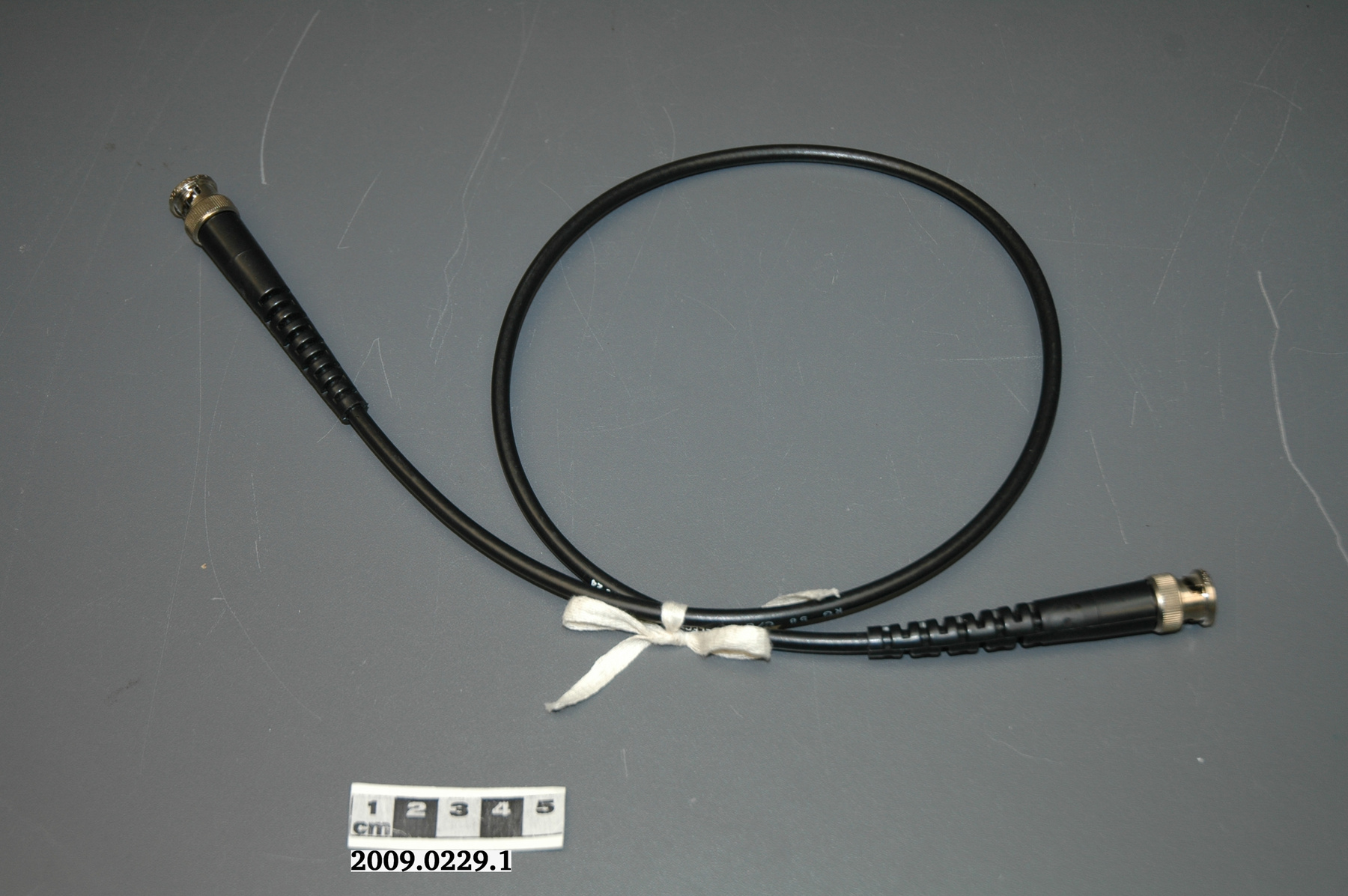
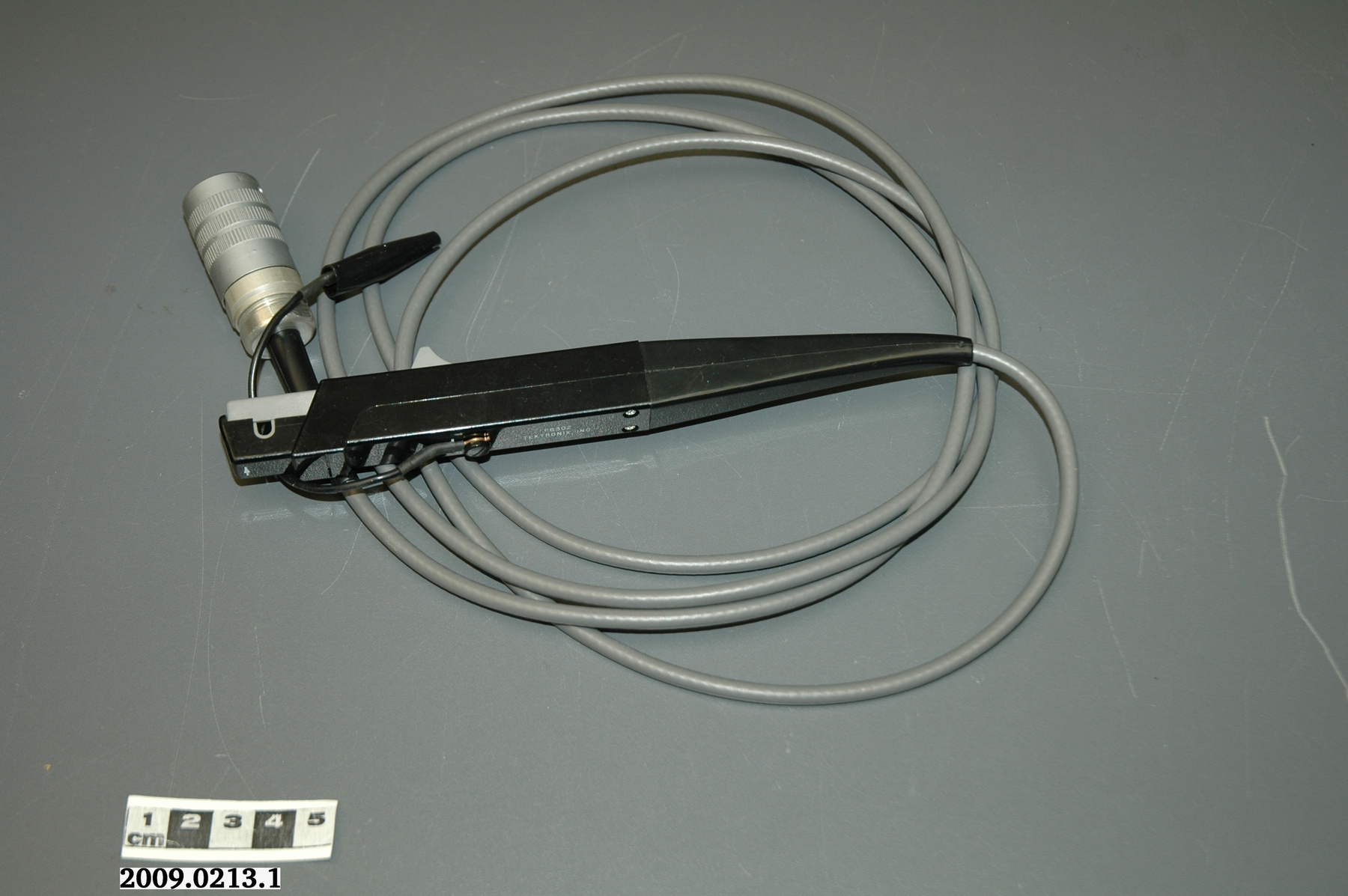
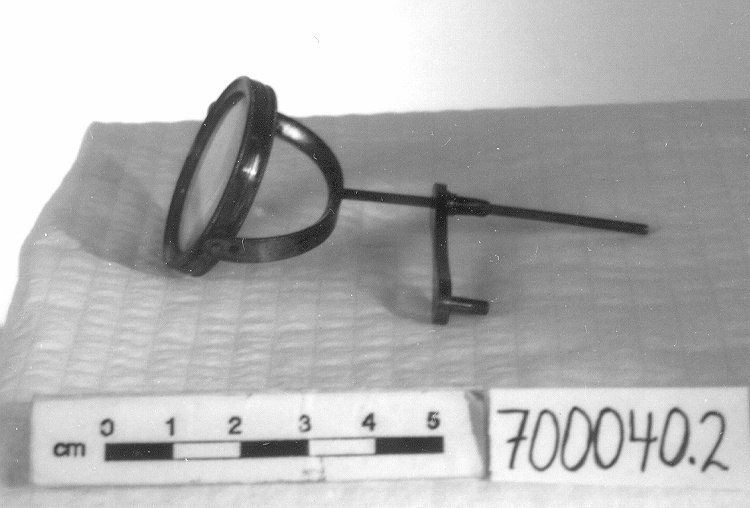
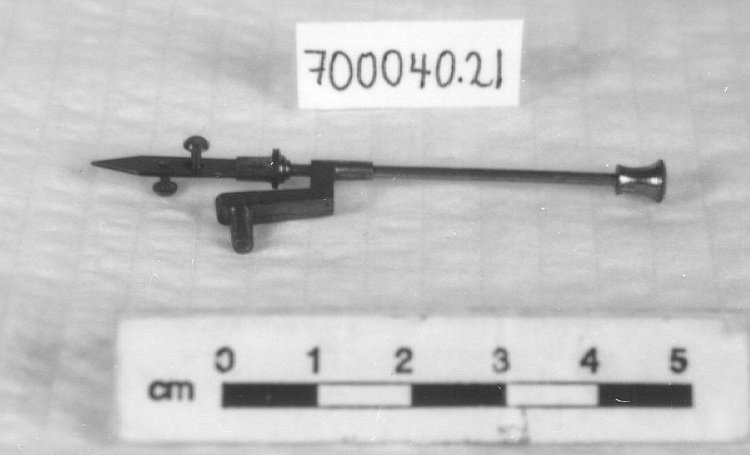
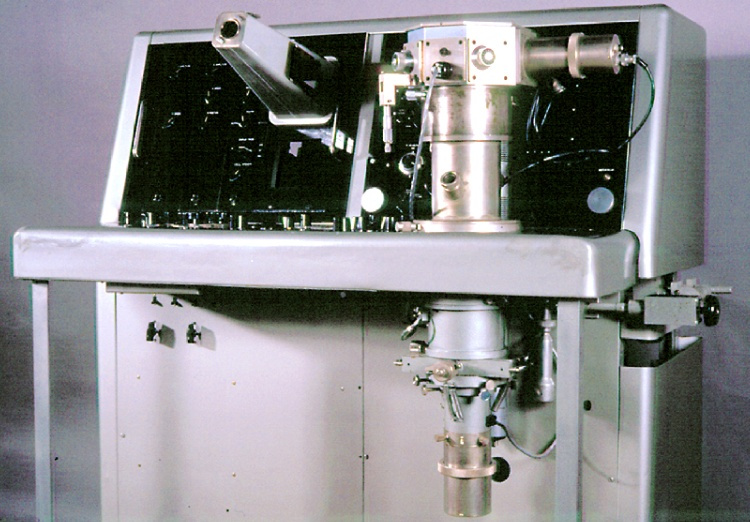
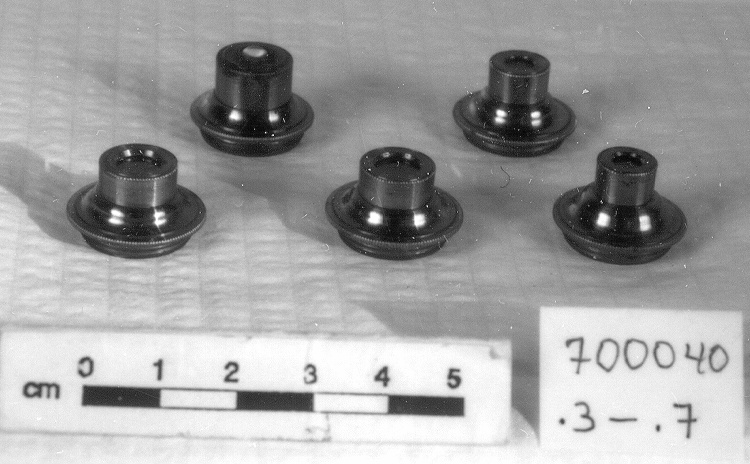
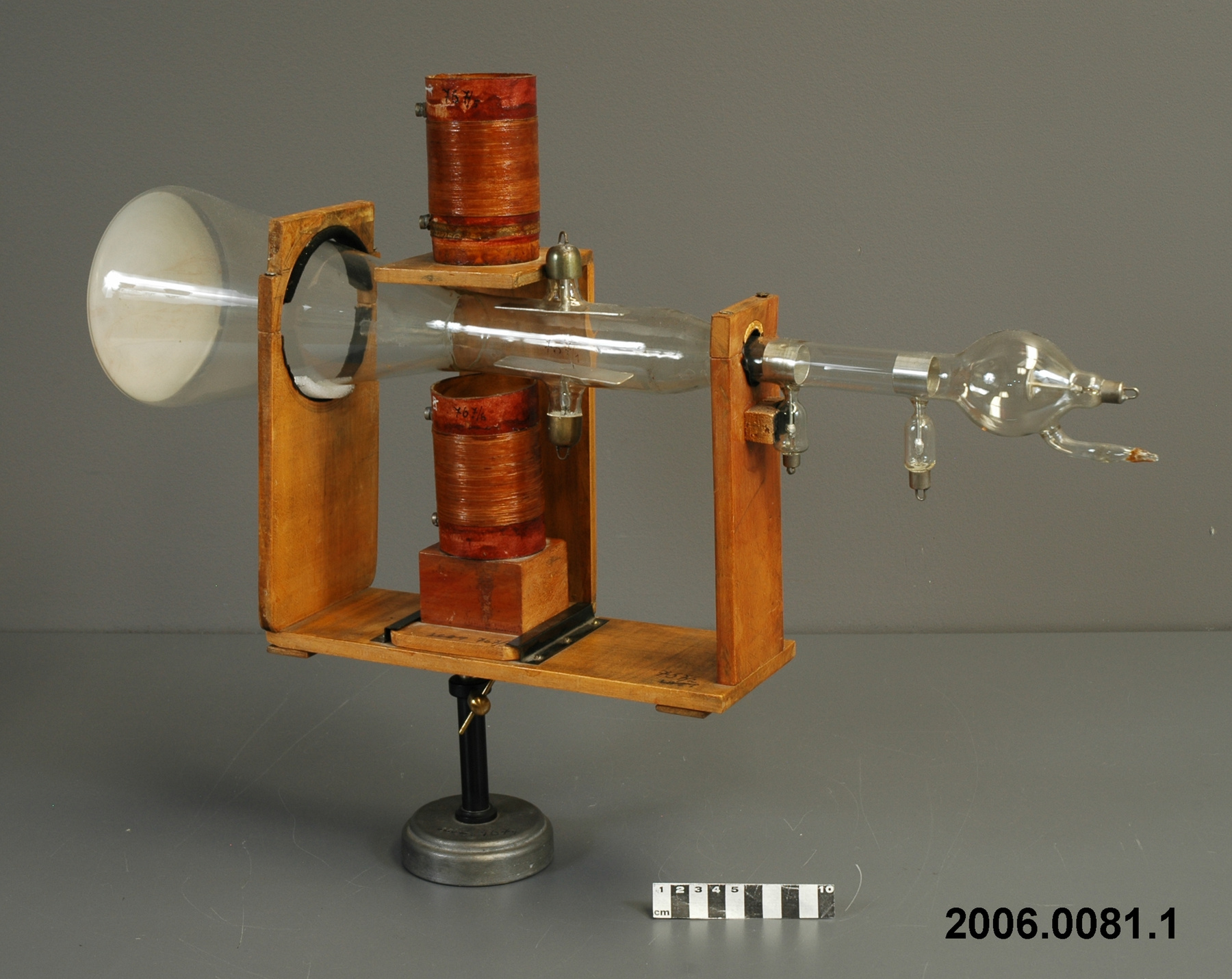
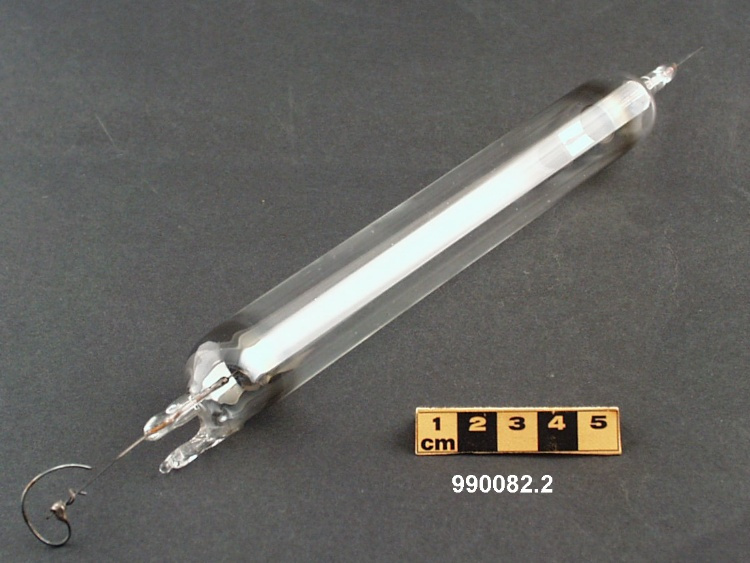
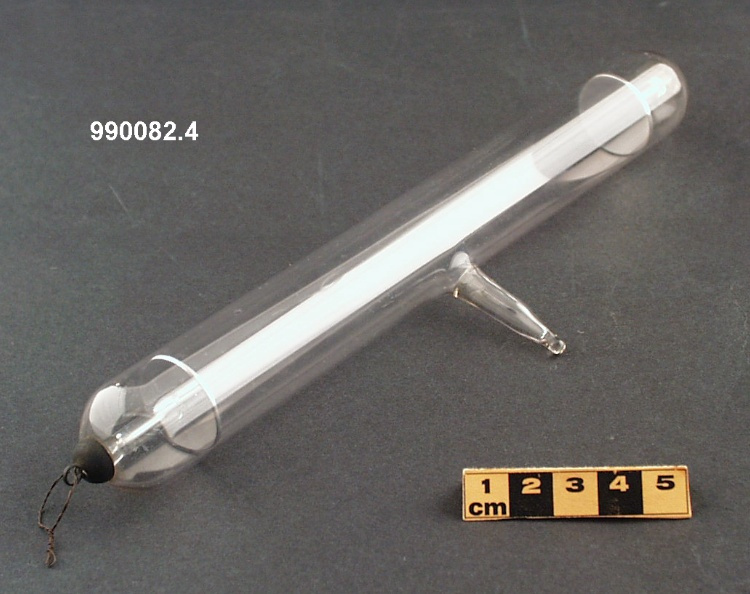
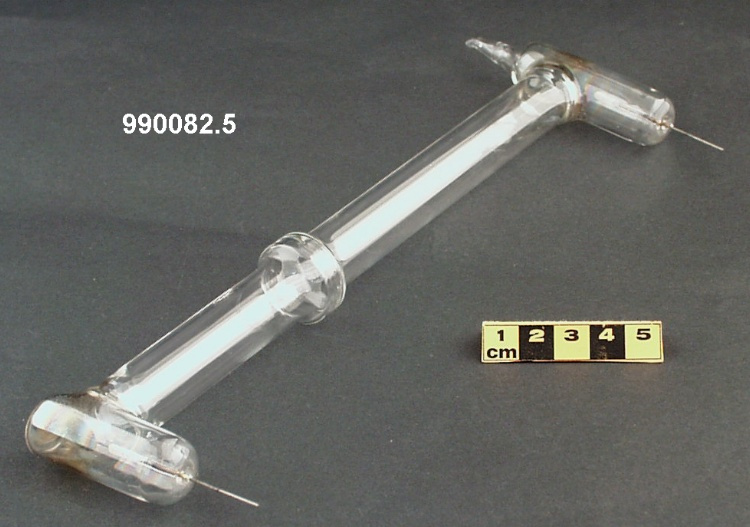
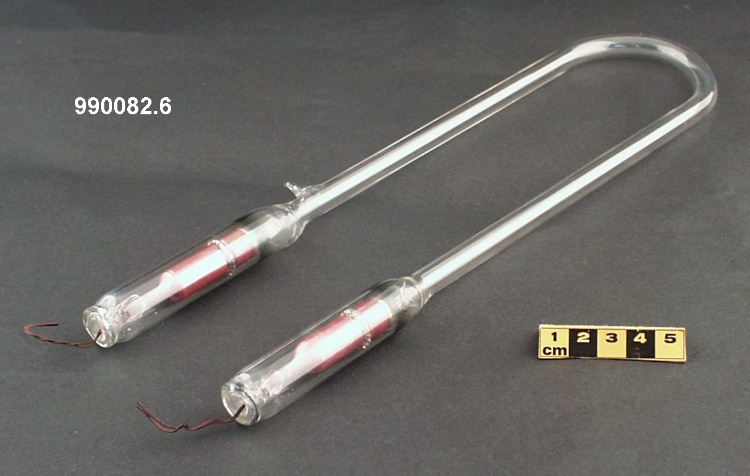
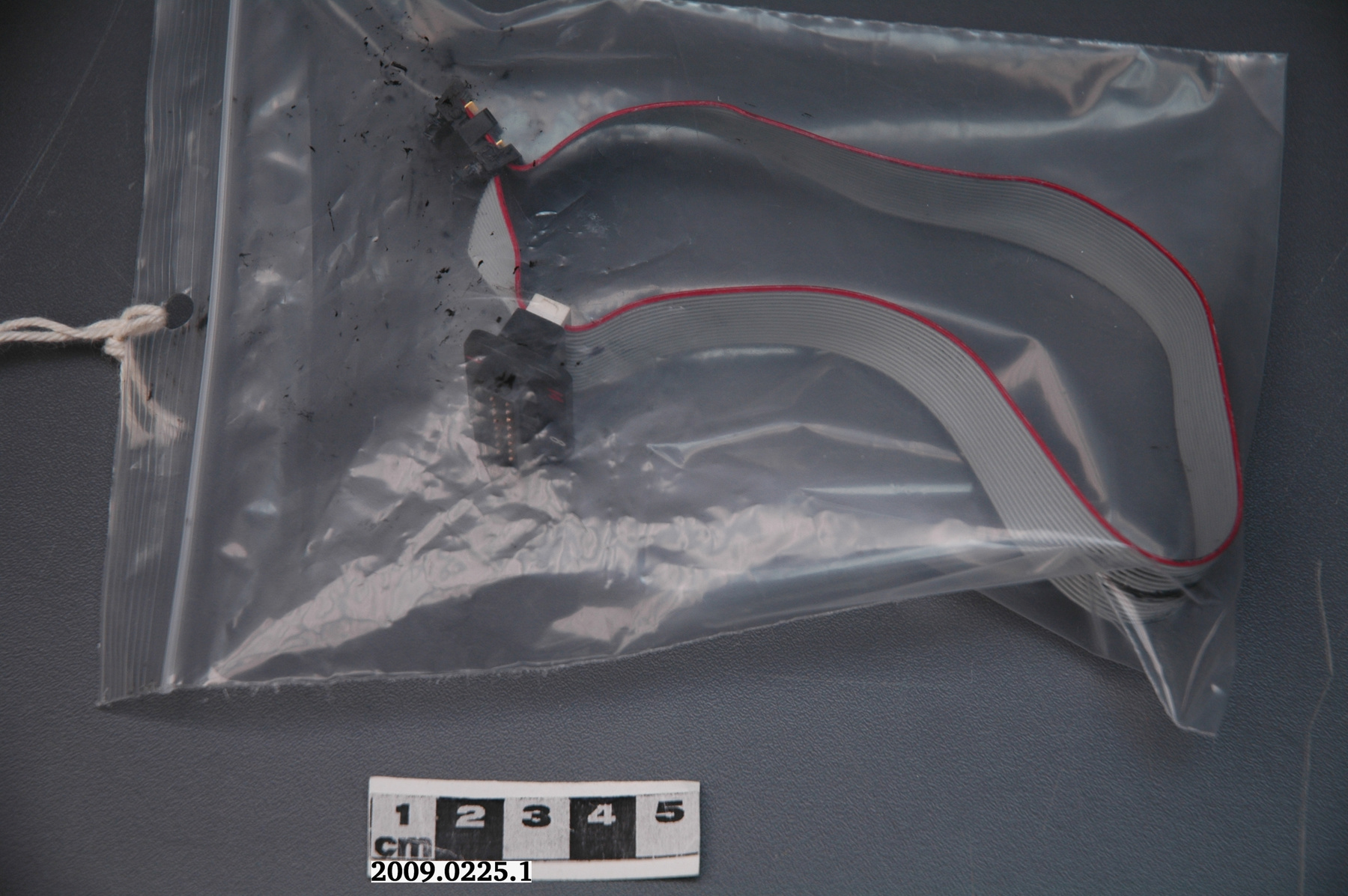
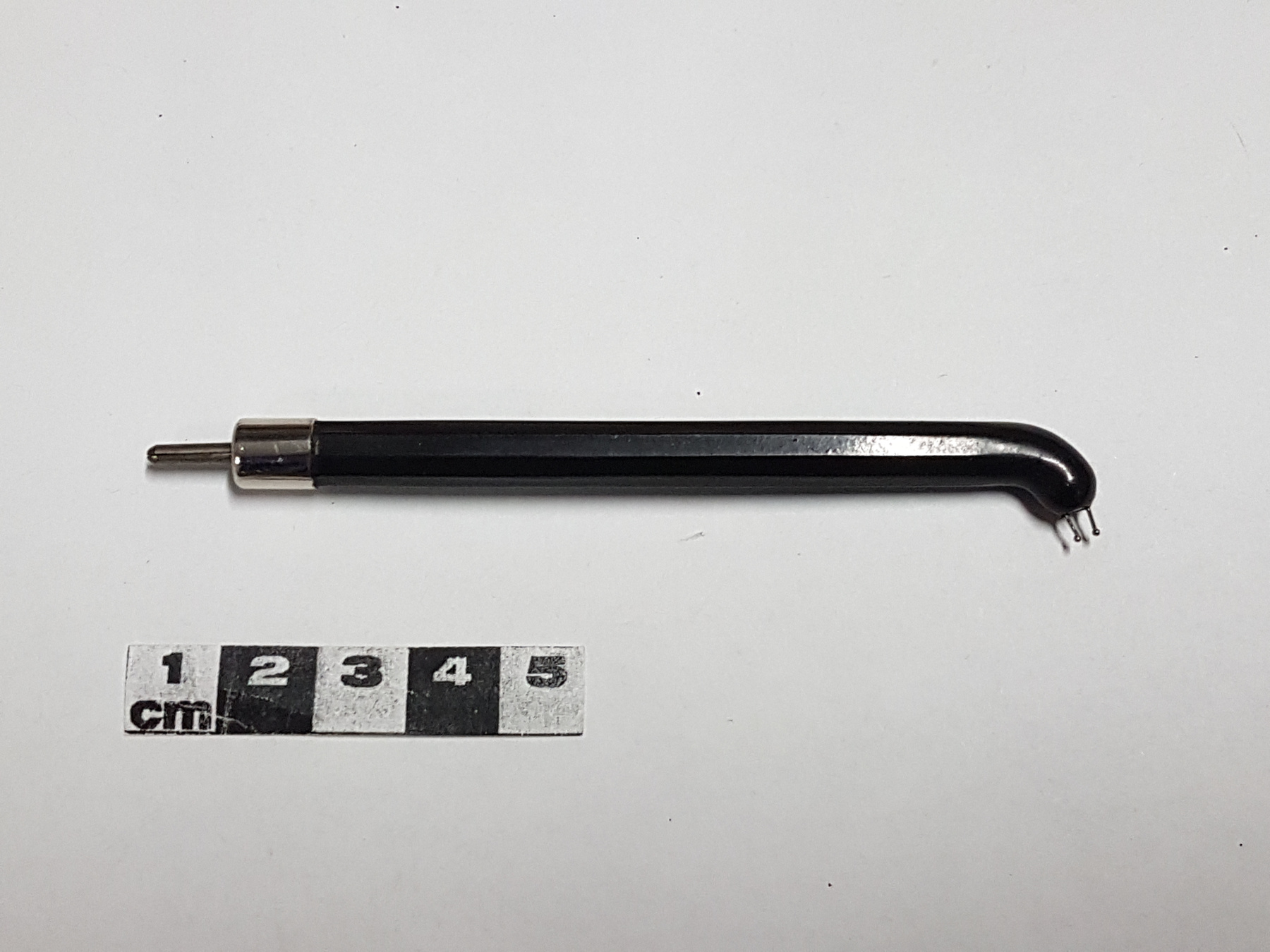
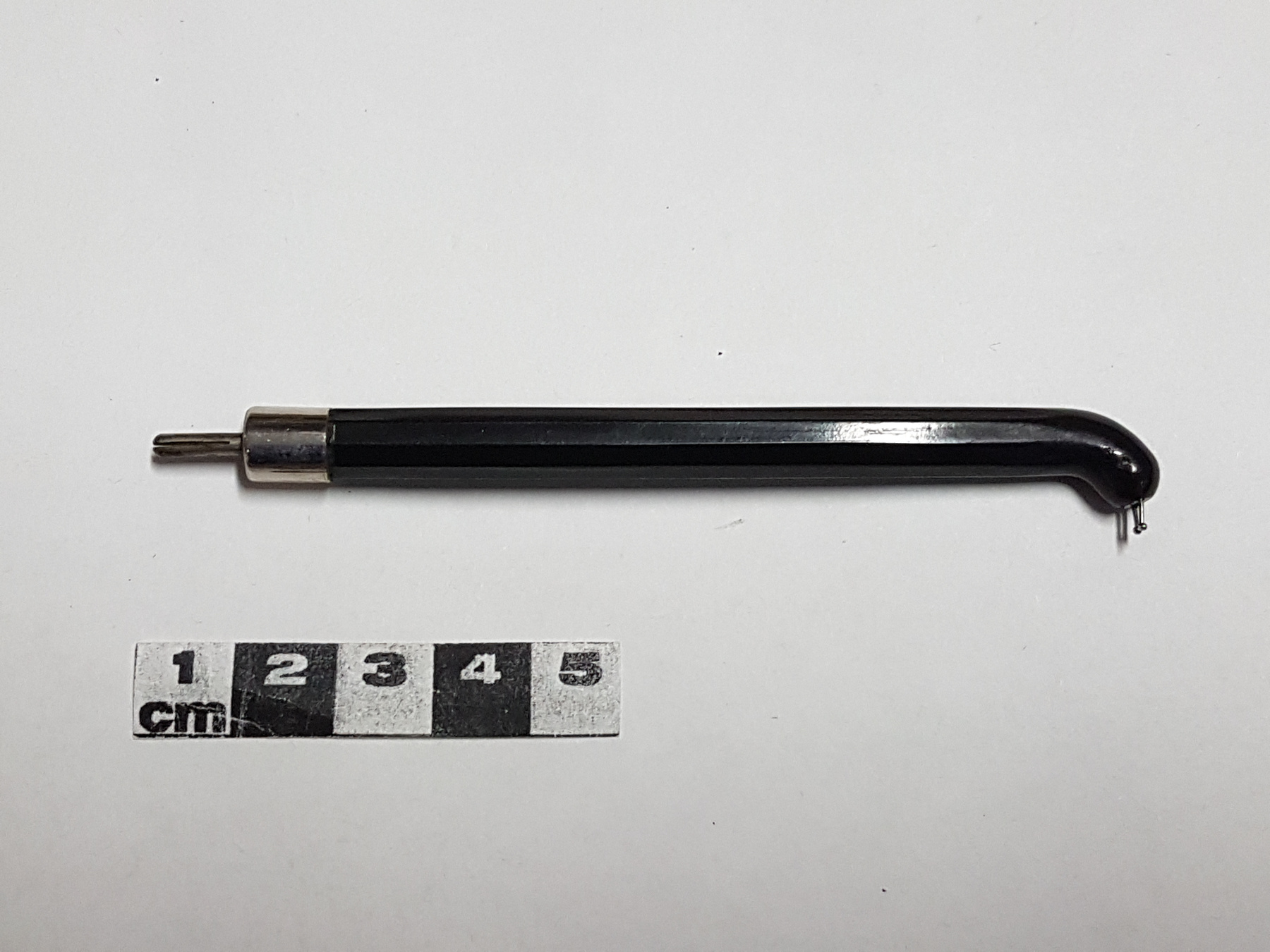
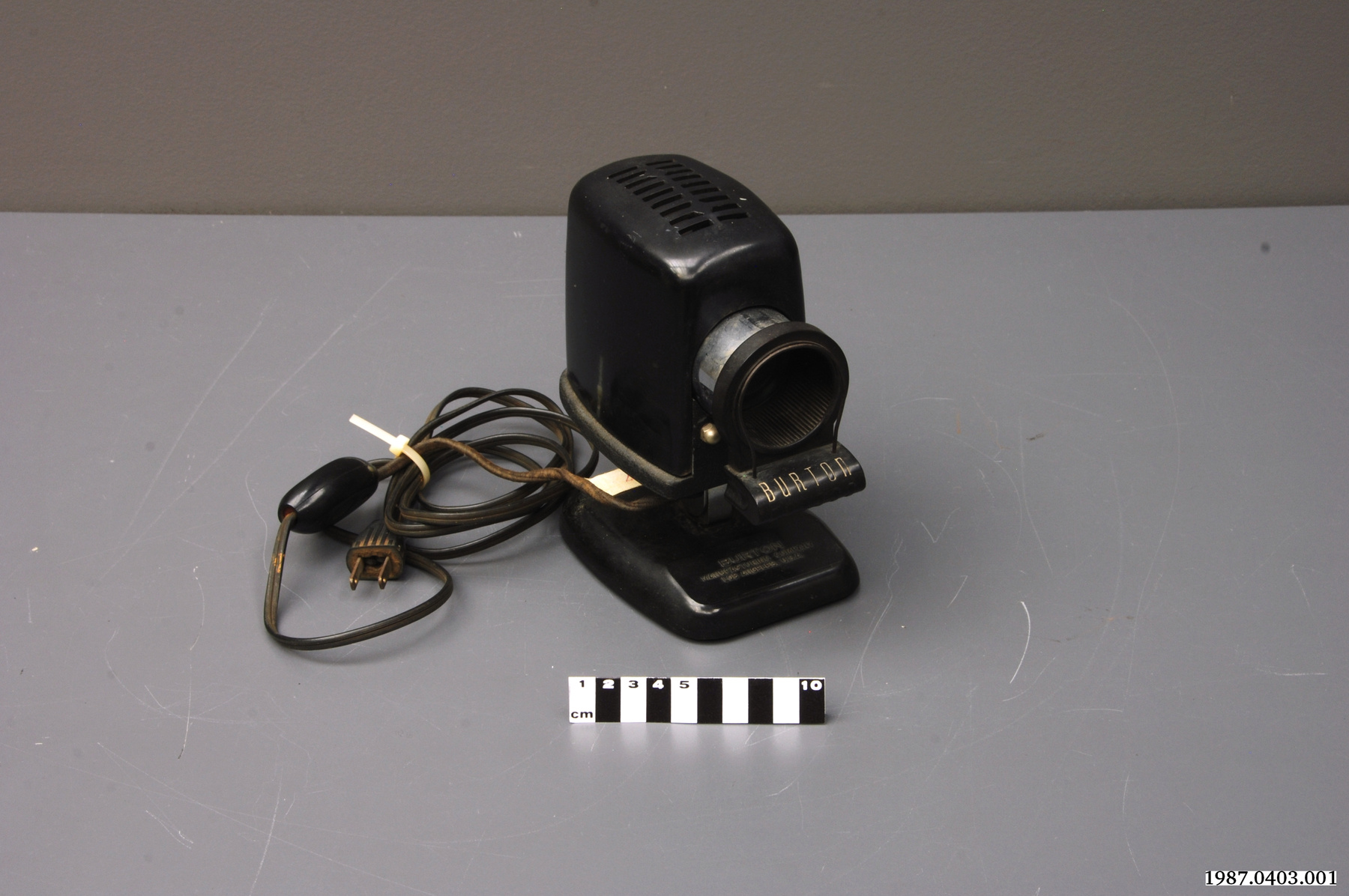
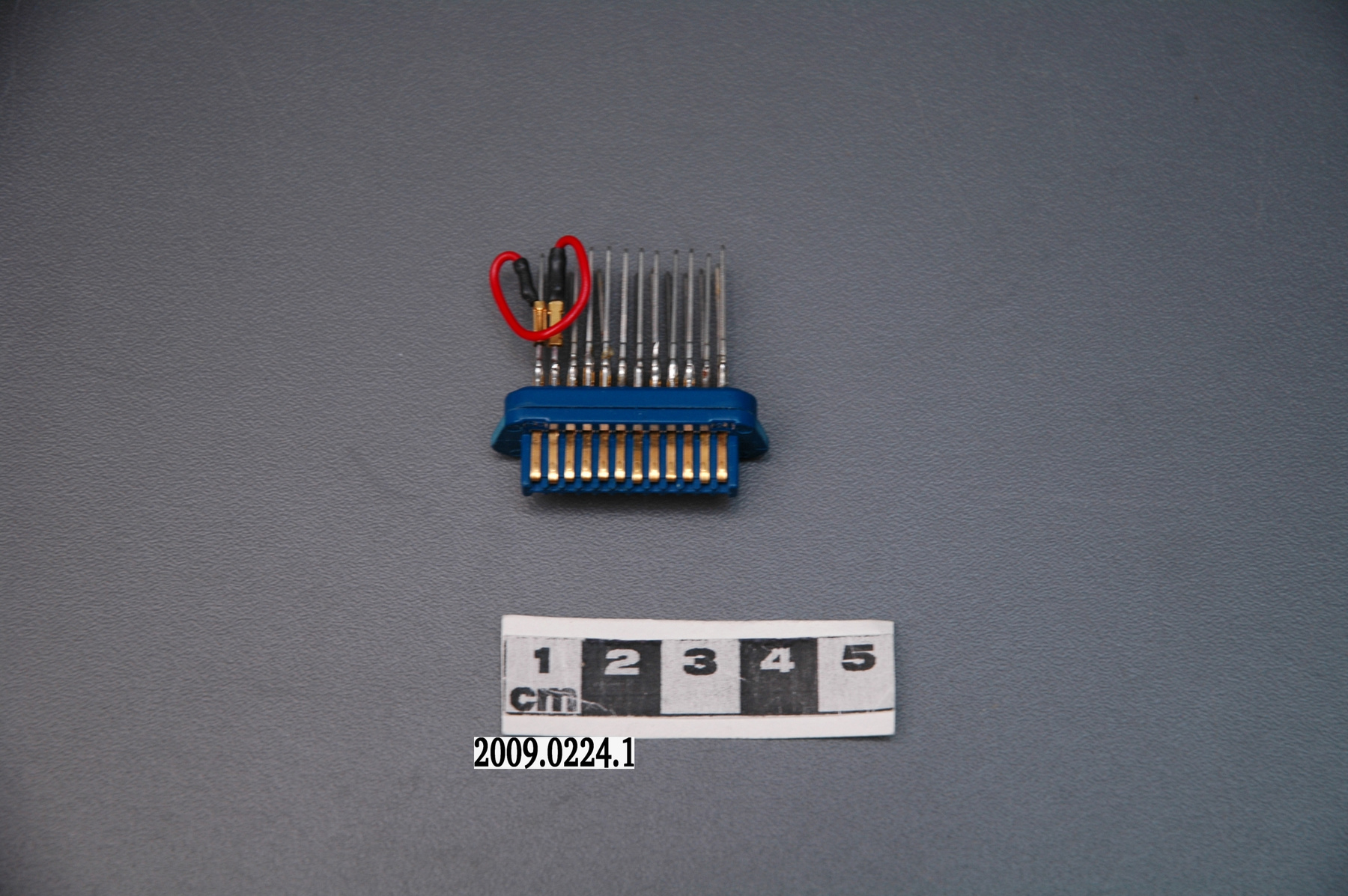
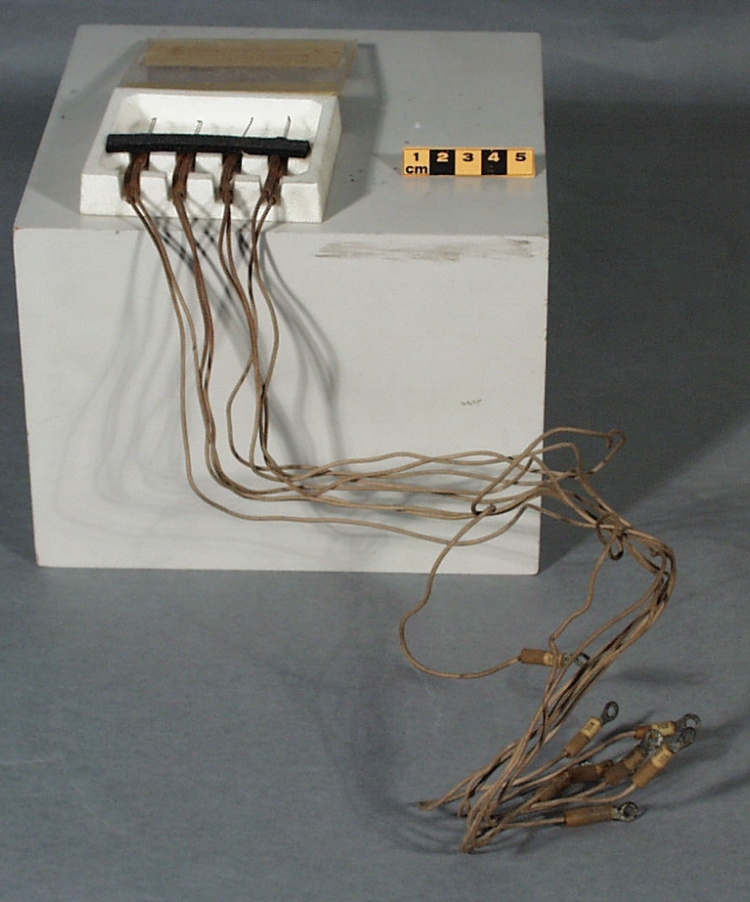
Potentiometer
Use this image
Can I reuse this image without permission? Yes
Object images on the Ingenium Collection’s portal have the following Creative Commons license:
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUTE THIS IMAGE
Ingenium,
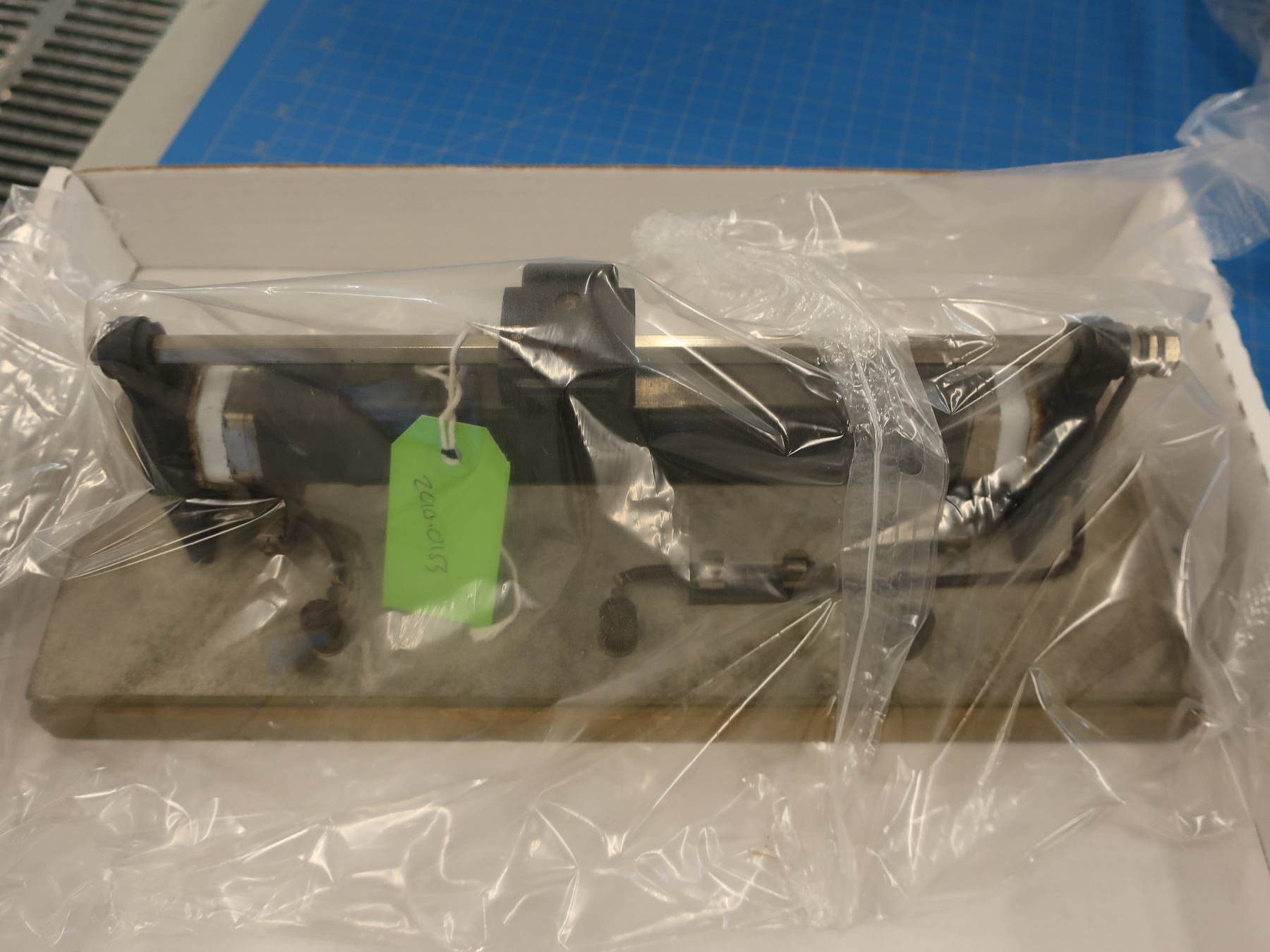
2010.0153.005
Permalink:
Ingenium is releasing this image under the Creative Commons licensing framework, and encourages downloading and reuse for non-commercial purposes. Please acknowledge Ingenium and cite the artifact number.
DOWNLOAD IMAGEPURCHASE THIS IMAGE
This image is free for non-commercial use.
For commercial use, please consult our Reproduction Fees and contact us to purchase the image.
- OBJECT TYPE
- N/A
- DATE
- 1938
- ARTIFACT NUMBER
- 2010.0153.005
- MANUFACTURER
- Unknown
- MODEL
- Unknown
- LOCATION
- Unknown
More Information
General Information
- Serial #
- N/A
- Part Number
- 5
- Total Parts
- 6
- AKA
- N/A
- Patents
- N/A
- General Description
- Unknown
Dimensions
Note: These reflect the general size for storage and are not necessarily representative of the object's true dimensions.
- Length
- N/A
- Width
- N/A
- Height
- N/A
- Thickness
- N/A
- Weight
- N/A
- Diameter
- N/A
- Volume
- N/A
Lexicon
- Group
- Medical Technology
- Category
- Light & electromagnetic radiation
- Sub-Category
- N/A
Manufacturer
- AKA
- Unknown
- Country
- Unknown
- State/Province
- Unknown
- City
- Unknown
Context
- Country
- Canada
- State/Province
- Ontario
- Period
- 1938-
- Canada
-
In the 1920s several groups were attempting to overcome the physical limitations imposed by light waves and the optical interference that arises from light reflecting from closely spaced features. In these experiments, electrons were the means of detecting tiny features but the nature of the electrons made them difficult to focus and detect. Ruska et al were the first to be successful at the Berlin Technische Hochschule (1933) where he and his colleagues were able to surpass the resolution of light microscopes. He had worked out the lend design with polepieces to concentrate the magnetic field required to focus and his 1933 instrument pioneered the two-stage transmission arrangement. Followed closely by Ladislaus Marton in Brussels in 1933, Marton built two successful models and he was the first to successfully produce micrographs of biological specimens--the specimens observed by others were "fried" by the electron beams. In Britain, L.C. Martin, R.V. Whelpton and D.H. Parnum produced what was to become the prototype Metropolitan Vickers instruments while in Japan, E. Sugata and T. Hibi were achieving some success as well. However, despite the successes, the micrographs remained blurred and astigmatism was a severe problem. In North America, the first (1)successful electron microscope was fabricated at the UofT by Albert Prebus and James Hillier, PhD students in physics. It is occasionally stated that this was the first electron microscope but this is certainly not the case though it had very considerable improved performance over its European predecessors. The driving force for the project was the head of the department, Eli Burton who had replaced McLennan in 1932 and Doane, et al suggest that some of his interests were driven by his own diabetes (p. 2-3). They state that due to his illness, he was interested in projects that could apply physics to medical problems and thus biophysics became on the research interests and there was collaboration with physicians such as A.C. Hendrick to study use of colloidal solutions of arsenic to cancer treatment. Burton had himself studied under J.J. Thompson, the discovered of the electron and he remained interested in electron topics throughout his career. Also critical to the eventual success was Walter Kohl who had a PhD in engineering physics from Dresden. He had come to Canada to work for Rogers Radio Tubes Ltd. to work on early TV and his work dealt with the deflection of electron beams. Beginning in 1932 he was a regular visitor at UofT giving lectures on various topics that were of direct application to electron microscopes. (Ruska and Zworykin also worked on design of tubes for TV.) **Con't Acquisition Proposal in O:\Cons & Coll Serv\Cons & Coll Serv\Collection Services\SUPPINFO\Artifact\2010\2010.0153 - Function
-
To provide extremely high magnification of materials being studied. - Technical
-
After Cecil Hall's departure, Eli Burton asked James Hillier, a B.A. graduate in Mathematics and Physics from the University of Toronto, and Albert Prebus, who had just received an MSc from the University of Alberta, to undertake the construction of a high-voltage magnetic compound electron microscope with the aim of applying it to the investigation of biological specimens. In the Fall of 1937, in order to accommodate their limited budgets, Albert Prebus moved in with Jim Hillier, his wife Florence and their two-month old baby (8). Much of the planning and designing of the microscope was carried out over the Christmas holidays in their shared quarters. By early 1938 they had constructed the instrument, completed in the astonishingly short period of four months (20, 35). To accomplish this feat they had at their disposal the thesis of Hall and the publications of Knoll, Ruska and Marton. They "borrowed" two high tension condensers from the University of Alberta and an old x-ray step-up transformer from a Toronto hospital to get their 45 kV source. From Kohl they obtained fluorescent screens. The rest of the instrument was manufactured by themselves with the help of the Physics Department workshop technicians. "Our greatest mechanical challenge was the design and construction of the components of the instrument" stated Hillier (10). Prebus recalls that "the shopwork was done on a two-shift basis; the professional machinists worked the day shift. Without their unreserved approval, Hillier and I worked the night shift, often until 4 a.m., and occasionally until the day shift was about to start" (10). Many parts of the design were innovative, and much of the machining was of very high quality. The transmission electron microscope completed in 1938 by Prebus and Hillier was an assembly of seven sections in a vertical column that were joined together by means of vacuum-tight plane-lapped grease seals. This construction facilitated adjustment of the horizontal displacement of each section relative to adjoining sections, for the purpose of aligning optical axes of the several sections, and for the selection of specimen areas to be imaged. In the first section was located the electron source, called the electron gun. Initially, a cold cathode gas discharge tube was chosen, on the basis of the assumption that it was the most likely type of source to provide a satisfactory approximation to the ideal point source. The assumption was based upon the observation that such sources were commonly used in high voltage oscilloscopes. The multitude of problems associated with this source quickly discouraged its use in their instrument. Despite the lack of axial symmetry of such a device, a hairpin tungsten filament provided the best approximation to a point source, and this hot cathode source, in addition to means to adjust the tilt of the beam emanating from it, eventually formed the topmost section of the microscope. A maximum of 45,000 volts, could be applied to the gun, and the filament current was supplied by two 2-volt batteries. The filament could be raised or lowered with respect to the rest of the cathode by a screw and bellows arrangement. The whole cathode assembly was sealed by wax to the upper end of a glass cylinder. To replace the filament the seal had to be broken and this seal was eventually replaced by a neoprene joint so that the filament could be changed in a few minutes. **Con't Acquisition Proposal in O:\Cons & Coll Serv\Cons & Coll Serv\Collection Services\SUPPINFO\Artifact\2010\2010.0153 - Area Notes
-
Unknown
Details
- Markings
- N/A
- Missing
- N/A
- Finish
- Wood base covered in asbestos sheet, glass tube, cast iron parts, copper wires
- Decoration
- N/A
CITE THIS OBJECT
If you choose to share our information about this collection object, please cite:
Unknown Manufacturer, Potentiometer, 1938, Artifact no. 2010.0153, Ingenium – Canada’s Museums of Science and Innovation, http://collection.ingeniumcanada.org/en/item/2010.0153.005/
FEEDBACK
Submit a question or comment about this artifact.
More Like This