Pyranometre
Utiliser cette image
Puis-je réutiliser cette image sans autorisation? Oui
Les images sur le portail de la collection d’Ingenium ont la licence Creative Commons suivante :
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUER CETTE IMAGE
Ingenium,
2004.0338.001
Permalien:
Ingenium diffuse cette image sous le cadre de licence Creative Commons et encourage son téléchargement et sa réutilisation à des fins non commerciales. Veuillez mentionner Ingenium et citer le numéro de l’artefact.
TÉLÉCHARGER L’IMAGEACHETER CETTE IMAGE
Cette image peut être utilisée gratuitement pour des fins non commerciales.
Pour un usage commercial, veuillez consulter nos frais de reproduction et communiquer avec nous pour acheter l’image.
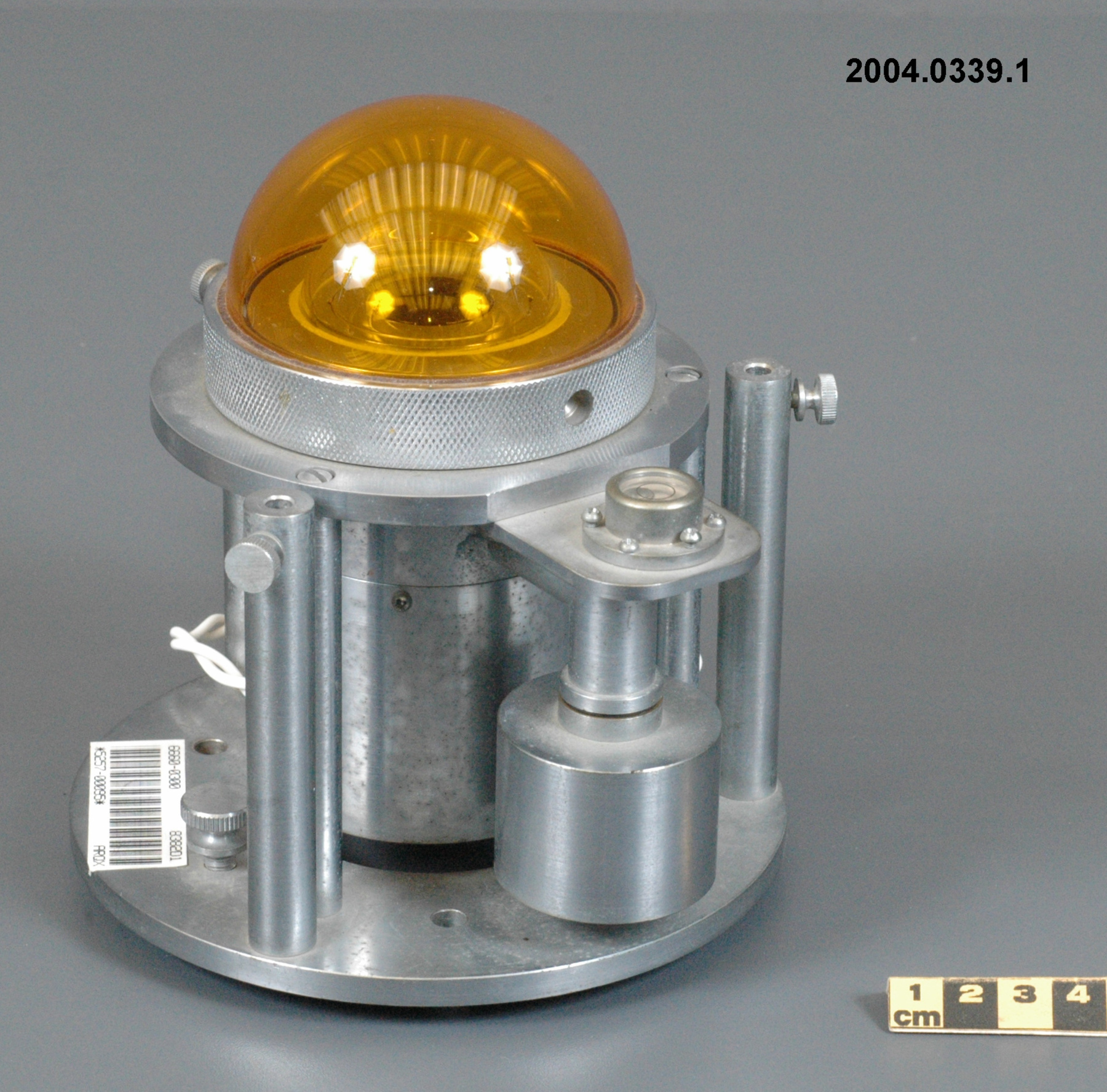
- TYPE D’OBJET
- double dome
- DATE
- 1967
- NUMÉRO DE L’ARTEFACT
- 2004.0338.001
- FABRICANT
- EPPLEY LABORATORY INC.
- MODÈLE
- 15
- EMPLACEMENT
- Newport, Rhode Island, United States of America
Plus d’information
Renseignements généraux
- Nº de série
- 8383D1
- Nº de partie
- 1
- Nombre total de parties
- 1
- Ou
- S/O
- Brevets
- S/O
- Description générale
- metal sensor with double glass bubble/ metal casing, frame, shield and parts/ synthetic wire covering/ liquid spirit in glass & metal level housing
Dimensions
Remarque : Cette information reflète la taille générale pour l’entreposage et ne représente pas nécessairement les véritables dimensions de l’objet.
- Longueur
- S/O
- Largeur
- S/O
- Hauteur
- 14,0 cm
- Épaisseur
- S/O
- Poids
- S/O
- Diamètre
- 20,2 cm
- Volume
- S/O
Lexique
- Groupe
- Météorologie
- Catégorie
- Mesure d'intensité et de durée de l'insolation
- Sous-catégorie
- S/O
Fabricant
- Ou
- EPLAB
- Pays
- United States of America
- État/province
- Rhode Island
- Ville
- Newport
Contexte
- Pays
- Canada
- État/province
- Inconnu
- Période
- 1967+; this instrument was apparently in use for 40 years (Ref. 9)
- Canada
-
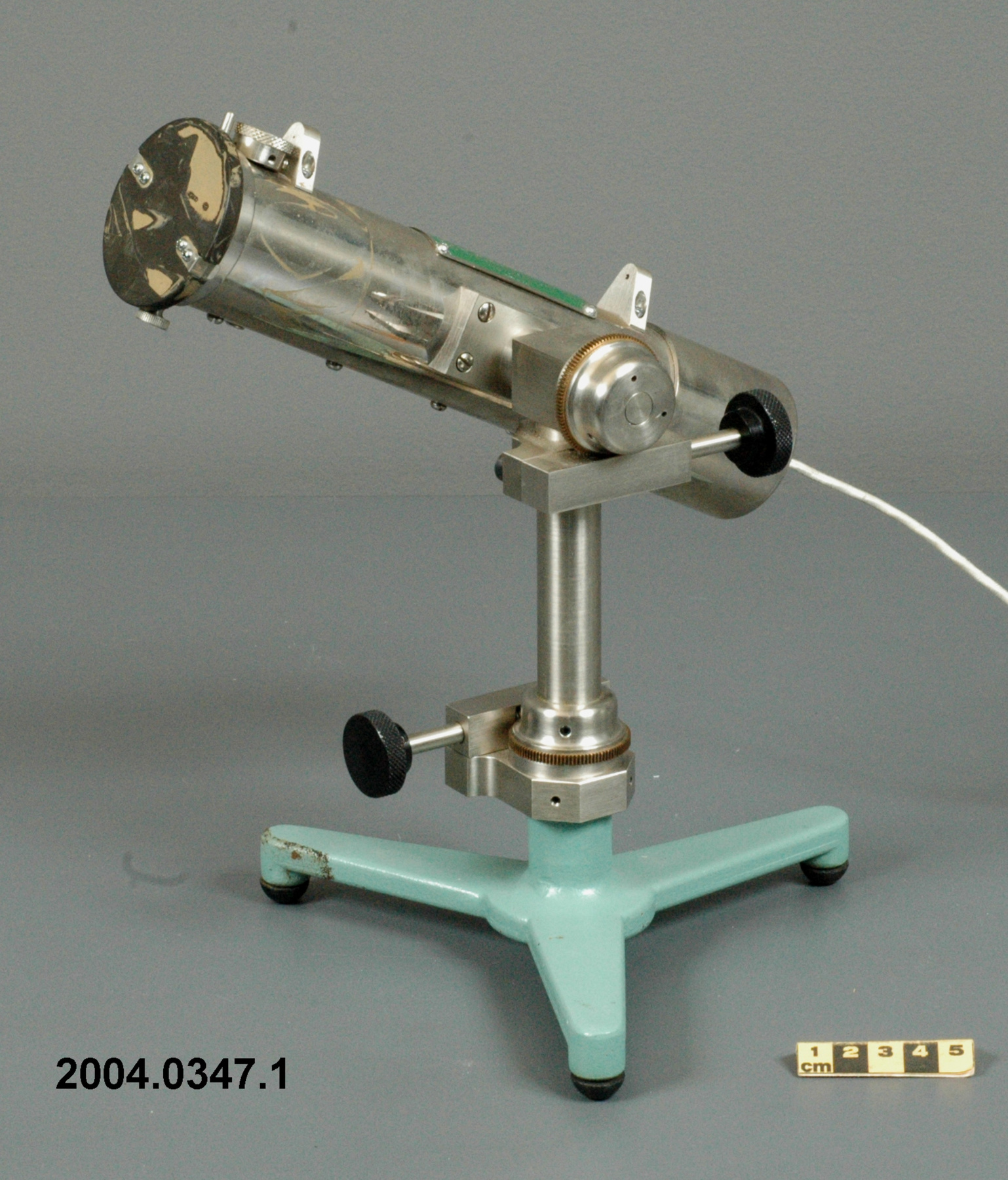
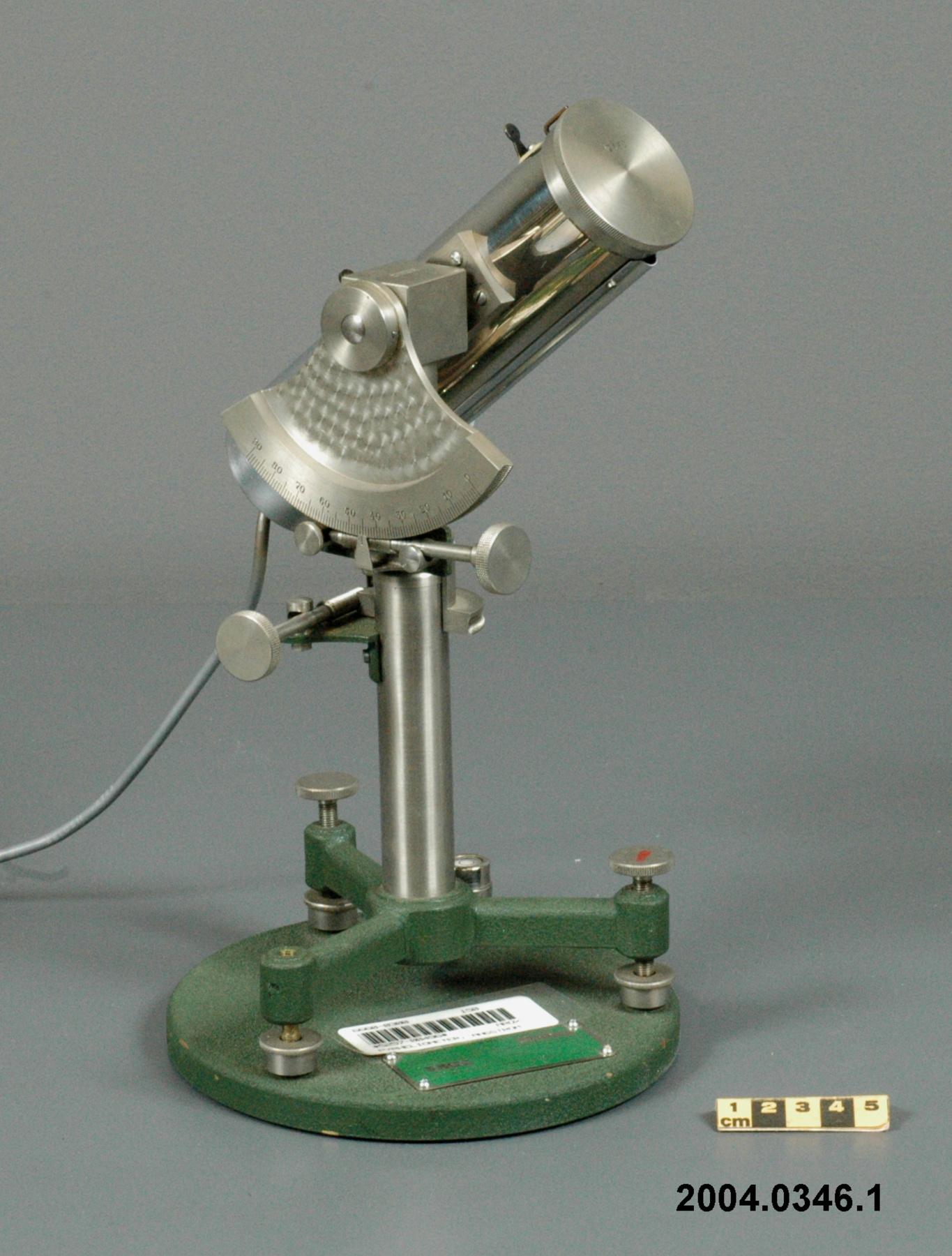
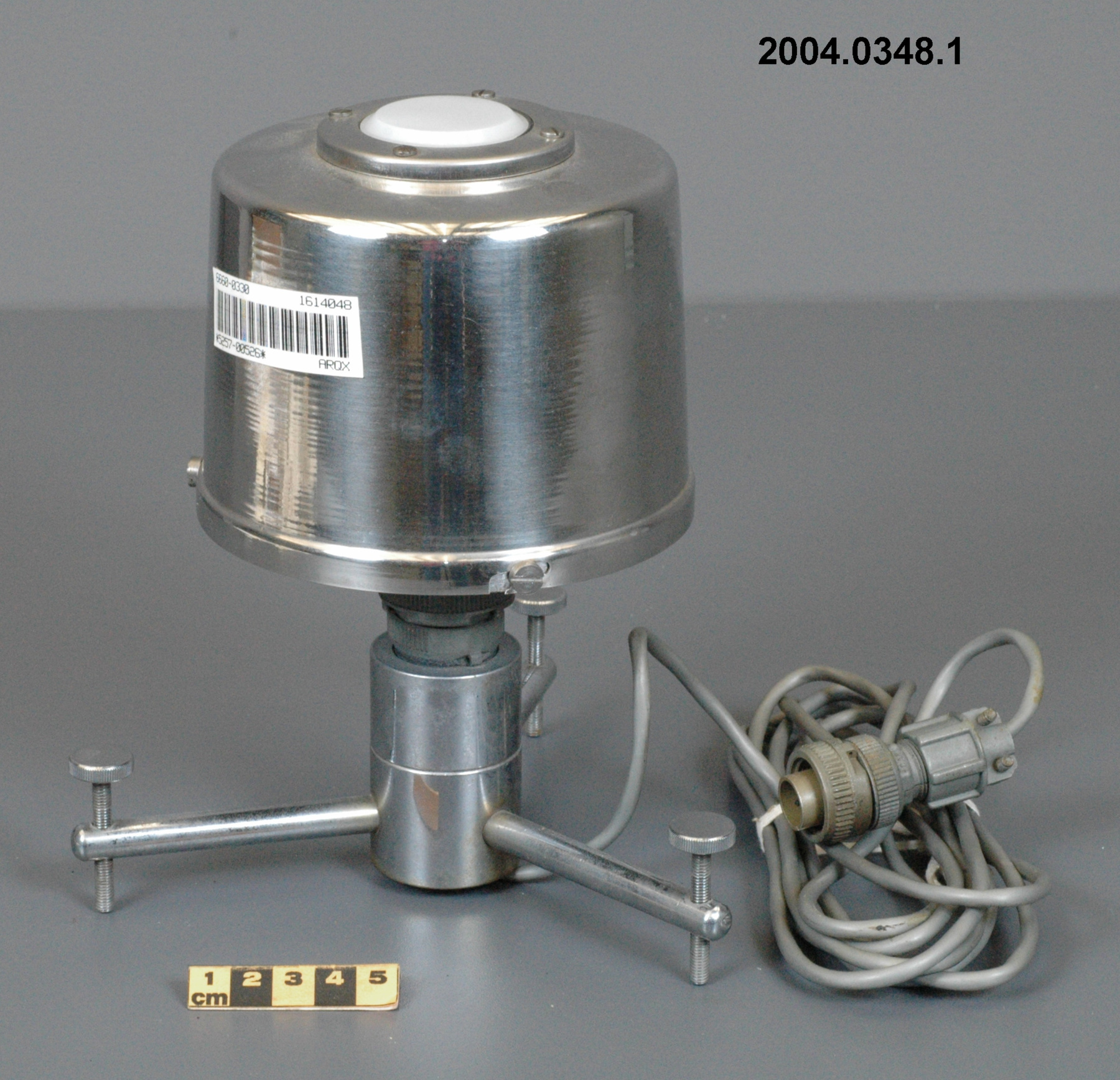
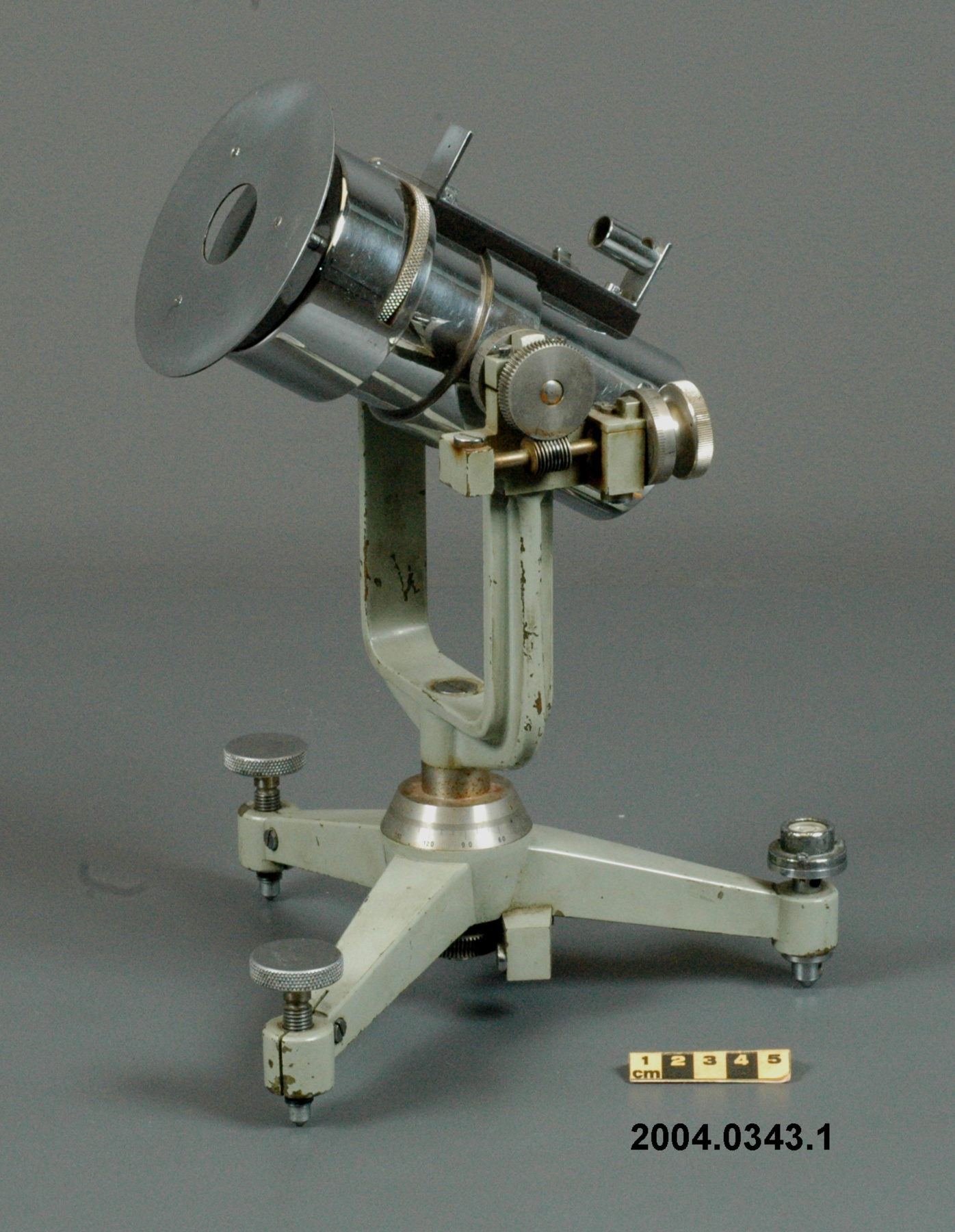
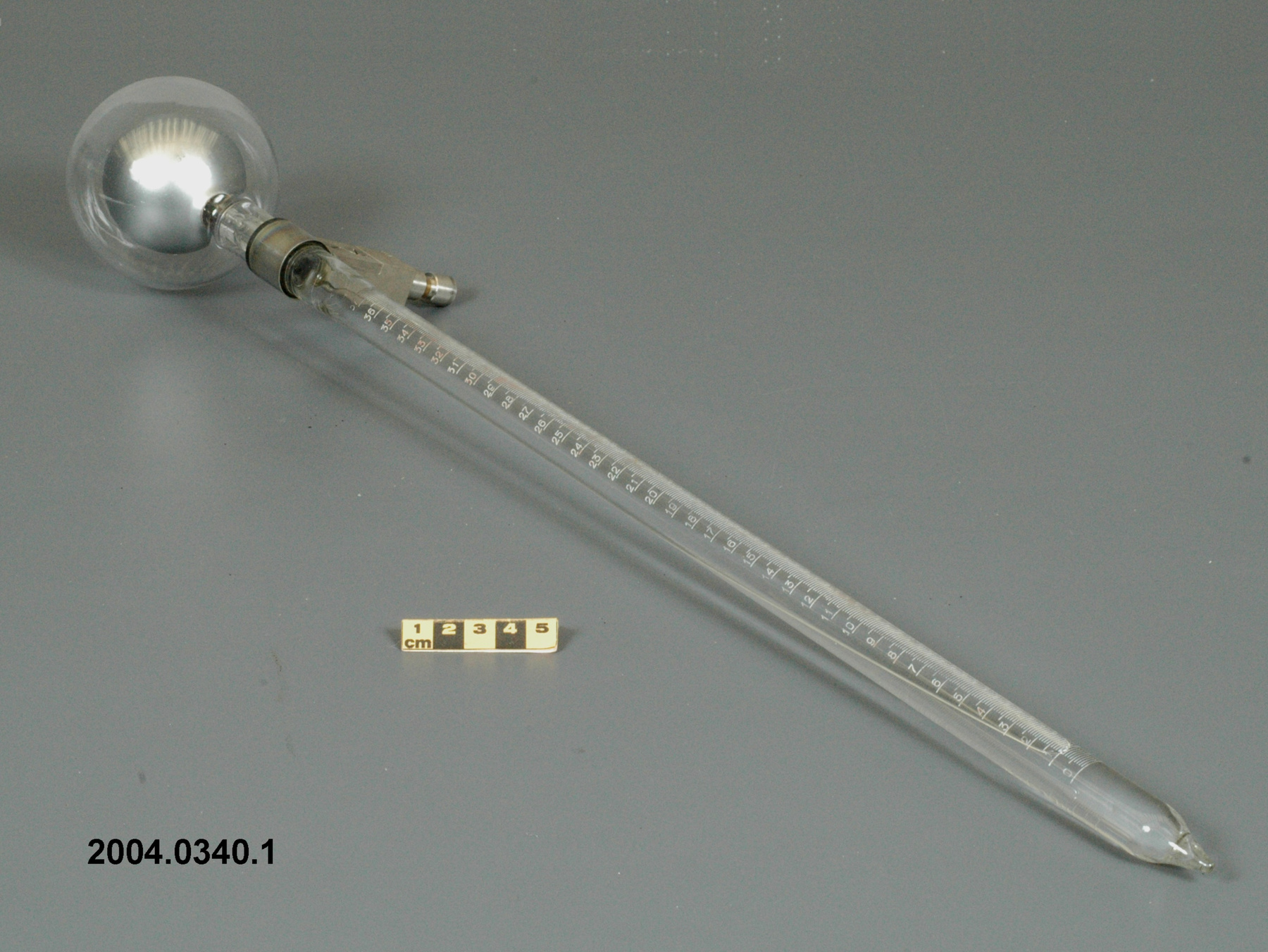
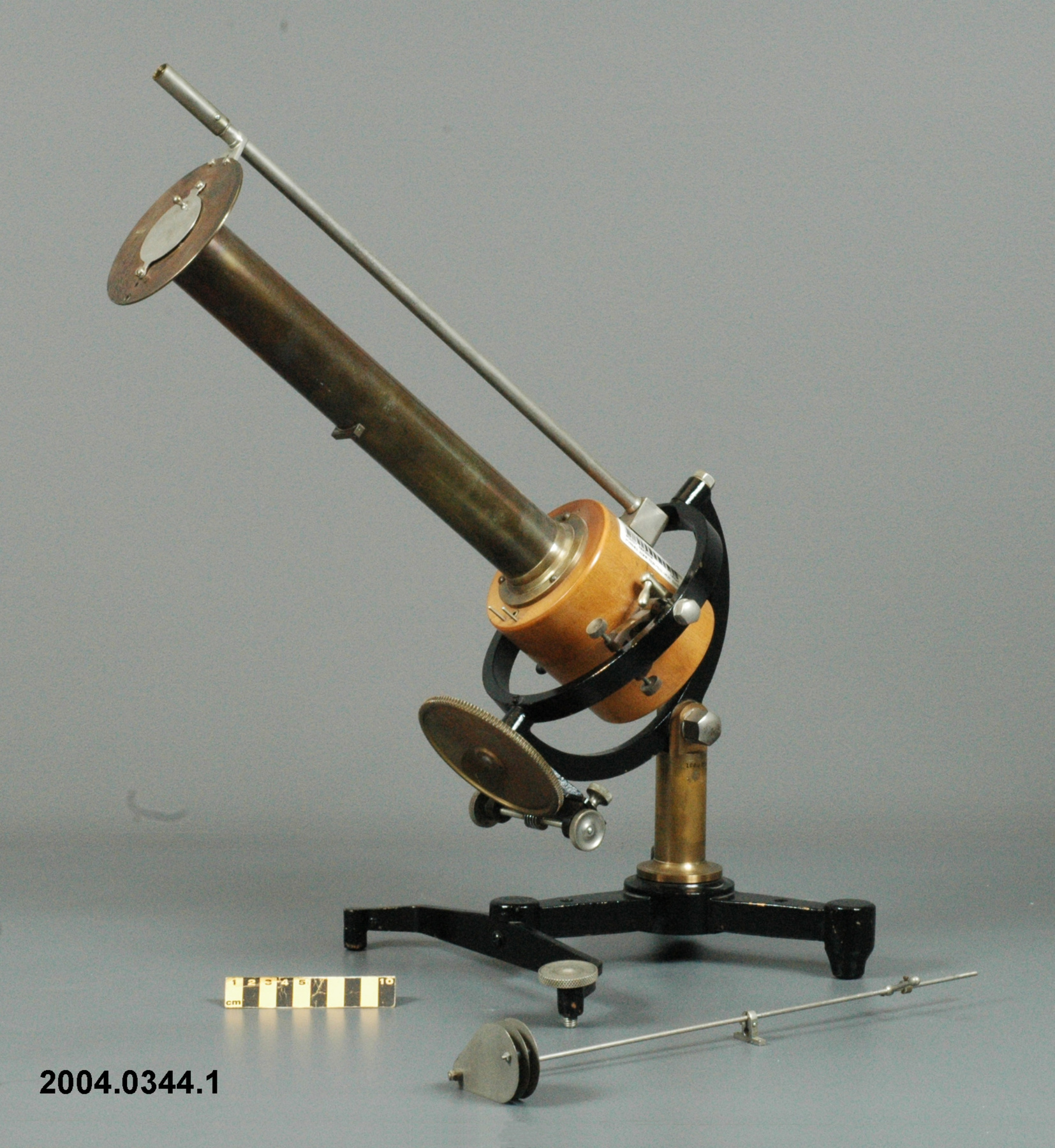
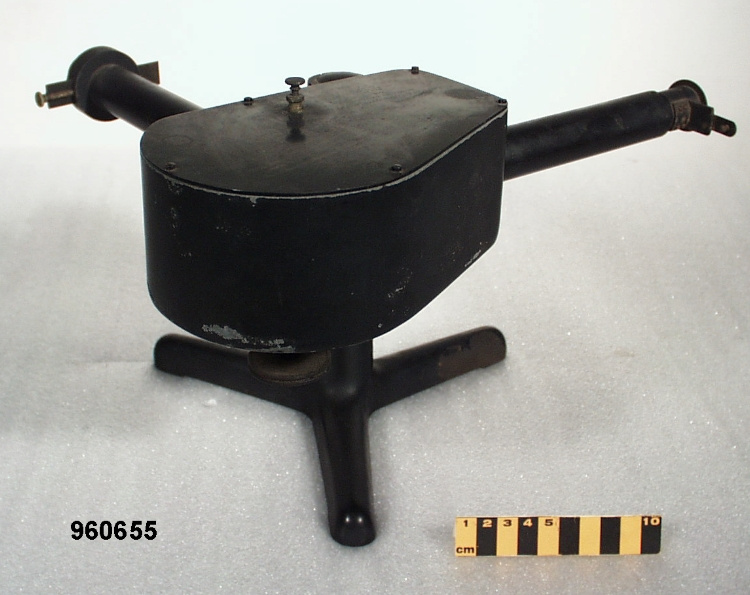
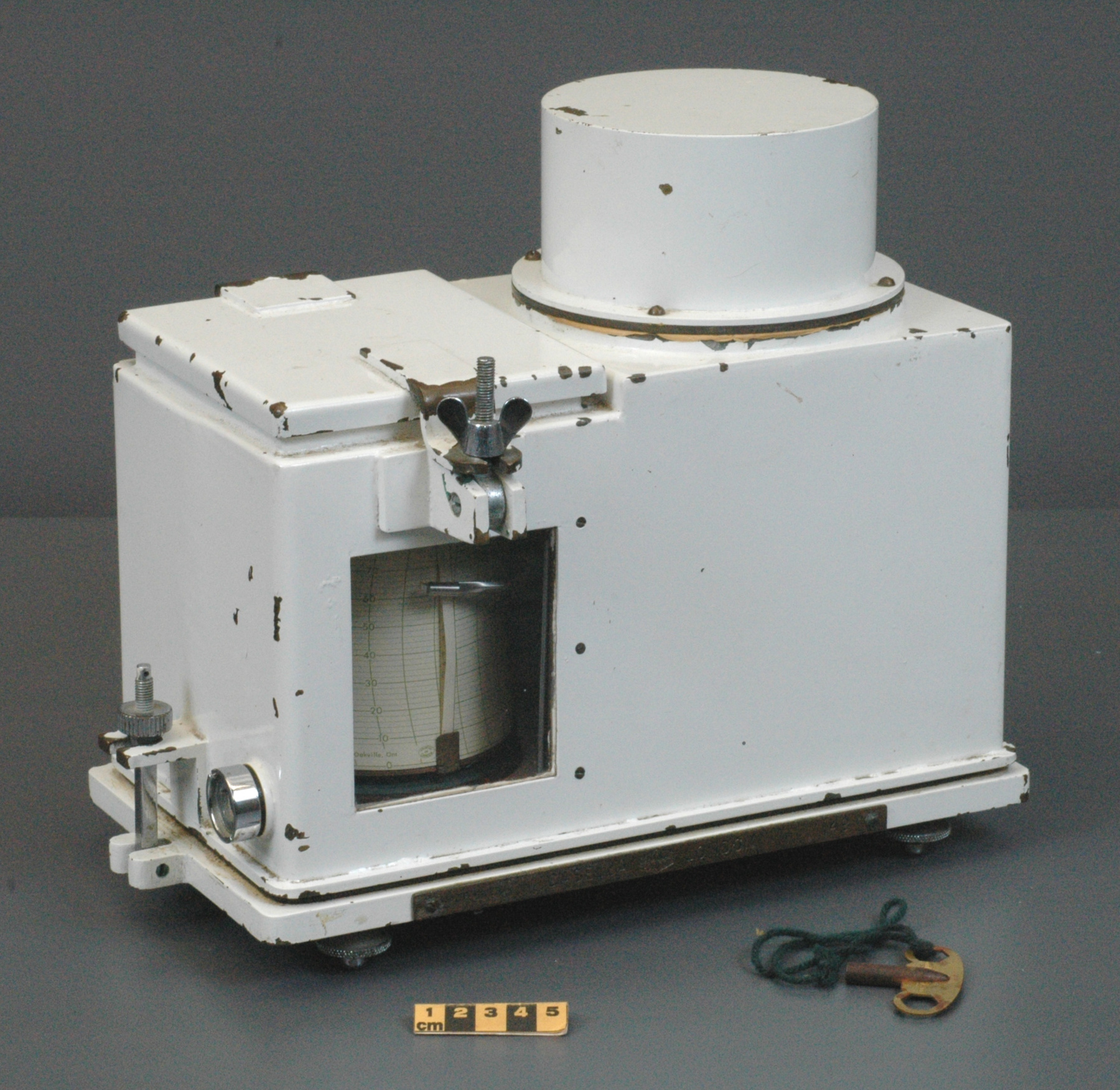
An example of a solar radiation measuring instrument of a type used by the Canadian Meteorological Service. The Eppley 50-K and Model 2 pyranometers, the Eppley Precision Spectral Pyranometer (PSP) and Precision Infrared Pyrgeometer (PIR) were all radiation instruments used to measure solar radiation at Canadian observing stations between 1970 and 1994 (Refs. 6-7). This model is not mentioned in the MSC literature available. Part of a large collection of meteorological instruments acquired from the Meteorological Service of Canada (previously Atmospheric Environment Service) by the CSTM since 1967. MSC is the government agency responsible for collecting and disseminating meteorological data and forecasts in Canada. It was founded in 1871 in Toronto where it is still headquartered. The MSC was originally on the University of Toronto downtown campus but moved to Downsview in 1971 on land owned by UofT. The headquarters houses laboratories, research facilities and calibration and instrument maintenance facilities (now largely contracted out). - Fonction
-
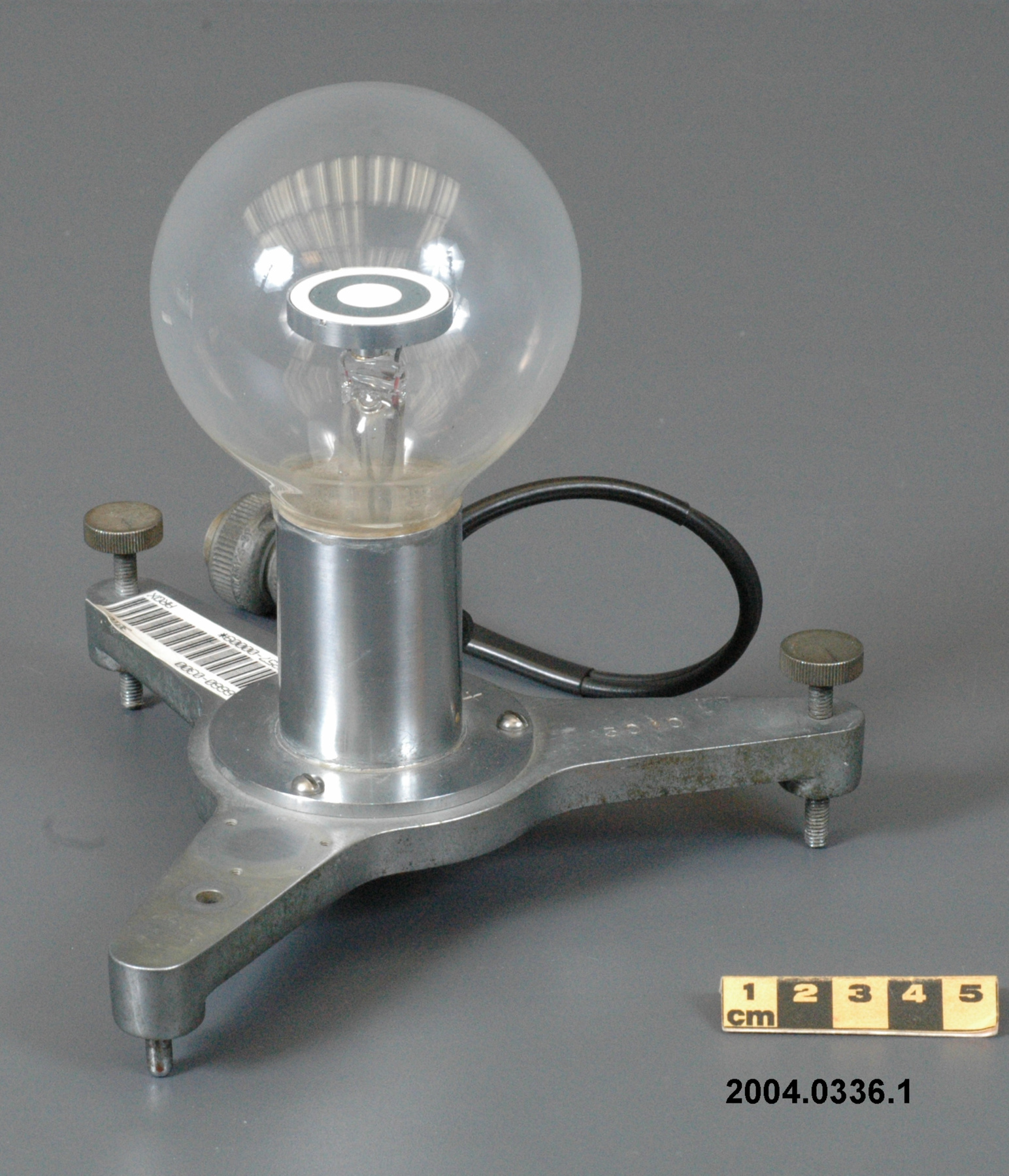
An instrument designed to measure global solar radiation (RF1), the total incoming short-wave radiation from the whole dome of the sky, as received on a flat, horizontally mounted thermopile sensor (Ref. 2) - Technique
-
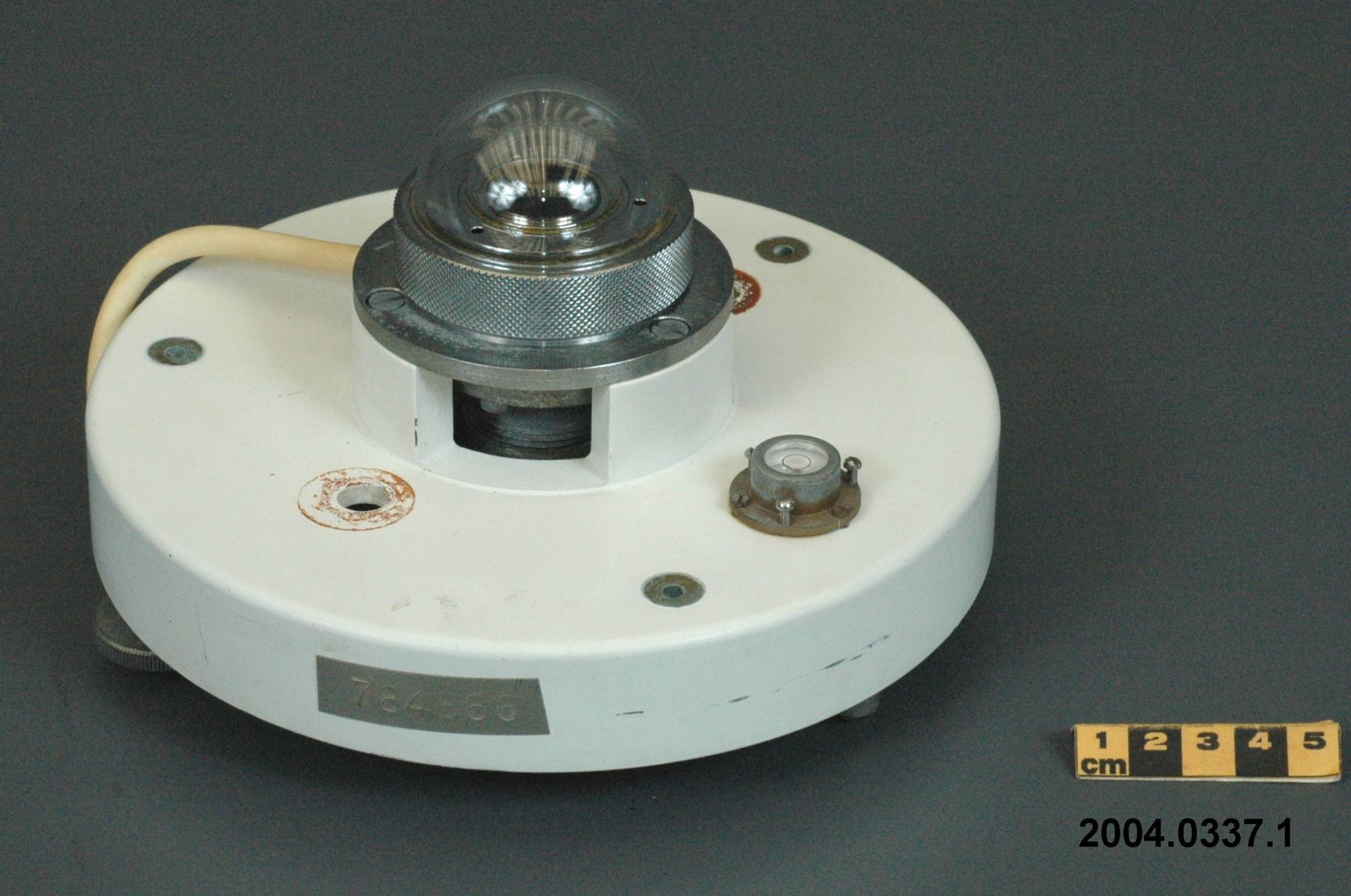
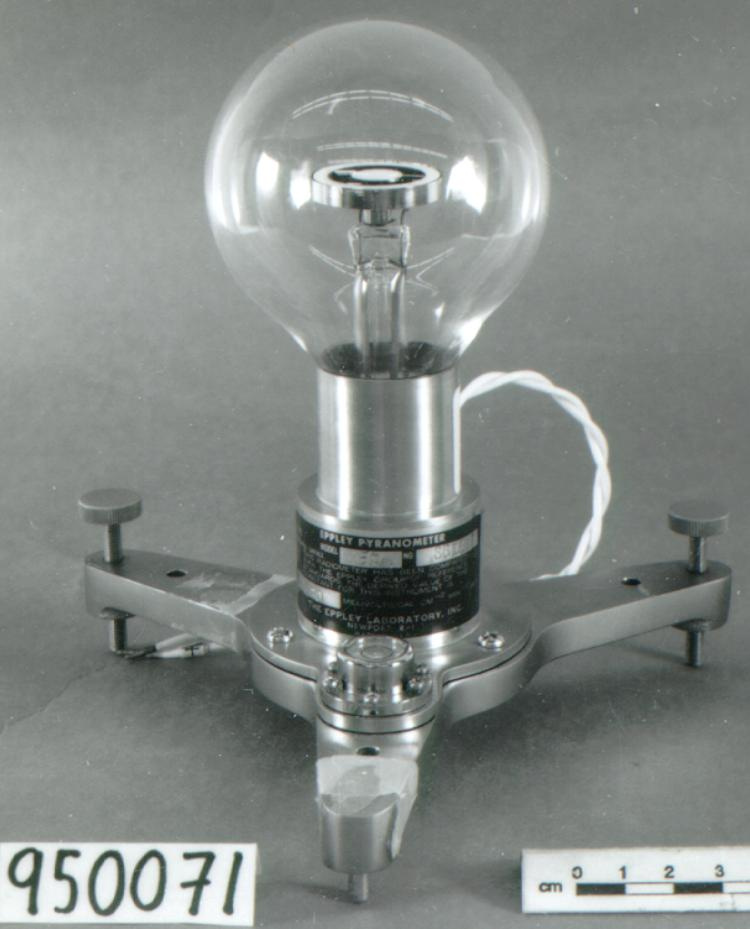
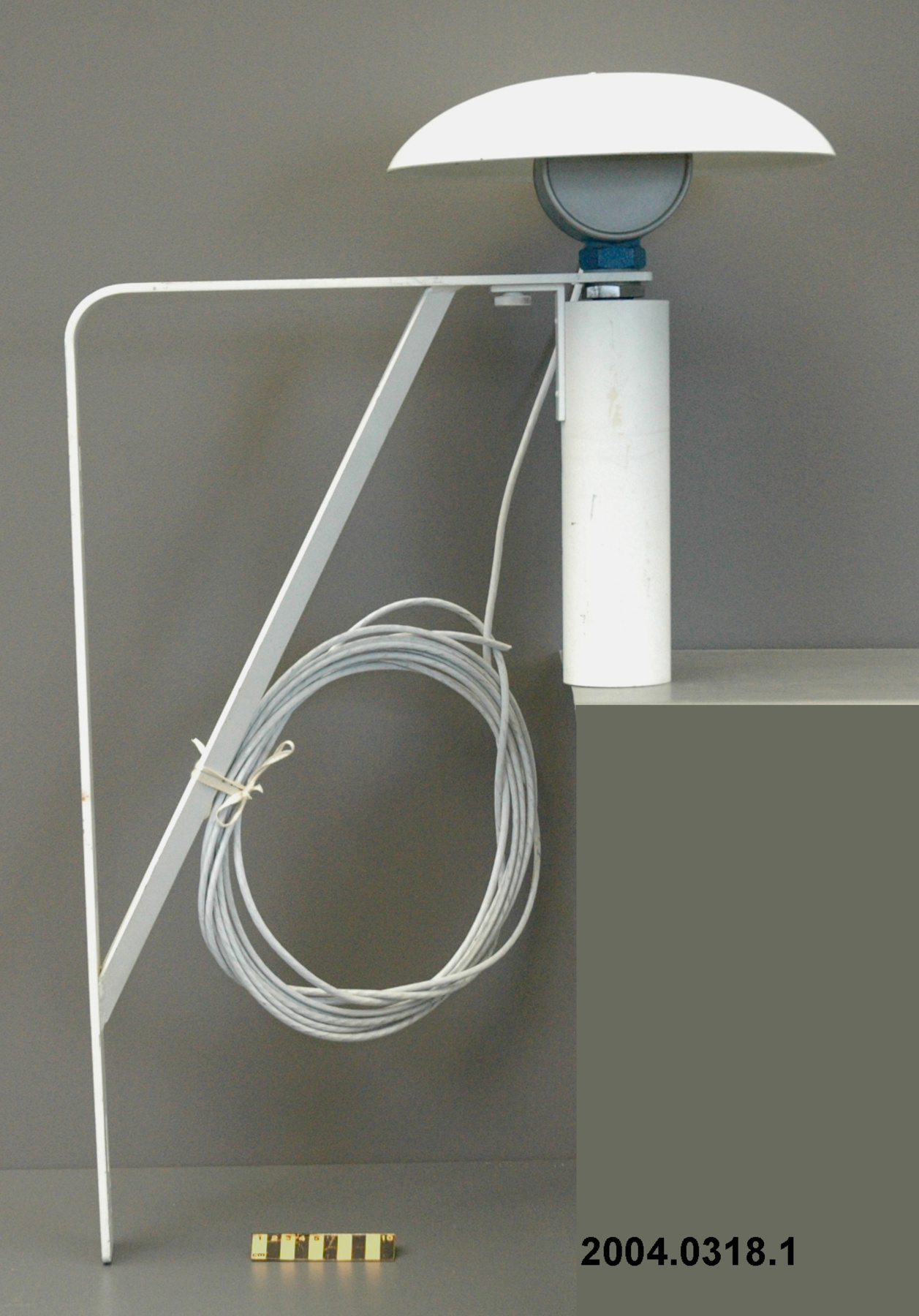
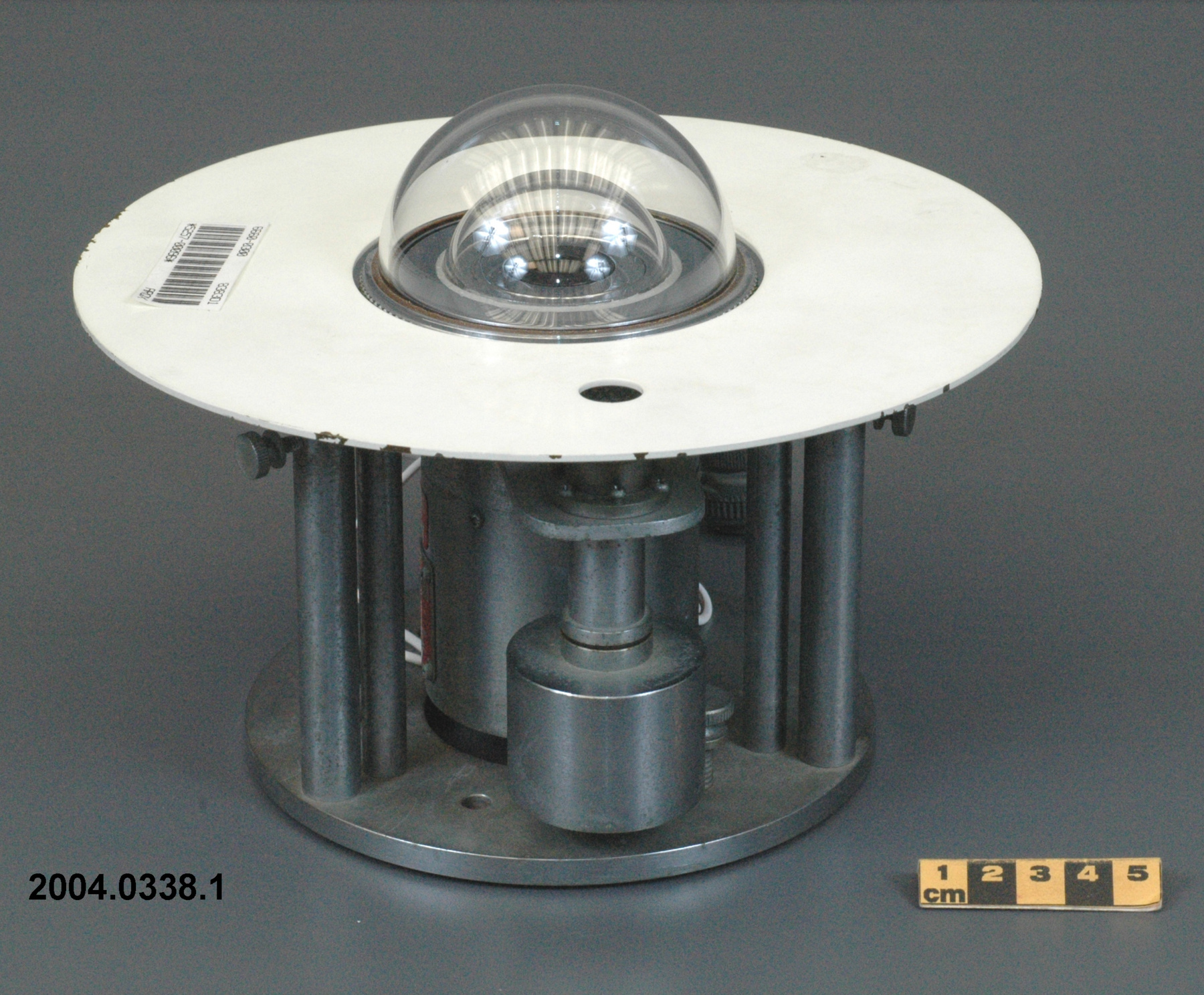
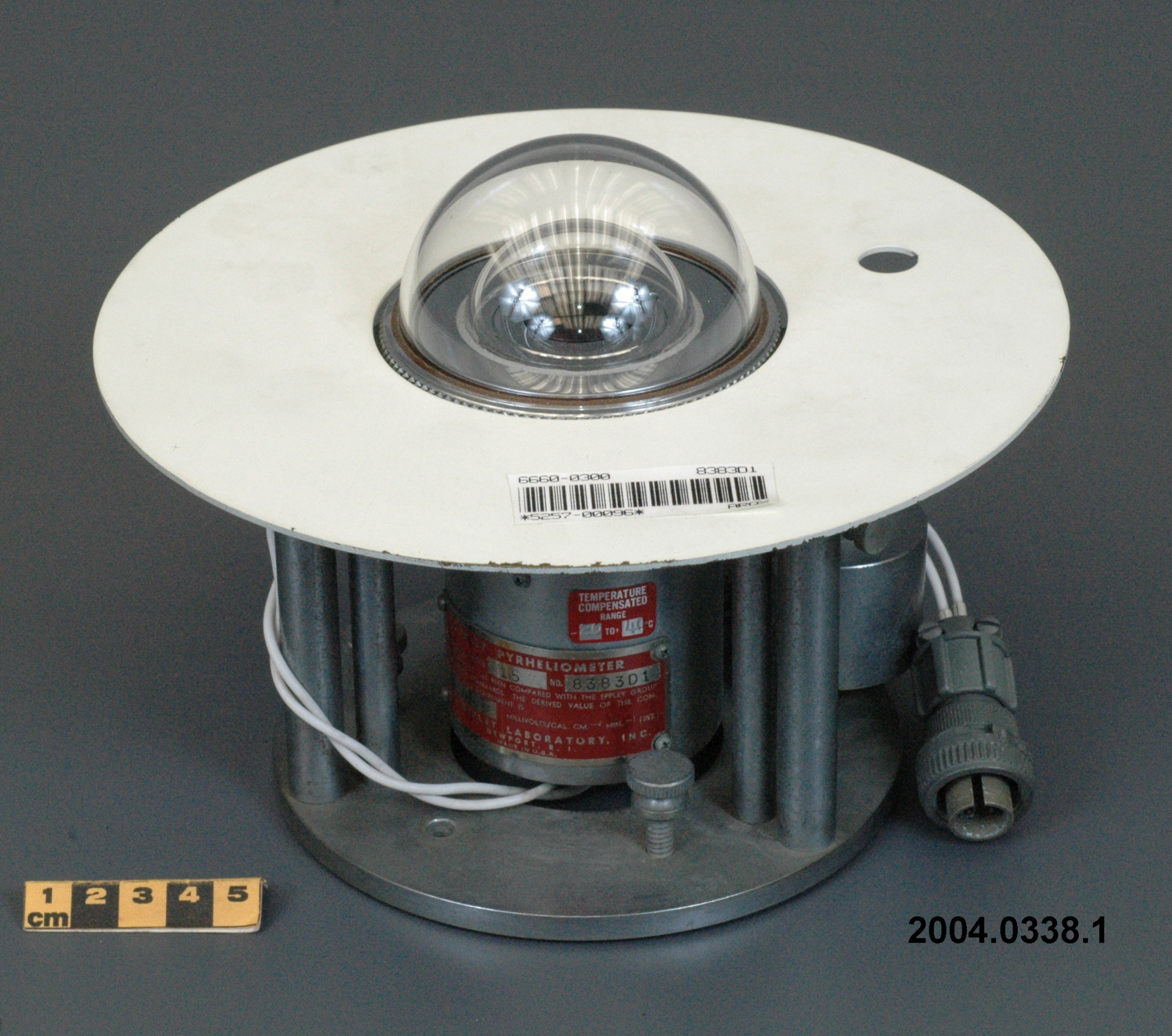
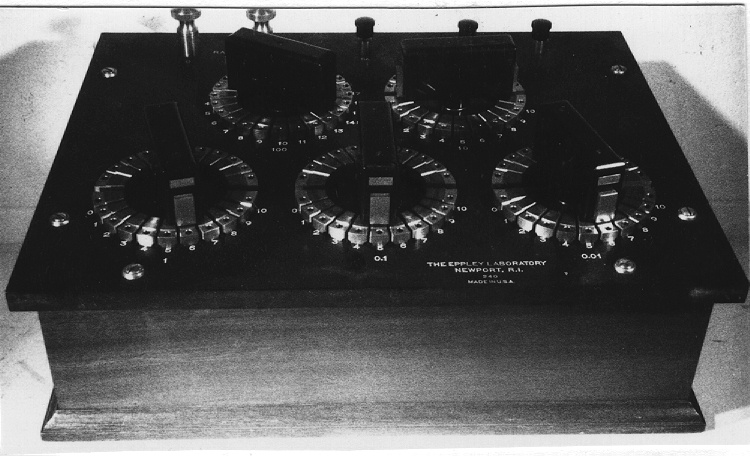
An Eppley horizontal surface pyranometer with a levelling base. It has a double glass dome protecting the sensor which consists of flat concentric rings, one ring silver, the inner one blackened. The double clear domes reduce the temperature variations between the sensor and its reference (Ref. 1). The model 15 appears to be another, possibly earlier, version of the1990's to present Eppley PSP (Precision Spectrum Pyranometer) (see. Refs. 2-3). This instrument was standardized on August 17, 1967 (Ref. 3) and according to the manufacturer, it was supplied (to MSC?) in 1967 (Ref. 4). Virtually all the energy available on the earth is dependant upon the energy received from the sun. The sun's output has varied by only 0.1% in recent times. Hence it is a source of very constant energy. This radiation arrives mostly in the form of visible radiation which peaks at the green 0.6 mm wavelength. Some of this radiation is lost by reflection from clouds or dust, and some by reradiation from the atmosphere. There is a delicate balance between gains and losses. A slight imbalance can shift the earth into an ice age or into runaway climate warming. For this reason alone it is necessary to monitor radiation. Solar radiation is the visible radiation from the sun with wavelengths from 0.3 mm (micrometres) (violet) to 0.9 mm (red). Global solar radiation (Radiation Field 1 or RF1) measurements are made using pyranometers at sites in the radiation network. This is a measurement of all the incoming solar radiation and comprises the bulk of radiation measurements in the radiation network of 43 stations as of 2002. The RF-1 instruments use a shrouded AES designed ventilator which prevents precipitation from landing on the sensor and reduces the collection of dirt on the domes (Ref. 1). - Notes sur la région
-
Inconnu
Détails
- Marques
- silver lettering on red plate reads 'EPPLEY PYRHELIOMETER/ TYPE HORIZONTAL SURFACE/ MODEL 15 NO. 8383D1/ THIS RADIOMETER HAS BEEN COMPARED WITH THE EPPLEY GROUP/ OF REFERENCE STANDARDS. THE DERIVED VALUE OF THE CON-/ STANT FOR THIS INSTRUMENT IS:/ 4.64 MILLIVOLTS /CAL. CM. -2 MIN.-1 (INT.)/ THE EPPLEY LABORATORY, INC./ NEWPORT, R.I./ MADE IN U.S.A.'/ plate reading 'TEMPERATURE/ COMPENSATED/ RANGE/ -20 TO +40 [degrees] C'/ white AES label with black lettering reading '6660-300 8383D1/ [bar code]/ *5257-00096* ARQX'/
- Manque
- appears complete
- Fini
- black and silver sensor/ colourless transparent glass/ metallic casing, frame and parts/ white painted shield/ white synthetic
- Décoration
- S/O
FAIRE RÉFÉRENCE À CET OBJET
Si vous souhaitez publier de l’information sur cet objet de collection, veuillez indiquer ce qui suit :
EPPLEY LABORATORY INC., Pyranometre, 1967, Numéro de l'artefact 2004.0338, Ingenium - Musées des sciences et de l'innovation du Canada, http://collection.ingeniumcanada.org/fr/id/2004.0338.001/
RÉTROACTION
Envoyer une question ou un commentaire sur cet artefact.
Plus comme ceci